Planetary Motion
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Planetary Motion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to talk about planetary motion. Can anyone tell me what they think planetary motion involves?

Is it about how planets go around the sun?

Yes! And I think it has to do with orbits and velocities.

That's correct! Planetary motion primarily describes how planets travel in elliptical orbits around the sun, which we'll explore in detail.
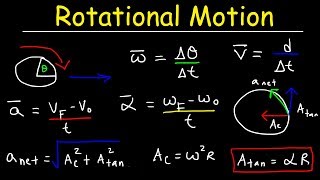
Angular Velocity in Planetary Motion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's dive deeper into angular velocity. Who can explain what angular velocity is?

Isn't it how fast something rotates? Like, how quickly a planet moves around the sun?

Exactly! Angular velocity (ω) is measured in radians per second and represents the rate of rotation. During a planet's journey, its angular velocity determines the time taken for one complete revolution. Why do you think that’s important?

So, if we know a planet's angular velocity, we can figure out how long its year is?

Precisely! Understanding this helps us know how long it takes for Earth and other planets to orbit the sun.
Application of Angular Motion Concepts
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's think of some applications. How do the concepts of angular velocity and angular acceleration aid in modern astronomy or space exploration?

Well, they're used to calculate the paths of spacecraft traveling to other planets.

And they help in programming satellites to stay in orbit around Earth!

Excellent! Both spacecraft and satellites utilize these principles to ensure they maintain their orbits effectively. This shows how theory translates into practice.

It's like using math to solve real-world problems!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we delve into planetary motion, emphasizing how planets in our solar system revolve around the sun. The angular velocity of these planets is crucial in determining the time required for them to complete one revolution, highlighting the practical applications of angular motion concepts.
Detailed
Planetary Motion
In the study of angular motion, one significant application is planetary motion, where the principles of angular velocity and angular acceleration play critical roles. Planets in our solar system revolve around the sun in elliptical orbits, influenced by gravitational forces. The concept of angular velocity (ω), which is the rate of angle change over time, is fundamental here. For example, the angular velocity of a planet determines the duration of its revolution around the sun, affecting its position across seasons. Moreover, understanding angular acceleration is vital when considering changes in a planet’s speed along its orbital path, whether accelerating or decelerating due to varying distances from the sun. This section explores not only the theoretical underpinnings but also practical implications in contexts such as satellite movement and space exploration.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Understanding Planetary Orbits
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The planets in our solar system revolve around the sun in elliptical orbits.
Detailed Explanation
Planetary motion describes how planets travel around the sun. Each planet follows a path called an elliptical orbit, which means the shape of the path is similar to a stretched circle. Unlike perfect circles, ellipses have two focal points, and the sun is located at one of these points. This means that the distance between the planet and the sun changes as the planet moves along its orbit.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a race track that is oval-shaped. If you are running on the track, sometimes you are closer to the center (where the sun is) and sometimes you are farther away. Just like racing on an oval track, planets speed up when they are closer to the sun and slow down when they are farther away.
The Role of Angular Velocity
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The angular velocity of planets determines the time it takes for them to complete one revolution around the sun.
Detailed Explanation
Angular velocity refers to how quickly something rotates around a point. In the case of planets, it tells us how fast each planet moves in its orbit around the sun. Each planet has a different angular velocity, which is influenced by its distance from the sun. For example, planets that are closer to the sun, like Mercury, travel faster than those that are farther away, like Neptune.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are on a merry-go-round. If you’re sitting close to the center, you might go around quickly, but if you sit on the edge, it takes longer to go around since you have to cover a larger distance. Similarly, planets that are closer to the sun move faster because they have a shorter path to cover.
Key Concepts
-
Angular Velocity: The speed at which an object rotates around an axis.
-
Planetary Orbits: The paths taken by planets as they revolve around stars, primarily elliptical.
-
Importance of Angular Motion: Understanding angular motion aids in real-life applications such as satellite positioning and spacecraft navigation.
Examples & Applications
The Earth takes 365 days to complete its orbit around the sun, influenced by its angular velocity.
Satellites in orbit rely on calculations of angular velocity and acceleration to maintain their trajectories.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Planets in motion, round the sun they spin,
Stories
Imagine a race where planets chase the sun, each moving in their own way, having their own fun!
Memory Tools
Remember 'PAUSE' for Planetary Angular Velocity: P for Planets, A for Angular, U for Uniform motion, S for Sun, E for Elliptical.
Acronyms
PEACE
Planetary motion
Ellipses
Angular speed
Circular orbits
Earth Days.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Planetary Motion
The movement of planets in elliptical orbits around a star, typically characterized by angular velocity.
- Angular Velocity
The rate of rotation around an axis, measured in radians per second.
- Elliptical Orbits
The elongated circular paths that planets follow as they revolve around the sun.
- Revolution
A complete orbit around a celestial body, like a planet around the sun.
- Angular Acceleration
The rate of change of angular velocity over time.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
