Mechanical and Environmental Constraints
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Mechanical Constraints
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will discuss the mechanical constraints faced by robots during automated soil sampling. Can anyone tell me what might affect a robot's ability to navigate different terrains?

Maybe the type of wheels or tracks can influence how well they move over rocky or uneven surfaces?

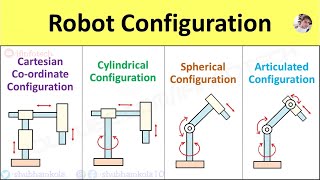
Exactly! The design of the robots, whether they have tracks like a tank or wheels, plays a significant role in maneuvering through challenging environments. Remember the acronym 'WHEEL' for 'Wheels, Hitches, Elevation, Environment, and Load' - these factors influence the performance of the sampling robots.

What happens if the robot gets stuck in mud or soft soil?

Good question! If a robot becomes immobilized, it may lead to time delays and inaccuracies in sampling. Unpredictable environments can hinder their operational efficiency.

So, if they're facing rough terrain, do engineers have to redesign these robots?

Yes, that's correct! Engineers may need to adapt the design depending on the environment where the robot will operate. Let's summarize this session: Mechanical constraints on sampling robots include the robot's design, terrain type, and environmental obstacles, which all affect operational effectiveness and mobility.
Exploring Environmental Constraints
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's shift our focus to environmental constraints. What do you think might be the environmental factors that can complicate soil sampling?

Well, contamination may be an issue, especially if the soil has chemicals or pollutants.

Great point! Soil contamination can significantly affect sampling results. The acronym 'CHEM' could help you remember - it stands for 'Chemical composition, Hazardous materials, Environmental regulations, and Microbial presence'.

What if the soil has a lot of variation in types and structure?

That's another excellent angle! Soil heterogeneity complicates sampling since different types yield varying results. It highlights the importance of targeted sampling strategies.

So, do we need to take special precautions when sampling in contaminated areas?

Absolutely! Proper protocols must be established to avoid contamination during the sampling process. To conclude this session, environmental constraints include soil contamination risks and variability, both of which require careful consideration to ensure the accuracy of automated sampling.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section outlines the mechanical challenges robots may face in difficult terrain along with issues related to soil heterogeneity, contamination, and risk factors that must be considered during automated soil sampling and testing processes.
Detailed
Mechanical and Environmental Constraints
Automated soil sampling and testing technologies revolutionize the agricultural and civil engineering fields, but they come with their own set of challenges. Among these, mechanical constraints arise when robots operate in difficult terrains, such as rocky surfaces, wetlands, or uneven ground. These environments hinder the robot's mobility and functionality, making it harder to obtain accurate soil samples. Additionally, the inherent variability of soil composition and structure can affect the accuracy of tests, particularly when contamination risks are present. Therefore, understanding these mechanical and environmental constraints is imperative for optimizing automated sampling techniques and ensuring reliable soil testing outcomes.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Challenges in Difficult Terrain
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Difficult terrain for robots
Detailed Explanation
This chunk discusses how challenging landscapes, such as rocky areas, steep slopes, or marshy ground, can hinder the movement and operation of robotic soil sampling equipment. Robots designed for flat and even surfaces may struggle to navigate or perform efficiently in such terrains. As a result, engineers need to consider the robot's design and capabilities based on the specific environment in which it will be used.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to ride a bicycle on a mountain trail versus a smooth road. On the bumpy, steep path, you would have a hard time balancing and moving forward, just like how a robot may have difficulties navigating through difficult terrains.
Soil Heterogeneity Issues
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Soil heterogeneity and contamination risks
Detailed Explanation
Soil heterogeneity refers to the variation in soil properties across a small area. This can pose a problem for automated sampling systems because a single sample may not accurately represent the wider area of soil. Additionally, contamination risks can arise from the equipment itself or the environment, making it crucial to ensure that samples are pure and representative. Proper calibration and avoidance strategies are essential for overcoming these challenges.
Examples & Analogies
Think of soil as a layered cake. If you cut a slice that only includes frosting without any cake, it’s not a true representation of the entire cake. Similarly, if soil samples collected by robots aren't diverse, they may misrepresent the area's overall soil condition.
Key Concepts
-
Mechanical Constraints: Physical challenges that affect robotic mobility and function.
-
Environmental Constraints: Factors such as soil contamination and variability that may influence sampling accuracy.
-
Soil Heterogeneity: The uneven distribution of soil properties across an area.
-
Contamination Risks: The potential presence of hazardous materials that could compromise sample integrity.
Examples & Applications
A wheeled robot may struggle to navigate over rocky terrain, leading to mobility issues.
Sampling in contaminated sites requires strict safety protocols to prevent data contamination.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In tough terrain, robots may strain, with design and soil affecting their gain.
Stories
Once, in a forest filled with rocky ground, a robot aimed to gather soil around. It struggled to move as it took a test, reminding all to think of design when navigating the quest.
Memory Tools
Remember 'CHEM' for Environmental considerations: Chemical composition, Hazardous materials, Environmental regulations, and Microbial presence.
Acronyms
WHEEL
Wheels
Hitches
Elevation
Environment
and Load—factors affecting robot mobility.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Mechanical Constraints
Challenges faced by automated systems related to their physical design and environment preventing optimal performance.
- Environmental Constraints
Limitations arising from environmental factors, including soil composition, contamination, and terrain challenges.
- Soil Heterogeneity
The variability in the composition and properties of soil across a given area.
- Contamination Risks
The potential for soil samples to be affected by chemicals or pollutants present in the soil.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
