Importance of Signal Processing in Communication
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
The Role of Signal Processing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're going to talk about the importance of signal processing in communication. Can anyone explain why it might be essential?

I think it helps to send and receive signals better.

Exactly! Signal processing is all about making signals easier to transmit and clearer for communication. What do you think happens without signal processing?

Maybe the signals would get mixed up or noisy?

Great point! Without it, we'd struggle with noise and interference. Now let's remember this with the acronym 'CLEAR'—C for Clarity, L for Loss reduction, E for Enhancement, A for Accurate transmission, and R for Recovery of signals.

How does it enhance clarity?

Signal processing uses techniques for noise removal, which helps in enhancing clarity.

What are examples of these technologies?

Excellent question! Technologies such as mobile phones, television, and satellite communication all rely on signal processing.

To summarize, signal processing improves transmission and reception by enhancing clarity and removing noise.
Noise in Communication
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dive deeper into noise. What do you think is noise in signals?

I imagine it as static or unwanted sounds in music.

Absolutely! Noise interferes with the original signal's quality. How do you think we can combat this?

By filtering out the noise?

Yes! Filtering is one significant function of signal processing. It helps us obtain the pure message. Remember the phrase 'Clear the noise to hear the voice'.

What kind of filtering is commonly used?

There are different types, such as low-pass filters, which let low frequencies through and block higher frequencies, improving clarity.

So, it's like a filter on social media?

Exactly! Just like a filter shapes our digital experience, filtering in signal processing shapes the quality of communication.

In summary, noise disrupts signals, but filtering helps regain clarity.
Applications of Signal Processing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's look into real-world applications. Can anyone name a technology that uses signal processing?

Mobile phones!

Television systems!

Absolutely right! Signal processing is vital in both mobile phones and televisions. It helps ensure our devices communicate effectively. What processes might be involved?

Maybe modulation and demodulation?

Correct! Modulation allows us to send data over carriers, and demodulation lets us retrieve it. Think 'MOD to Send and DEMOD to Receive'.

What about the internet?

Great point! The internet relies heavily on digital signal processing techniques to ensure data is sent and received accurately.

In conclusion, applications of signal processing span across all modern communication technologies, emphasizing its importance.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section highlights the significance of signal processing in communication systems, addressing how it improves transmission, reception, and modification of signals while ensuring clarity and reducing noise. It underscores the applications of signal processing in technologies like mobile phones and the internet.
Detailed
Importance of Signal Processing in Communication
Signal processing serves as a fundamental element in communication technologies, facilitating the effective transmission, reception, and modification of signals. Within this section, we explore three primary roles of signal processing: noise reduction, signal clarity enhancement, and its application in various modulation and encoding processes. This is particularly vital for communication systems found in mobile phones, television broadcasting, satellite communication, and internet services. The integration of these processes ensures that information is conveyed accurately, ultimately leading to improved connectivity and user experience across different platforms.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
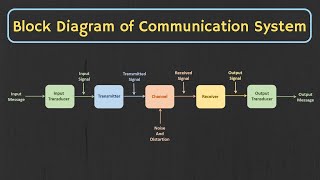
Efficient Signal Transmission
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Enables efficient transmission, reception, and modification of signals.
Detailed Explanation
This point emphasizes that signal processing plays a crucial role in how we send, receive, and adjust signals to ensure they are transmitted effectively. When we communicate, whether through a phone call or an internet connection, signals need to be handled carefully to maintain their integrity. Signal processing techniques help in optimizing these processes so that information can be sent quickly and accurately.
Examples & Analogies
Think of signal processing like a mail sorting system. Just as a mailroom sorts letters to ensure they reach their correct destinations without delay, signal processing helps manage and direct signals so that they arrive as intended.
Noise Reduction and Signal Clarity
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Removes noise and enhances signal clarity.
Detailed Explanation
Noise can be any unwanted or irrelevant signal that interferes with the desired information signal. Signal processing involves techniques that filter out this noise, making the desired signal clearer and more understandable. This is vital for communication systems where clear reception of the message is necessary to avoid misunderstandings.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to listen to your favorite song in a crowded restaurant. The background chatter is like noise in a signal. If someone turns down the volume of the chatter (filters the noise), you can hear your song better, just like signal processing helps clarify signals by reducing noise.
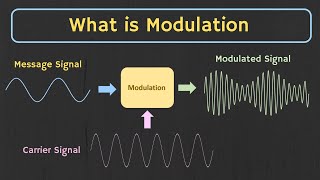
Modulation, Encoding, and Decoding
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Used in modulation, encoding, and decoding processes in communication systems.
Detailed Explanation
In communication systems, modulation is the process of varying a carrier signal to transmit information. Encoding converts this information into a format suitable for transmission, while decoding retrieves the original information at the receiving end. Signal processing techniques are essential for these processes, ensuring that messages can be sent and received accurately over various mediums.
Examples & Analogies
Consider sending a secret message. You might write it in a special code (encoding) that only your friend knows how to decode. During transmission, you may need to adjust how you write the message based on the medium (like writing on paper vs. shouting), similar to modulation in communication.
Applications in Modern Technology
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Essential for mobile phones, television, satellite, and internet systems.
Detailed Explanation
Signal processing is integrated into many of the devices we use daily, such as mobile phones for voice and video calls, televisions for broadcasting signals, satellites for GPS and communications, and the internet for streaming data. The effectiveness of these technologies relies heavily on advanced signal processing techniques to ensure quality and reliability.
Examples & Analogies
When you watch your favorite show on TV, you might not realize that signal processing is at work ensuring that the audio and video are synced and clear. Just like a team of chefs working together to create a perfect dish, various signal processing functions collaborate to provide a seamless communication experience.
Key Concepts
-
Signal Processing: Fundamental for efficient transmission and reception of signals.
-
Noise Reduction: Vital for improving signal clarity.
-
Modulation/Demodulation: Essential processes in communication for sending and receiving information.
Examples & Applications
Mobile phones use signal processing to enhance voice clarity and reduce background noise.
Television systems employ modulation techniques to transmit audio and video signals effectively.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To send and receive, we must strive, Filter the noise to help clarity thrive.
Stories
Imagine a radio voice muddled with static, until it’s finally tuned to pure clarity, allowing the singer's sweet voice to be heard—thanks to signal processing.
Memory Tools
To remember the key roles of signal processing, think CLEAR: Clarity, Loss reduction, Enhancement, Accurate transmission, Recovery.
Acronyms
The acronym MOD helps recall modulation related to the transmission
for Modulation
for Overlying data
for Delivering effectively.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Signal Processing
The analysis and transformation of signals to extract useful information or enable transmission.
- Noise
Unwanted interference that disrupts the clarity of the signal.
- Modulation
The process of imposing information onto a carrier wave for signal transmission.
- Clarity
The quality of being clear and easily understood, particularly in signal quality.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
