Spiral Model
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to the Spiral Model
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're discussing the Spiral Model. Does anyone know why 'spiral' is an appropriate name for this model?

Maybe because it involves going around in loops?

Exactly, Student_1! Each loop is a phase in the development process. This model focuses on iterative development and risk assessment. Let's remember the key steps: Planning, Risk Analysis, Engineering, and Evaluation. You can think of them as P-R-E-E, or 'PREP' for short!

What’s the point of doing risk analysis?

Great question! Risk analysis helps in identifying potential problems early, allowing teams to address issues before they escalate. It's like spotting a storm before you head out to sea.

So it helps make the project safer?

Exactly, Student_3! By integrating risk management, the Spiral Model enhances the likelihood of project success. Always keep in mind the acronym's meaning: PREP!
The Phases of the Spiral Model
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dive deeper into the cycles of the Spiral Model. Can someone name one of the phases?

Planning?

Exactly! Planning is the first phase. We should identify goals and gather requirements. Why do you think it’s critical?

Because it sets the direction for the whole project?

Right! Now after planning, we have risk analysis. What comes next?

Engineering, where we actually write code?

That's correct! Then we move to evaluation, where we gather feedback. So, who can summarize the four phases?

'PREP': Planning, Risk Analysis, Engineering, and Evaluation!

Excellent summary, Student_3! The process enhances software quality and minimizes risks effectively.
Applications of the Spiral Model
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand the Spiral Model, when do you think it might be most beneficial to use this model?

Maybe for large projects where requirements change a lot?

Absolutely! The Spiral Model excels in environments characterized by high complexity and risk. Can anyone think of a real example?

What about software for medical devices? They must be very carefully designed!

Exactly! Medical software has stringent requirements and high stakes. This is where the iterative, risk-focused approach of the Spiral Model shines.

What if the project has a fixed scope and requirements?

Then, more traditional models like Waterfall might be more suitable. The Spiral Model is all about flexibility.

So, it's about knowing when to apply it?

Exactly! It's essential to assess the project's needs before selecting the model. Remember: flexibility in development can lead to project resilience!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
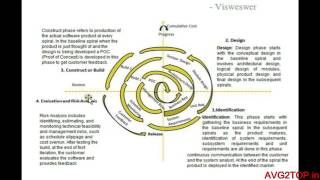
The Spiral Model is a framework in software development that integrates iterative development with risk assessment at every phase or loop. It promotes continuous refinement through planning, risk analysis, engineering, and evaluation, making it an effective choice for handling complex projects.
Detailed
Spiral Model
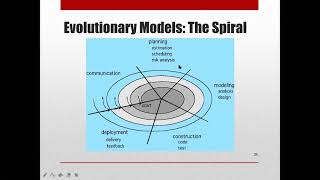
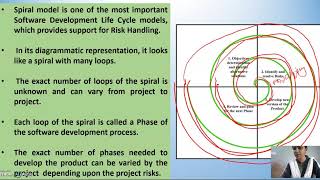
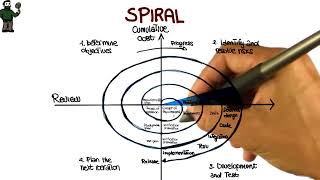
The Spiral Model is a sophisticated software development framework that combines elements of both iterative and incremental models while emphasizing risk management. By organizing the development process into modules called "spirals," each loop in the spiral consists of four main phases:
- Planning: Identifying goals, objectives, and requirements while considering potential risks that can affect the project.
- Risk Analysis: Assessing risks associated with the current project phase and determining how they can influence the development process.
- Engineering: The actual coding and development of the project, adhering to the design that arises from prior engineering tasks.
- Evaluation: Gathering feedback from stakeholders to evaluate the product against user expectations and requirements, enabling iterative refinements.
This iterative process makes the Spiral Model particularly suited for large, complex, and high-risk projects where requirements may evolve considerably as the project progresses. Its main goal is to produce quality software while minimizing risks and maximizing the chances of project success.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of the Spiral Model
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Combines iterative development with risk analysis.
• Each loop = planning + risk analysis + engineering + evaluation.
Detailed Explanation
The Spiral Model is a software development methodology that integrates elements of both iterative development and risk management. It consists of multiple loops or cycles, where each loop represents a mini-project. These loops involve important activities like planning, analyzing risks, engineering, and evaluating outcomes. The goal is to gradually refine the product while continually assessing and mitigating potential risks that could hinder the project's success.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the Spiral Model like planning a journey. Each loop represents a different leg of the journey, where you first plan your route, evaluate potential risks (like bad weather), and make adjustments (in terms of routes or mode of transport) before continuing onward. This approach ensures a safer trip as you adapt to changing circumstances.
Phases of Each Loop
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Planning: Define goals, resources, and timelines.
• Risk Analysis: Identify potential risks and their impact.
• Engineering: Develop components or features based on the current loop's goals.
• Evaluation: Review progress, gather feedback, and make adjustments.
Detailed Explanation
Each loop in the Spiral Model consists of four key phases. In the planning phase, project goals, resources, and timelines are defined to set a clear direction. The risk analysis phase focuses on identifying potential risks that could derail the project, evaluating their potential impact, and devising strategies to mitigate them. During the engineering phase, actual development work takes place, where components or new features are created. Finally, during the evaluation phase, the outcomes of the loop are reviewed. Feedback is gathered from stakeholders, allowing teams to make necessary adjustments in subsequent loops.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a chef perfecting a new recipe. The planning phase involves gathering ingredients and deciding on cooking times. The risk analysis may involve considering if an ingredient might spoil or if a cooking method could fail. In the engineering phase, the chef prepares the dish, and in the evaluation phase, they taste it, possibly gathering opinions from others and making adjustments for the next attempt. Each time they go through this loop, they move closer to the perfect recipe.
Benefits of the Spiral Model
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Flexible to changes during development.
• Emphasizes continuous risk assessment.
• Suitable for large, complex projects that require significant funding and time.
Detailed Explanation
The Spiral Model offers several advantages, particularly its flexibility. Since it involves a series of iterations, teams can adapt to changes in requirements or technology throughout the development process. Additionally, the constant emphasis on risk assessment allows teams to proactively address issues before they become problematic. This model is particularly beneficial for large and complex projects, where the stakes are high, and extensive resources are invested.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a city planner designing a new complex infrastructure project. With the Spiral Model approach, after each phase of planning (or construction), they reassess the project's progress and the risks involved, such as budget overruns or community feedback. If issues arise, they can tweak plans in subsequent phases, ensuring that by the end of the project, the city has a well-planned and executed infrastructure that meets community needs.
Key Concepts
-
Spiral Model: A software development framework that integrates iterative development with risk analysis.
-
Risk Analysis: A critical phase assessing potential project risks to ensure success.
-
Iterative Development: The process of progressively refining software through cycles.
-
Phases: Main phases include Planning, Risk Analysis, Engineering, and Evaluation.
Examples & Applications
Developing software for defense systems where outcomes must be rigorously tested for reliability.
Creating a new mobile application that requires evolving features based on user feedback during iterations.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the Spiral, we PREP, every loop we won't forget.
Stories
Imagine a spiral staircase where every step is a phase. As you ascend, you check for hidden dangers and ensure everything is in place before moving up!
Memory Tools
Use 'PREP' to remember: Planning, Risk analysis, Engineering, Evaluation.
Acronyms
P-R-E-E stands for Planning, Risk Analysis, Engineering, Evaluation.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Spiral Model
A software development model that combines iterative development with risk analysis, organized into phases referred to as loops.
- Risk Analysis
The process of assessing potential risks that may affect a project's success.
- Iterative Development
A process that allows for gradual refinement of software through multiple iterations or cycles.
- Planning
The phase where goals, objectives, and requirements are identified for the project.
- Evaluation
The phase of reviewing and gathering feedback on the software product to ensure it meets expectations.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
