Uniform Angular Motion - 2.4.1
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Uniform Angular Motion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we'll explore uniform angular motion, which is when an object rotates at a constant speed without any change in its angular velocity. Can anyone tell me what this means?

Does it mean that there's no acceleration?

Exactly! In uniform angular motion, we have no angular acceleration, meaning the object moves through equal angular displacements in equal time. Let's strengthen our memory on this—think of the acronym 'UAM' for Uniform Angular Motion!

So, it’s like the Earth spinning at a steady pace?

Great example! The Earth rotates uniformly, completing a rotation every 24 hours.
Characteristics of Uniform Angular Motion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss some everyday examples of uniform angular motion. Can anyone name one?

A ceiling fan when it’s turned on at the same speed!

Exactly! A ceiling fan is a clear example of uniform angular motion. How about another example?

The hands of a clock?

Yes! The hands of a clock also move uniformly. Now, remember that in uniform angular motion, the angular displacement does not change over time intervals. Can someone explain why this is important?

It’s important because it helps us predict the position of rotating objects!

Spot on! Predictability is crucial in many applications.
Real-World Applications of Uniform Angular Motion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we have a solid understanding of uniform angular motion, let’s delve into its applications. Can anyone think of where we might see this in action?

In machinery, like how engines utilize rotational motion?

Absolutely! Motors and engines revolve utilizing uniform angular motion principles. How else does this apply to our daily lives?

Planetary orbits maybe?

Exactly! The planets move around the sun exhibiting uniform angular motion. Great thoughts everyone!
Reviewing Key Concepts
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Before we wrap up, let’s review what we’ve learned. Who can summarize what uniform angular motion entails?

It's when an object rotates with a constant angular velocity, without any acceleration.

Great! And why is this concept important?

It helps us predict the motion of objects, which is crucial in engineering and daily life!

Exactly! Understanding these concepts can make us better at problem-solving in real-world applications.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In uniform angular motion, the angular velocity remains constant over time, implying that there is no angular acceleration. Examples include a ceiling fan operating at a steady speed and the Earth's rotation around its axis.
Detailed
Uniform Angular Motion
Uniform angular motion is defined as the motion of an object that rotates steadily about a specific point or axis with a constant angular velocity. This means that the object does not experience any angular acceleration, thus implying that its angular displacement over equal time intervals remains constant. The primary characteristics include:
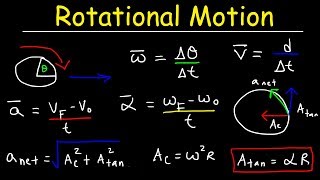
- Constant Angular Velocity: The angular velocity (ω) remains unchanged, which suggests that the rate of rotation is uniform.
- No Angular Acceleration: Since the speed does not change, the angular acceleration (α) is zero (α = 0).
Examples of Uniform Angular Motion
- Ceiling Fan: A ceiling fan rotating at a constant speed exemplifies uniform angular motion since its blades maintain a steady angular velocity.
- Earth’s Rotation: The Earth completes one full rotation on its axis approximately every 24 hours, illustrating uniform angular motion as its angular velocity is consistent.
Understanding uniform angular motion is crucial in analyzing various real-world applications of rotational dynamics, particularly in machinery and planetary motion.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Uniform Angular Motion
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Uniform Angular Motion
Uniform angular motion occurs when the angular velocity remains constant over time. In such cases, there is no angular acceleration, i.e., α=0.
Detailed Explanation
Uniform angular motion is when an object rotates at a constant rate, meaning its speed does not change. Angular velocity is the speed of rotation, and if it stays the same, the motion is termed 'uniform.' Since the speed is constant, there is no angular acceleration, which is defined as the change in angular velocity over time. In this situation, the acceleration (α) equals zero.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine riding a bicycle at a steady pace. If you keep pedaling at the same speed without speeding up or slowing down, your motion is similar to uniform angular motion. Just like how the wheels spin at a constant rate without any changes, in uniform angular motion the rotation is steady.
Equal Angular Displacements
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In this case, the object moves through equal angular displacements in equal time intervals.
Detailed Explanation
When we say the object moves through equal angular displacements in uniform angular motion, it means that for every unit of time, it covers the same angle. For example, if a wheel completes 1 radian every second, it will continue to do so for each subsequent second as long as the motion is uniform. This constancy helps in predicting the position of the object at any given time.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a clock. Each second, the minute hand of a clock moves the same angle. If it moves 6 degrees every minute, it will continue to do so consistently. This regular movement exemplifies uniform angular motion, as the hand rotates through equal angles over equal time intervals.
Examples of Uniform Angular Motion
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Examples of Uniform Angular Motion
- A ceiling fan rotating at a constant speed.
- The Earth’s rotation around its axis, as it completes one rotation every 24 hours.
Detailed Explanation
Examples help illustrate the concept of uniform angular motion. A ceiling fan that is set to a constant speed does not speed up or slow down, thus exhibiting uniform angular motion. Similarly, the Earth rotates at a consistent rate, completing one full rotation every 24 hours, which is also a perfect example of uniform angular motion.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a carousel at an amusement park that is running at a steady speed. The horses are moving in circles at the same rate, which means they are undergoing uniform angular motion. Everyone riding has the same experience as they circle around, akin to the consistent speed of a ceiling fan or Earth’s rotation.
Key Concepts
-
Uniform Angular Motion: The consistent rotation of an object at a constant angular speed without acceleration.
-
Constant Angular Velocity: The rate of rotation remains unchanged over time periods.
-
Real-World Applications: Practical uses of uniform angular motion, including machinery and celestial movements.
Examples & Applications
Ceiling Fan: A ceiling fan rotating at a constant speed exemplifies uniform angular motion since its blades maintain a steady angular velocity.
Earth’s Rotation: The Earth completes one full rotation on its axis approximately every 24 hours, illustrating uniform angular motion as its angular velocity is consistent.
Understanding uniform angular motion is crucial in analyzing various real-world applications of rotational dynamics, particularly in machinery and planetary motion.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Rotate, rotate, at a steady rate, no speed change, it's just great!
Stories
Imagine a clock that never speeds up or slows down, just like time ticking away evenly, illustrating uniform angular motion in our lives.
Memory Tools
Remember 'RPM' - Rotation Per Minute for thinking about uniform angular motion as it keeps going smoothly.
Acronyms
UAM = Uniform Angular Motion; think of it as an object's rotation that stays even and steady!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Uniform Angular Motion
Motion in which the angular velocity of an object remains constant over time with no angular acceleration.
- Angular Velocity
The rate at which an object rotates around a specific point or axis, measured in radians per second (rad/s).
- Angular Acceleration
The rate of change of angular velocity with respect to time, measured in radians per second squared (rad/s²).
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
