Accounting Rate of Return (ARR)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to ARR
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to learn about the Accounting Rate of Return, or ARR. ARR is a method that helps companies evaluate how much profit they can expect from an investment as a percentage of its cost.

Why do we use percentage instead of just stating the profit amount?

Great question! Using a percentage allows for easier comparison between different investments, regardless of their size. This concept ties back to our understanding of profitability.

Can you remind us how the formula works?

Certainly! The formula is ARR = (Average Annual Profit / Initial Investment) x 100. It shows how much return you're making relative to your investment.

What are the advantages of using ARR?

One major advantage is its simplicity; it’s easy to calculate using available accounting data. However, let me highlight that it has limitations too!

Like what?

One significant limitation is that it ignores the time value of money, meaning it doesn't take into account when the profit is earned. That's why we consider other methods, too.

In summary, ARR is valuable for its simplicity and ease of use, but we must be cautious about the insights we derive from it.
Advantages and Disadvantages of ARR
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s dive deeper into the advantages of ARR. Can anyone tell me why simplicity is essential in financial analysis?

It keeps things straightforward, helping financial managers make quick decisions.

Exactly! Quick calculations allow decision-makers to assess many projects without overly complicated computations. Now, what about the disadvantages?

Ignoring the time value of money can mislead investors, right?

Yes! If two projects have the same ARR, it doesn't mean they're equally viable. A cash flow that occurs earlier is generally more valuable, which ARR doesn’t acknowledge.

So it's better to use ARR alongside other methods?

Correct! ARR should be one tool in your toolbox. When used with NPV or IRR, you get a fuller picture of investment returns. Let’s summarize: ARR is simple but can be misleading if used alone.
Practical Applications of ARR
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s look at some practical applications of ARR. How do you think a company could utilize ARR in their decision-making?

They might use it to compare various capital investments to see which gives the best return.

Exactly! For instance, a tech company could use ARR when deciding to invest in a new software tool or hardware upgrade. Anyone else?

They could also use it in budgeting to forecast expected profit from projects!

Great point! Companies can set profit expectations, but always remember they need to supplement ARR with other metrics for a complete analysis. Remember, applying multiple methods enhances decision-making effectiveness.

So, when in a situation to invest, I would check ARR, NPV, and IRR together?

Exactly! Each method provides different insights into financial viability. In summary, always consider using ARR along with other metrics for a comprehensive assessment.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The ARR highlights the return on investment based on projected accounting profits rather than actual cash flows. It is simple to calculate and based on available accounting data but does not account for the time value of money. Understanding ARR is essential for evaluating investment feasibility.
Detailed
Accounting Rate of Return (ARR)
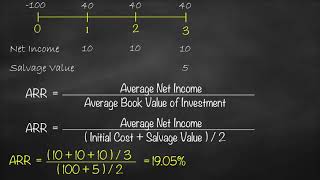
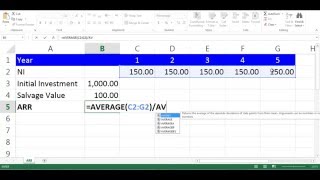
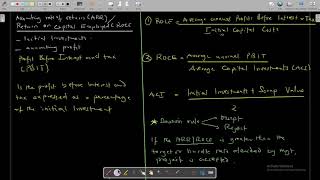
The Accounting Rate of Return (ARR) is a financial metric used to evaluate the profitability of an investment. It is calculated by taking the average annual profit generated by an investment and dividing it by the initial investment cost, then multiplying by 100 to express it as a percentage. This technique is a part of traditional capital budgeting methods and is particularly favored for its simplicity.
Formula
The ARR formula can be represented as:
ARR = (Average Annual Profit / Initial Investment) x 100
Key Points of ARR:
- Advantages:
- Simple and easy to understand, making it accessible for quick evaluations.
- Based on readily available accounting data, which facilitates its use in various industries.
- Disadvantages:
- Ignores the time value of money, thus it may not accurately reflect the investment's true return over time.
- Focuses on accounting profits rather than actual cash flows, which could mislead decision-making if profits differ significantly from cash inflows.
While ARR is a useful tool for assessing the profitability of an investment, savvy investors often pair it with more comprehensive metrics, especially discounted cash flow techniques like NPV and IRR, for a holistic understanding of investment viability.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of ARR
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Accounting Rate of Return (ARR) measures return based on accounting profits.
Detailed Explanation
The Accounting Rate of Return (ARR) is a financial metric that helps businesses evaluate the profitability of an investment. It is calculated by taking the average annual profit generated from an investment and dividing it by the initial investment cost. This metric is essential for companies as it provides insight into how effectively they are using their resources to generate profits.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a small bakery decides to invest in a new oven that costs $5,000. If the new oven helps increase profits by an average of $1,000 each year, the ARR would be 20%. This means for every dollar spent on the oven, the bakery earns back 20 cents in profit every year from that investment.
Formula for ARR
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The formula for ARR is:
Average Annual Profit
ARR = × 100
Initial Investment
Detailed Explanation
The formula used to calculate the ARR is fairly straightforward. It takes the average annual profit produced by the investment—which is the total profit generated from the investment divided by the number of years it is expected to generate profit—and divides it by the initial investment cost. The result is then multiplied by 100 to express it as a percentage. This makes it easier to compare the ARR of different projects or investments.
Examples & Analogies
Continuing with the bakery example: if the average profit from the new oven is $1,000 and the initial investment is $5,000, the ARR would be calculated as ($1,000 / $5,000) × 100 = 20%. This percentage helps the bakery understand the return on their investment in the new oven.
Advantages of ARR
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Advantages of ARR include:
- Simple and easy to understand.
- Based on accounting data.
Detailed Explanation
One of the primary advantages of using the ARR is its simplicity. It doesn’t require complex calculations, making it accessible for managers and decision-makers who may not have a finance background. Additionally, as ARR is based on accounting data, it aligns well with the information accountants regularly track, making it easier to integrate into financial evaluations.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a student deciding whether to buy a new laptop for $800. If this laptop can help them earn $200 more per year with their studies (through better performance and efficiency), calculating the ARR is simple. They don't need advanced mathematics; they can directly see how much extra money the laptop helps them earn relative to the cost.
Disadvantages of ARR
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Disadvantages of ARR include:
- Ignores time value of money.
- Uses accounting profit, not cash flow.
Detailed Explanation
While ARR has its advantages, it also has some notable disadvantages. A significant drawback is that it ignores the time value of money, which means it doesn't consider the fact that money received in the future is worth less than money received today. Additionally, ARR focuses on accounting profit rather than actual cash flow, which can be misleading as accounting profits can be influenced by various non-cash items (like depreciation). This can make ARR less useful for evaluating the true profitability of an investment.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a situation where two investments show the same ARR but differ in cash flow timing. One investment gains a profit of $1,000 in the first year, while another investment gains $1,200 but only after three years. The fact that the first investment provides cash flow sooner is important for a business when assessing liquidity and investment decisions, which ARR does not account for.
Key Concepts
-
ARR: A method for evaluating profitability as a percentage of initial investment.
-
Formula: ARR = (Average Annual Profit / Initial Investment) x 100.
-
Advantages: Simple to compute and useful for quick comparisons.
-
Disadvantages: Ignores time value of money and uses accounting profits instead of cash flows.
Examples & Applications
If a company invests $100,000 in a project and expects an average annual profit of $20,000, the ARR would be (20,000 / 100,000) x 100 = 20%.
A software company calculates its ARR for a $50,000 investment yielding $5,000 per year, resulting in an ARR of (5,000 / 50,000) x 100 = 10%.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To find returns with simple flair, divide the profit, show you care. Initial cost, don’t forget; percentage shows how good your bet!
Stories
Once upon a time in a financial office, there was a manager named Sam who had to choose between five investments. He calculated the ARR for each case and saw that not only was it simple to compute, but it also helped him easily decide which investment would be the best and ultimately saved his company money.
Memory Tools
A-R-R - Average, Return, Rate. Remember to divide and then negotiate!
Acronyms
ARR - A Quick Way to Assess Right Returns!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Accounting Rate of Return (ARR)
A financial metric that calculates the expected profitability of an investment as a percentage of the initial investment.
- Average Annual Profit
The mean profit a project is expected to generate per year over its useful life.
- Initial Investment
The total amount invested at the start of a project.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
