Non-Uniform Angular Motion - 2.5
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Non-Uniform Angular Motion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to learn about non-uniform angular motion. This type of motion occurs when the angular velocity changes over time. Can anyone give me an example of this?

Is it like a spinning top that slows down?

Exactly! A spinning top starts fast but decelerates because of friction, showing non-uniform angular motion. This means it has angular acceleration, which we can denote as α.

So, when speed changes, we have angular acceleration, right?

Correct! And remember, when acceleration is present, we denote it mathematically as α ≠ 0.
Characteristics of Non-Uniform Angular Motion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's discuss the characteristics of non-uniform angular motion. Unlike uniform motion, where the object travels equal angles in equal time intervals, non-uniform does not follow that rule. Can you think of a situation where this happens?

A car wheel would accelerate when the car speeds up!

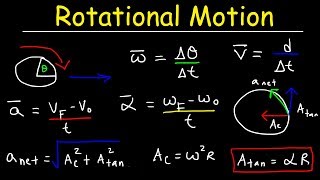
Spot on! In this case, the angular velocity increases, making it non-uniform. The formula for angular acceleration is α = Δω / Δt. Does anyone know what Δω represents?

It's the change in angular velocity!

Right! Good job! So when we have a change in speed, we can calculate the angular acceleration using that formula.
Practical Examples of Non-Uniform Angular Motion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s look at more examples. Besides the spinning top and car wheel, what else could demonstrate non-uniform angular motion?

How about a roller coaster?

Yes! A roller coaster can speed up and slow down on its tracks. These changes in speed indicate non-uniform motion too. Now, can anyone summarize why these examples matter?

They show how angular acceleration affects motion in real life!

Exactly! Understanding non-uniform angular motion helps us to design and operate machines efficiently.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In non-uniform angular motion, the angular velocity is not constant, leading to changes in the speed of rotation. This section explains the concept of angular acceleration, provides examples, and differentiates this type of motion from uniform angular motion.
Detailed
Non-Uniform Angular Motion
Non-uniform angular motion refers to the situation where the angular velocity of an object varies with time, unlike in uniform angular motion where it remains constant. This type of motion is accompanied by angular acceleration, defined as the rate at which the angular velocity changes over time. The concept is crucial for understanding various real-world phenomena, such as a car wheel accelerating as the vehicle speeds up or a spinning top slowing down due to friction. In this section, we explore the characteristics of non-uniform angular motion, along with practical examples to illustrate its occurrence. Recognizing the transition between uniform and non-uniform motion is essential for analyzing rotational dynamics effectively.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Non-Uniform Angular Motion
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Non-uniform angular motion occurs when the angular velocity changes with time, meaning the object has angular acceleration (α≠0). This type of motion occurs when the object speeds up or slows down as it rotates.
Detailed Explanation
Non-uniform angular motion refers to a situation where the angular velocity of an object is not constant over time. This means that the object either accelerates (speeds up) or decelerates (slows down) during its rotation. When an object experiences non-uniform angular motion, it has angular acceleration, which is indicated by the symbol α (alpha). If α is not equal to zero (α≠0), it shows that the angular velocity is changing.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine riding a bicycle. When you start pedaling gently, you accelerate, and the angular velocity of the bicycle wheels increases. If you start going downhill, the wheels speed up even more. Conversely, when you apply brakes, the wheels slow down, illustrating non-uniform angular motion as angular velocity changes.
Examples of Non-Uniform Angular Motion
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Examples of Non-Uniform Angular Motion
- A spinning top that starts fast and then gradually slows down due to friction.
- A car wheel accelerating or decelerating as the vehicle speeds up or slows down.
Detailed Explanation
Non-uniform angular motion can be seen in various real-world examples. For instance, when a spinning top is initially flicked, it spins quickly at first but gradually slows down as friction from the surface acts against it. This reduction in speed means its angular velocity decreases over time, demonstrating non-uniform angular motion. Another example is a car wheel. When a car accelerates, the wheels rotate faster, increasing their angular velocity. Conversely, when the car brakes, the wheels slow down, thus reducing their angular velocity. Both scenarios illustrate the concept of non-uniform angular motion where the speed of rotation changes over time.
Examples & Analogies
Think about a merry-go-round at the playground. If you push it firmly, it spins rapidly at first but gradually slows down as the friction with the ground starts to take its effect. Just like the merry-go-round, a bicycle or a car experiences non-uniform angular motion under different driving conditions, such as starting, stopping, or making turns.
Key Concepts
-
Angular Acceleration: The rate of change of angular velocity, indicating a change in speed.
-
Non-Uniform Motion: Motion characterized by a change in angular velocity over time.
-
Examples: Instances of non-uniform angular motion include a car wheel accelerating or a spinning top slowing down.
Examples & Applications
A spinning top that starts fast but gradually slows down due to friction.
A car wheel that accelerates as the vehicle speeds up or decelerates as it slows down.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When the speed does change and swirls away, it's non-uniform in every way!
Stories
Imagine a top that spins with grace. It slows down, reducing its pace, demonstrating non-uniform space!
Memory Tools
Remember 'CAN' for Non-Uniform: Change, Acceleration, Non-uniform motion.
Acronyms
N-U-A-M
Non-Uniform Angular Motion.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Angular Velocity
The rate of rotation of an object around a particular point or axis, measured in radians per second (rad/s).
- Angular Acceleration
The rate of change of angular velocity over time, measured in radians per second squared (rad/s²).
- NonUniform Angular Motion
Motion where the angular velocity changes over time, indicating the presence of angular acceleration.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
