Units of Angular Velocity
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Angular Velocity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're discussing angular velocity. Can anyone tell me what angular velocity measures?

Is it about how fast something rotates?

Exactly! Angular velocity measures the rate at which an object rotates around an axis, and it’s expressed in radians per second.

Why do we use radians?

Good question! Radians provide a natural way to measure angles in circular motion, aligning with the geometry of circles.

How do we calculate it?

We calculate it using the formula ω = θ/t, where θ is the angular displacement, and t is the time taken. Remember, 'ω' stands for angular velocity!

Can you give us a real-world example?

Of course! Think of a wheel spinning. If it makes 3 full rotations in 6 seconds, we can find its angular velocity using the formula we just discussed.

In summary, angular velocity is crucial in understanding motion, especially in circular paths. Keep this formula in mind as we move forward!
Units of Angular Velocity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s dive into how we express angular velocity. What unit do we use?

It's measured in radians per second, right?

Absolutely right! In the SI system, angular velocity is expressed in radians per second or rad/s.

What about other units?

"Great observation! Sometimes we use revolutions per minute (rpm). To convert rpm to rad/s, we multiply by
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
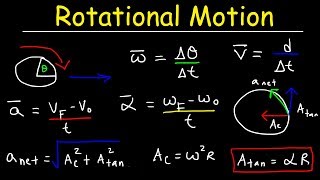
The section dives into the concept of angular velocity, which is the rate of rotation around an axis, typically expressed in radians per second. It covers the corresponding units in the SI system and how angular velocity relates to linear velocity through a defined formula.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
Angular velocity (ω) is a vector quantity that measures the rate of rotation of an object around an axis, quantified in radians per second (rad/s). The formula for calculating angular velocity is given by:
ω = θ/t
where θ represents the angular displacement in radians, and t is the time taken for that displacement.
In the SI system, angular velocity is measured in radians per second. Alternatively, when expressing angular velocity in terms of revolutions per minute (rpm), one can convert it into rad/s using the conversion factor
2π/60. Moreover, the relationship between linear velocity (v) and angular velocity (ω) is depicted through the equation:
v = r * ω,
where r signifies the radius from the axis of rotation to the point in question. This section is critical for understanding not only rotational dynamics but also how angular motion integrates with linear motion in practical applications.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
SI Units of Angular Velocity
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In the SI system, angular velocity is measured in radians per second (rad/s).
Detailed Explanation
Angular velocity quantifies how fast an object rotates around an axis. In the International System of Units (SI), we use radians per second to express angular velocity. This unit tells us how many radians an object rotates through for each second of time.
Examples & Analogies
Think of spinning a basketball on your finger. If the ball makes a complete rotation (which is 2π radians) in 2 seconds, its angular velocity would be 2π radians divided by 2 seconds, or π rad/s.
Converting Revolutions per Minute to Radians per Second
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
If the rotation is in terms of revolutions per minute (rpm), it can be converted to rad/s by multiplying by \( \frac{2\pi}{60} \).
Detailed Explanation
Often, we express rotational speeds in revolutions per minute (rpm). To relate this unit to radians per second, we use a conversion factor. Since one revolution equals 2π radians, we multiply the number of revolutions per minute by \( \frac{2\pi}{60} \) to convert to radians per second because there are 60 seconds in a minute.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a merry-go-round that completes 30 revolutions every minute. To find the angular velocity in radians per second, you would calculate 30 rev/min multiplied by \( \frac{2\pi}{60} \), resulting in 3π rad/s.
Key Concepts
-
Angular Velocity: A vector quantity measured in radians per second indicating the rotation rate.
-
Units of Measurement: Angular velocity primarily uses rad/s, but can also be expressed in rpm.
-
Relationship to Linear Velocity: The formula v = r * ω links linear and angular velocities.
Examples & Applications
A wheel rotating at 5 rad/s achieves an angular velocity of 5 rad/s.
A bicycle going through a curve has its wheel's linear velocity expressed through the formula v = r * ω.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When wheels go round and round, rad/s can be found.
Stories
Imagine a spinning wheel at the carnival. As it rotates, we measure how fast it turns in radians per second!
Memory Tools
Remember 'RAV' - Radius x Angular Velocity gives Linear Velocity.
Acronyms
GLAR - 'Get Linear from Angular by Radius' helps recall the relationship.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Angular Velocity (ω)
The rate of rotation around a specific point or axis, measured in radians per second (rad/s).
- Radians (rad)
A unit of angular measure based on the radius of the circle.
- Revolutions per Minute (rpm)
A unit of angular velocity indicating the number of complete rotations in one minute.
- Linear Velocity (v)
The distance traveled per unit time by a point on a rotating object, related to angular velocity by v = r * ω.
- Radius (r)
The distance from the axis of rotation to a point on the rotating object.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
