Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding IRR
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’re learning about the Internal Rate of Return, commonly referred to as IRR. Can anyone tell me what they think IRR represents?

Is it the rate at which a project becomes profitable?

Good start! IRR is actually the discount rate at which the NPV of an investment equals zero. This means it's the expected return from the investment.

So if I understand it right, a higher IRR means a more profitable project, right?

Exactly! When you compare IRR with the required rate of return, if IRR is greater, the project is likely worth pursuing. Remember the acronym IRR: Investment Returns Rank!
Calculating IRR
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Calculating IRR can be tricky due to its iterative nature, but we can understand it conceptually. Can anyone explain how you might calculate IRR?

I think you start with estimating cash flows and then find the rate where NPV is zero?

That's correct! It involves finding the discount rate where the cash inflows and outflows balance out. Remember, this is often done using financial calculators or software due to its complexity.

Are there any situations where IRR might not be reliable?

Great question! Yes, if a project has unconventional cash flows—meaning they switch from negative to positive multiple times—there could be multiple IRRs, making decision-making confusing.

So, it's best used when cash flows are consistent?

Exactly! Let’s summarize: IRR is useful, but be cautious with its limitations.
Comparing Projects Using IRR
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s discuss how IRR can be used to compare multiple projects. Why do you think this is important?

So we can decide where to invest limited resources effectively?

Correct! Evaluating projects in relation to their IRR helps in determining which projects align with the overall financial strategy.

So if one project has an IRR of 10% and another has 15%, we should prefer the 15%, right?

Yes! Always compare their IRRs against the required rate of return and select the highest that exceeds expectations.
Limitations of IRR
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let's reflect on the limitations of using IRR. What should we be cautious about?

Multiple IRRs can confuse things, right?

Exactly! Also, IRR assumes reinvestment at the same rate, which may not be realistic in many scenarios.

So it’s important to use IRR alongside other analysis methods?

Yes, combining IRR with NPV or other methods enriches your investment analysis. Alright, let’s summarize what we covered today.

We discussed how IRR is calculated, its importance in project evaluation, and its limitations. Remember: IRR stands for Investment Returns Rank and is vital for strategic decision-making!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
IRR represents the discount rate at which the Net Present Value (NPV) of an investment is zero. It allows companies to compare and assess the feasibility of different projects, guiding strategic investment decisions.
Detailed
Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
The Internal Rate of Return (IRR) is a crucial concept in capital budgeting that helps businesses determine the profitability of an investment. It is defined as the discount rate that makes the NPV of all cash flows from a project equal to zero. Essentially, it provides insight into the rate of return expected from each dollar invested in a project, allowing for direct comparison with the company's required rate of return or cost of capital.
Importance of IRR
- Decision Rule: The general guideline is if the IRR exceeds the required rate of return, the project should be accepted, whereas if it falls below the required rate, the project should be rejected.
- Time Value of Money: IRR accounts for the time value of money, making it a reliable metric for investment comparisons.
- Investment Ranking: Projects can be ranked based on their IRR, facilitating strategic resource allocation.
However, it is essential to note potential drawbacks:
- Multiple IRRs: Non-conventional cash flows may result in multiple IRRs, complicating decision-making.
- Complexity: Manual calculation of IRR can be challenging, often necessitating software or iterative approaches for accuracy.
Understanding IRR is vital for BTech CSE students as it forms a foundation for analyzing investment projects in technology-driven enterprises, ultimately influencing corporate financial strategies.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Definition: Discount rate at which NPV is zero.
• Formula:
0=∑¿
Detailed Explanation
The Internal Rate of Return (IRR) represents the discount rate that makes the net present value (NPV) of all cash flows from a particular investment equal to zero. In simpler terms, if you discount future cash flows back to the present using the IRR, the total amount you get will equal your initial investment, meaning you're neither making nor losing money on the investment.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you invest in a lemonade stand. If you want to know what rate of return you're getting, you can calculate the rate at which the present value of your lemonade sales equals the cost you paid to set up the stand. If that rate is, say, 10%, that's your IRR, showing that you're breaking even at that discount rate.
Decision Rule for IRR
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Decision Rule:
o If IRR > Required Rate of Return: Accept the project.
o If IRR < Required Rate: Reject.
Detailed Explanation
The decision rule for IRR is straightforward: compare the calculated IRR to the minimum required rate of return set by the organization. If the IRR exceeds this required rate, the investment should be accepted, as it's expected to yield a good return exceeding the cost of capital. Conversely, if the IRR is lower than the required return, the investment is deemed unattractive and should be rejected.
Examples & Analogies
Think about a savings account that offers 2% interest. If you find an investment that promises a return of 5% (its IRR), you'd choose the investment because it exceeds your savings account interest rate. But if it only offers a return of 1%, you would likely pass on that investment, preferring your savings account instead.
Advantages of IRR
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Advantages:
o Considers time value of money.
o Easy to compare with cost of capital.
Detailed Explanation
One of the major advantages of the Internal Rate of Return is that it takes into account the time value of money, which means it acknowledges that money available today is worth more than the same amount in the future. This makes IRR a relevant metric in assessing an investment's profitability over time. Moreover, IRR provides a simple way to compare different investments against the cost of capital, making it easier for managers to make informed decisions.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the decision to buy a new smartphone. If the smartphone costs $1,000 now but is expected to save you $250 a year in costs, you want to know how long it will take before those savings cover the phone's cost and how that compares to other potential purchases. By calculating the IRR, you get a clear picture of whether this is a smart investment compared to other options.
Disadvantages of IRR
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Disadvantages:
o May produce multiple IRRs for non-conventional cash flows.
o Difficult to calculate manually.
Detailed Explanation
While IRR is a useful metric, it has its downsides. For projects with non-standard cash flows (for example, cash inflows and outflows occurring at different times), the calculation can yield multiple IRRs, complicating the decision-making process. Additionally, calculating the IRR, especially manually or without financial software, can be challenging and time-consuming, which may discourage its use in some cases.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you're trying to calculate your savings from several projects, but different projects yield cash in different amounts and times throughout their life. It's like trying to navigate a maze with multiple exits—sometimes you end up at a dead end because your calculations lead you to more than one 'answer,' making it hard to choose the right path.
Key Concepts
-
IRR: The discount rate at which the Net Present Value (NPV) equals zero.
-
NPV: The net value of cash inflows minus cash outflows discounted to present value.
-
Investment Ranking: Projects can be directly compared based on their IRR.
-
Complexity: Calculating IRR requires iterative or software-based methods.
Examples & Applications
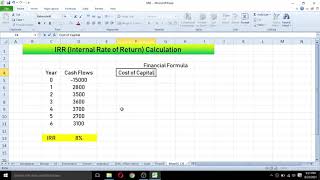
Example 1: A project has cash inflows of $1,000 per year for 5 years, with an initial investment of $3,000. By calculating the discount rate where NPV=0, suppose you find the IRR is 12%. If your required rate of return is 10%, you would accept the project.
Example 2: If a project has alternating cash flows that shift from negative to positive, it may result in two IRRs, complicating the decision process.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When NPV’s nothi's but zero, IRR is our hero!
Stories
Imagine a treasure map leading to a hidden chest. If each step costs you gold but yields shiny doubloons equivalent to IRR, only if the chest's value is less than what you expect would you go searching.
Memory Tools
IRR - Invest, Rank, Return!
Acronyms
IRR - Internal Rate Return!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
The discount rate that makes the NPV of a project zero, indicating the expected return from the investment.
- Net Present Value (NPV)
The difference between the present value of cash inflows and outflows over a period of time.
- Required Rate of Return
The minimum return an investor expects to achieve from an investment, used for comparison with IRR.
- Discount Rate
The interest rate used to determine the present value of future cash flows.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
