Interpreter Pattern
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding the Basics of the Interpreter Pattern
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to learn about the Interpreter Pattern. Can anyone tell me what they understand by the term 'Interpreter' in programming?

Is it something that runs code like a compiler?

Good thought! However, an interpreter translates high-level language code into executable code at runtime, defining how expressions and statements are evaluated and interpreted. The Interpreter Pattern, specifically, provides a structured way to define a language's grammar.

What does it mean to define a grammar?

Defining grammar means specifying the rules and structure of the language. It helps in understanding how sentences are formed and guides the interpreter in processing them. Think of grammar as the blueprint that outlines valid expressions.
Key Components of the Interpreter Pattern
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's discuss the specific components that are vital in the Interpreter Pattern. Can anyone guess what those components might be?

Maybe the rules for the language and the parts that do the interpreting?

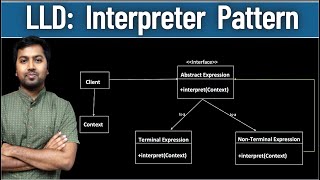
Exactly! The main components are usually the abstract expression, terminal expressions, and non-terminal expressions. The abstract expression defines an interface for the interpret method, while terminal and non-terminal expressions implement the rules. Can anyone give an example of where we might use this?

SQL queries!

Correct! In SQL interpreters, you define expressions to evaluate queries and process results according to predefined rules.
Real-World Applications of the Interpreter Pattern
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s discuss some real-world applications where we might apply the Interpreter Pattern. What can come to mind?

Maybe mathematical expression evaluators?

Yes, mathematical expression evaluators are a classic use case. They require a well-defined grammar to handle mathematical syntax and logical expressions. Another common application could be in developing scripting languages for applications.

Why is this important in software design?

Great question! Using the Interpreter Pattern allows developers to create flexible and extensible systems where new expressions can be added without altering the existing structure. This ensures your system can evolve alongside your project needs.
Design Considerations for the Interpreter Pattern
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

As we wrap up, what are some design considerations we should keep in mind when implementing the Interpreter Pattern?

I guess we should think about when to use it and if it will really simplify things?

Exactly! The Interpreter Pattern is powerful but can become complex if overused, making it essential to evaluate if the added complexity is justified. If a language's grammar becomes too intricate, the interpreter might result in excessive overhead.

What about performance? Does it impact that?

Yes, performance can be a consideration as well. Interpreters can be slower than direct execution due to the parsing process, so it's essential to balance the clarity and necessity of the Interpreter Pattern with potential performance implications. Always assess the project's specific requirements.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The Interpreter Pattern is a behavioral design pattern that specifies how to interpret a language's grammar and define rules for interpreting sentences from that grammar. It is often utilized in applications like SQL interpreters and expression evaluators, where the grammar and the corresponding logic for interpreting it are crucial for functionality.
Detailed
Interpreter Pattern
The Interpreter Pattern is a behavioral design pattern that defines a representation for a language's grammar along with an interpreter that uses the representation to interpret sentences in the language. This pattern is particularly useful in scenarios where a specific language is defined - meaning that the syntax and overall structure of expressions must be understood and processed.
Key Features:
- Grammar Definition: It allows you to define a grammar for a language in a way that is easy to manage and extends.
- Interpretation Logic: The interpreter translates sentences from a language into actions or other forms of representations, often encapsulating complex logic.
Use Cases:
Common use cases for the Interpreter Pattern include:
- SQL interpreters that execute statements in a database.
- Expression evaluation, where expressions (like mathematical expressions) need to be parsed and interpreted properly.
This design pattern is significant because it simplifies complex interpretation logic by breaking the grammar into manageable components, making the application easier to extend and maintain.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Interpreter Pattern
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Defines a grammar and provides an interpreter to interpret sentences of the grammar.
Detailed Explanation
The Interpreter Pattern is a design pattern used in software engineering to parse and execute sentences in a specific language defined by a grammar. In simpler terms, it enables a program to translate statements into executable actions based on the language rules it is designed to understand. This pattern is particularly useful for building compilers or interpreters for programming languages or scripting tasks where the syntax or commands need to be parsed and executed.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the Interpreter Pattern like a translator for languages. Just as a translator takes a sentence in French, deciphers its meaning based on the grammar rules of French, and then translates it into English, the Interpreter Pattern interprets input based on a defined set of rules and executes the corresponding actions in the system. For instance, if you command a virtual assistant with a specific phrase, the assistant interprets the request and carries out the appropriate action.
Use Case of the Interpreter Pattern
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Use Case: SQL interpreters, expression evaluation.
Detailed Explanation
The Interpreter Pattern commonly finds use in scenarios like SQL interpreters and expression evaluators. In these contexts, it allows for the parsing of SQL commands or mathematical expressions that consist of unique syntax and operations. By defining a grammar for these commands, an interpreter can read the expressions and execute the necessary operations, such as querying a database or calculating a result.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you're a chef following a recipe that contains specific instructions for making a dish. Each instruction corresponds to an action you need to take in the kitchen (like chopping vegetables or boiling water). Similarly, an SQL interpreter takes a structured query (the recipe) and processes it to fetch or manipulate data in a database (cooking the dish). Just as you rely on your understanding of the recipe to create a tasty meal, a program relies on the Interpreter Pattern to accurately execute SQL statements.
Key Concepts
-
Interpreter Pattern: A design pattern that defines a grammar and an interpreter for interpreting sentences from that grammar.
-
Grammar: Rules that define the structure of a language, allowing the interpreter to parse and evaluate expressions.
-
Abstract Expression: An interface that all expression classes implement in the Interpreter Pattern.
-
Terminal and Non-terminal Expressions: Components that represent specific parts of the grammar that can be executed or further decomposed for interpretation.
Examples & Applications
Developing a SQL interpreter where different SQL commands are parsed and executed based on language grammar.
Creating a mathematical expression evaluator where input expressions are parsed and resolved into calculated values.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Interpreter, syntax creator; rules in place, for code to cater.
Stories
Imagine a wizard who knows the way of a mystical language. This wizard deciphers sentences spoken in that language, following strict rules just like the Interpreter Pattern guides how code gets processed.
Memory Tools
GRACE - Grammar, Rules, Abstract, Components, Evaluation. Remember these to understand the core of the Interpreter Pattern.
Acronyms
GAP - Grammar, Abstract Expression, Processing. Use this to remember the structure of the Interpreter Pattern.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Interpreter Pattern
A behavioral design pattern that defines a grammar for a language and an interpreter for interpreting sentences of that grammar.
- Grammar
The set of rules that define the structure of a language, including syntax and sentence formation.
- Abstract Expression
An interface that declares an 'interpret' method in the Interpreter Pattern.
- Terminal Expression
Implements the abstract expression interface for productions in the grammar that can be directly interpreted.
- Nonterminal Expression
Represents a complex structure in grammar that can be broken down into simpler expressions.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
