Chain of Responsibility Pattern
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to the Chain of Responsibility Pattern
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we'll discuss the Chain of Responsibility Pattern. This pattern allows a request to be passed along a chain of handlers. Who can tell me why we might want to use this pattern instead of a direct call?

Maybe for better organization of code?

Exactly! It helps decouple the sender and receiver. When we decouple, it makes the handling of requests more flexible.

What types of situations is this pattern usually used?

Great question! It's particularly useful in event handling systems and middleware applications.

Can we create multiple handlers for a single request?

Yes! Each handler can decide to process the request or pass it along. Let's remember this with the acronym 'CHAIN': Chain, Handle, Action, Independent, Node.
Components of the Pattern
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s discuss the components of the Chain of Responsibility Pattern. Can anyone name a component used in this pattern?

I think there's something called a handler?

Correct! In this pattern, a handler processes requests and can either handle them or pass them along the chain. Let’s think of this as a relay race where each runner has a chance to take the baton.

What happens if no handler can process the request?

If no handler is capable of processing the request, it simply gets dropped. We want to avoid having unhandled requests, which brings us to careful design considerations in choosing the right handlers.
Real-Life Applications of the Pattern
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's look at real-life applications of the Chain of Responsibility Pattern. Can anyone give me an example?

Event handling in a GUI application?

Exactly! In a GUI, a single event can be processed by multiple handlers. Think about clicking a button; it can trigger multiple actions based on the app's business logic.

What about middleware, is it used there as well?

Yes! Middleware uses this pattern extensively to process incoming requests in a web application. Modular processing can speed up development and make adding new features simpler.
Advantages and Disadvantages
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

What do you think are the advantages of using the Chain of Responsibility Pattern?

It makes the code more flexible and reusable?

Right! And what about drawbacks?

What if we have too many handlers? That could complicate things.

Exactly, too many handlers can lead to unpredictable behavior and can be difficult to debug. It's important to balance the use of handlers in your design.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This pattern allows for multiple objects to process a request without knowing which object will handle it. It's useful for managing event handling systems and can improve code decoupling and flexibility in processing requests.
Detailed
Chain of Responsibility Pattern
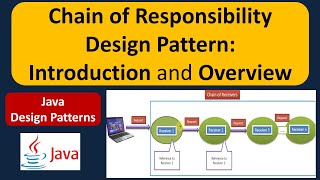
The Chain of Responsibility Pattern is classified as a behavioral design pattern that allows an object to delegate a request to a chain of potential handlers. Instead of having a single handler process a request, the request passes through a chain where each handler has the opportunity to process the request or pass it along to the next handler in the chain. This structure decouples the sender of the request from its receiver, allowing for more flexible and manageable code structures.
Key Points
- Decoupling: The pattern promotes loose coupling, letting objects pass along requests without needing to know about the specifics of the processing logic of the receivers.
- Event Handling: It is commonly used in event handling systems, where a single event may need to be processed differently by various handlers depending on the context.
- Middleware: In middleware applications, this pattern is particularly beneficial as it allows for modular processing where various components can handle requests independently.
By implementing this pattern, developers can add new handlers dynamically at runtime, reassign them, or skip them without modifying the entire processing logic of the application.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Chain of Responsibility Pattern
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Chain of Responsibility Pattern passes a request along a chain of handlers until one handles it.
Detailed Explanation
The Chain of Responsibility Pattern is a behavioral design pattern used to pass requests along a chain of potential handlers until one of them handles the request. Rather than having a single handler responsible for fulfilling a request, this pattern allows multiple objects to process the request, each in turn. This creates a flexible and decoupled structure since the sender of the request does not need to know which handler will ultimately process it.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a customer service center where a call might be directed through a series of representatives. If the first representative cannot resolve the issue, they pass the call to their supervisor, and if that supervisor can’t help, it goes to the manager. The request keeps moving until someone has the proper authority or knowledge to solve the problem, analogous to how requests travel through a chain of handlers in this pattern.
Use Cases of the Chain of Responsibility Pattern
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Use Case: Event handling systems, middleware.
Detailed Explanation
The Chain of Responsibility Pattern is particularly useful in scenarios such as event handling and middleware processing. In an event handling system, an event like a mouse click might need to be processed by several components (e.g., buttons, menus, or panels) that might respond to it. Each component can either handle the event or pass it along to the next component in the chain. This allows for a clean separation of concerns, where each component knows what types of events it can handle, but the system does not have to be rigidly defined at the outset.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a multi-tier support system for a software product. The initial request could go to the frontline support agent. If they can't resolve the issue, it escalates to a technical team, and if they can't fix it, it goes to product development. Each level is responsible for addressing specific issues, and by using the Chain of Responsibility, the user experience remains smooth, without requiring the user to know who exactly will be handling their concern.
Key Concepts
-
Decoupling: Breaking dependencies between sender and receiver objects.
-
Request Passing: The process of passing requests through multiple handlers.
-
Event Handling: Managing responses to user actions in applications.
-
Middleware: Facilitates processing requests in web applications.
Examples & Applications
In a GUI application, a button click can trigger multiple actions based on different event handlers.
Middleware in web applications can use the Chain of Responsibility to process requests across different services.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In a chain, requests move down, handlers wait, ready to astound.
Stories
Imagine a relay team where each runner has a chance to pass the baton, ensuring teamwork and efficiency in reaching the finish line.
Memory Tools
Remember 'CHAIN': Chain of requests, Handlers in play, Actions taken, Independent processing, Node of decision.
Acronyms
CHAIN stands for Chain, Handle, Action, Independent, Node.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Handler
An object that processes incoming requests and either handles or forwards them in the Chain of Responsibility.
- Request
The input or action that is passed along the chain to be handled by specific handlers.
- Event Handling System
A system designed to respond to user or application-generated events.
- Middleware
Software that acts as a bridge between an operating system or database and applications, often used to manage requests.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
