Role of Robotics and Automation in Geotechnical Engineering
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Need for Automation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will talk about the need for automation in geotechnical engineering. Why do you think it's important to reduce human exposure in hazardous investigations?

So that people don't get hurt, right?

Exactly! Automation helps to minimize risks to human safety while also improving data accuracy. Can anyone think of another benefit?

It probably makes the process faster too!

Yes! Automation enables real-time data collection, which enhances efficiency. Here's a memory aid: just think ‘A Fast Safe Study’ to remember the core benefits: Automation, Fast, Safety, Study. Let's now explore the advantages in detail.
Advantages of Robotics in Geotechnical Engineering
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss the advantages of using robotics in our field. Who can name one?

Real-time monitoring of soil conditions!

Right! This helps in immediate decision-making. Can someone explain how autonomous data collection might work?

Machines can gather and send data back without needing a person there all the time.

Exactly! This is a major advantage as it reduces human error. Here’s a mnemonic: ‘R.A.R.E.’ for Real-Time, Autonomous, Reduced error. Great job! Let's summarize these key points.
Enhancing Safety
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

One of the most critical aspects is safety. How does automation contribute to safety during site evaluations?

It keeps people away from dangerous areas!

Exactly! Using robotic systems, we can conduct evaluations without putting ourselves in harm's way. Can anyone recall a situation where this might be particularly useful?

What about landslide-prone areas?

Spot on! That's a perfect example. Remember: 'Safety First, Automation Right!' Let’s wrap up by revisiting why these advancements are critical.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The integration of robotics and automation in geotechnical engineering addresses the challenges of hazardous and time-consuming processes, providing real-time monitoring, autonomous data collection, and reduced human error. This leads to safer site evaluations and informed decision-making.
Detailed
In geotechnical engineering, the incorporation of robotics and automation has transformed traditional methods of soil investigations. Automation is vital for reducing human exposure to hazardous environments, increasing data accuracy, and enabling data-driven decision-making. Key advantages include real-time monitoring of soil conditions, autonomous collection and processing of data, reduced reliance on manpower, and enhanced safety during site evaluations. These technological advancements facilitate better analysis and prediction of slope stability, ultimately contributing to safer and more economical infrastructure development.
Youtube Videos
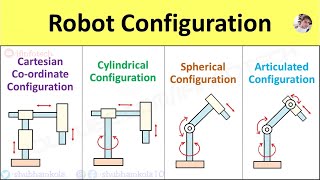







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Need for Automation
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Geotechnical investigations involve hazardous and time-consuming processes. Automation reduces human exposure, increases accuracy, and enables data-driven decision-making.
Detailed Explanation
Geotechnical investigations are essential for understanding soil and site conditions, which can be hazardous because they often take place in unstable environments like construction sites or landslide-prone areas. By introducing automation into these tasks, we minimize the risk to human workers. Automation allows for the collection of more precise data than manual methods, leading to better-informed decisions. Additionally, by relying on automated systems to gather and analyze data, we can make decisions based on solid, real-time information rather than estimates or incomplete data.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a fireman using a drone to survey a burning building from the air rather than entering the hazardous environment directly. The drone collects vital information that can help in strategizing the firefighting effort safely and efficiently, just like automation in geotechnical work allows for safer and more accurate site assessments.
Advantages of Robotics and Automation
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Real-time monitoring of soil conditions. Autonomous data collection and processing. Reduction in manpower and human error. Increased safety during hazardous site evaluations.
Detailed Explanation
Robotics and automation provide several advantages in geotechnical engineering. Firstly, they facilitate real-time monitoring, which allows engineers to track changes in soil conditions as they happen, providing quicker responses to any potential issues. Secondly, automated systems can collect and process data without human intervention, increasing efficiency and reducing the likelihood of human error. This not only speeds up data collection but also enhances the reliability of the results. Lastly, using these technologies in hazardous environments reduces the number of workers needed onsite, thereby minimizing exposure to dangerous situations, which increases overall safety.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a weather station that gathers data about conditions like temperature and humidity continuously and sends it to meteorologists in real-time. This automatic process helps keep people informed about weather changes without direct human input. Similarly, in geotechnical engineering, automated systems constantly monitor soil conditions to alert engineers about any potential risks without putting human workers at risk.
Key Concepts
-
Robotics and Automation: The integration of technology to perform tasks efficiently and safely.
-
Real-time Monitoring: Continuous observation allowing for immediate response.
-
Autonomous Data Collection: Machines collect and send data independently, minimizing human labor.
-
Increased Safety: Reduced risk for human operators in hazardous conditions.
Examples & Applications
Automated drilling rigs that gather soil samples from difficult terrains.
Usage of UAVs for rapid aerial surveys in landslide-prone regions.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In geotech, automation's the key, for safe work and data faster, you'll see.
Stories
A geotechnical engineer once stood at a cliff fearing a landslide. He called upon his robotic assistant, who gathered data and assured him it was safe, leading to his fame for the swiftest, safest evaluation in history.
Memory Tools
Remember 'S.A.F.E' for Safety, Automation, Fast, Efficiency in robotics.
Acronyms
Use 'R.A.R.E.' for remembering Real-time, Autonomous, Reduced error during robotics applications.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Robotics
Technology that uses machines to perform tasks automatically.
- Automation
Use of technology to perform tasks with minimal human assistance.
- Realtime Monitoring
Continuous observation of data as it is generated.
- Data Acquisition
The process of collecting and measuring data from signals or sensors.
- Slope Stability
The condition in which a slope is able to sustain itself against sliding or collapse.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
