Conclusion
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Angular Motion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’re talking about angular motion. Can anyone tell me what we measure when we talk about angular velocity?

Isn't that how fast something is rotating?

Exactly! Angular velocity measures how quickly an angle is changing over time. It's expressed in radians per second. Now, who can tell me what angular acceleration is?

It's the rate at which angular velocity changes, right?

Great job! Remember, angular acceleration is also a vector quantity, measured in radians per second squared.

So, both of them are important for understanding how things rotate?

Yes! By knowing both, you can solve complex rotational dynamics problems.

How do we apply these concepts?

Excellent question! These concepts apply in machinery, sports, and even in celestial movements like planets rotating around the sun. In summary, angular velocity and acceleration allow us to understand and predict rotational motion!
Applications of Angular Dynamics
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's talk about applications. Can anyone share an example of where angular velocity is critical?

Well, in machines like motors or turbines!

Absolutely! Motors operate on rotational dynamics. How about another example?

What about a bicycle?

Exactly, the bike wheels involve rotation where angular velocity and acceleration matter a lot. What about in nature?

The Earth's rotation?

Perfect! The Earth rotates around its axis, and understanding angular motion helps us determine things like day length. So remember, angular motion has wide-ranging applications!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The Conclusion encapsulates the core principles of angular velocity and angular acceleration, emphasizing their importance in solving rotational dynamics problems and their applications in real-world scenarios, including machinery, sports, and planetary motion.
Detailed
In this concluding section, we summarize the key concepts related to angular velocity and angular acceleration. Angular velocity is defined as the rate of change of angular displacement, while angular acceleration signifies the rate of change of angular velocity. The section highlights how both concepts are measured in rad/s and rad/s² respectively. It also refers to the equations of angular motion that mirror those in linear dynamics, thus aiding in problem-solving related to rotation. The significance of angular motion is reiterated through its diverse applications, which range from engineering technologies like machinery to natural phenomena such as planetary movements.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Summary of Key Points
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
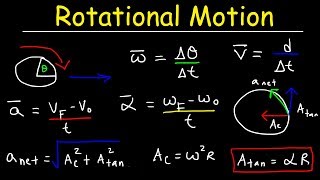
● Angular velocity measures the rate of change of angular displacement, while angular acceleration measures the rate of change of angular velocity.
● The equations of angular motion, similar to linear motion, help in solving problems related to rotational dynamics.
● Angular motion is essential in various applications, from machinery to planetary movement and everyday life.
Detailed Explanation
In this chunk, we summarize the core themes of the section on angular motion. First, we define angular velocity and angular acceleration. Angular velocity refers to how quickly an object rotates, while angular acceleration concerns how quickly that rotation is changing. Both concepts are closely related to motion, whether it be rotating objects like wheels or celestial bodies. Next, we point out the importance of equations of motion for angular movement. These equations are similar to those in linear motion, providing a framework for solving problems involving rotation. Finally, we highlight the practical significance of angular motion, noting its relevance in different fields such as machinery (think of engines and motors), the movements of planets, and even everyday activities like riding a bicycle or driving a car.
Examples & Analogies
To relate this concept to everyday life, imagine riding a merry-go-round. The speed at which it turns is the angular velocity, which changes if someone pushes it faster or if the brakes are applied, demonstrating angular acceleration. If we consider the equations for calculating how fast the merry-go-round spins at different points, we can see how the principles of angular motion apply everywhere in our lives, making them not just theoretical but highly practical.
Key Concepts
-
Angular Velocity: Measures the rate of change of angular displacement.
-
Angular Acceleration: Describes how quickly angular velocity changes.
-
Applications: Relevant in machinery, sports, and planetary motions.
Examples & Applications
A ceiling fan rotating at a constant speed demonstrates uniform angular motion.
The Earth’s daily rotation showcases the concept of angular velocity.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In a whirl and twirl, our velocities spin, Angular measures show if we're out or in.
Stories
Imagine a magical world where the sun spins slowly. As it speeds up, the flowers bloom faster—this is like angular acceleration transforming the beauty of rotation.
Memory Tools
Remember 'A.V.A.' for Angular Velocity and Angular Acceleration—always visit the axes!
Acronyms
MRA
Measure Rotation Acceleration to understand motion better.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Angular Velocity
The rate at which an object rotates around a specific point or axis; measured in radians per second (rad/s).
- Angular Acceleration
The rate of change of angular velocity with respect to time; measured in radians per second squared (rad/s²).
- Angular Displacement
The angle through which a point or line has been rotated in a specified sense about a specified axis.
- Rad/s
Standard unit of angular velocity, representing radians per second.
- Radians
A unit of angular measurement that is defined as the angle subtended at the center of a circle by an arc equal in length to the radius of the circle.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
