Key Definitions
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Signals
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's start by discussing what a signal is. Can anyone tell me how we define a signal?

Isn't it like a wave or something that carries information?

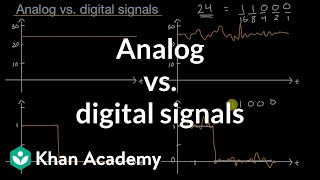
Good point! A signal is indeed a function that conveys information about a physical phenomenon. Now, can someone differentiate between an analog signal and a digital signal?

Analog signals are continuous, right? Like music that keeps flowing?

And digital signals are discrete, like the 0s and 1s in a computer?

Exactly! Analog signals vary continuously over time, while digital signals take discrete values. This distinction is crucial. Let's think of a memory aid: for 'Analog', think 'a wave'; for 'Digital', think 'dots'.

That makes it easier to remember!

Great! Remember that both types are essential in signal processing.
Categories of Signals
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, we need to address the various categories of signals. Who can tell me the difference between continuous-time and discrete-time signals?

Continuous-time signals are defined at every moment, while discrete-time signals only exist at specific moments.

Like a video versus a photo; one captures all moments while the other captures just one at a time!

That's a perfect analogy! Continuous-time signals are compared to sine waves, while discrete-time signals are like samples of those waves. Let's remember this as 'Video vs. Photo'.

So, a sine wave is an example of a continuous signal?

Correct! Now let’s consider other types, such as deterministic and random signals. What do you think about those?

Deterministic sounds predictable, while random would be chaotic and unpredictable!

Exactly! Deterministic signals have a predictable behavior, while random signals do not. Great insights so far!
Understanding Systems in Signal Processing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

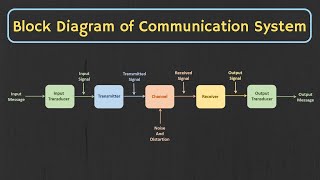
Let’s shift our focus to the concept of a system in signal processing. Can someone explain what a system does?

A system is something that processes an input signal to create an output signal!

Is it like a machine that modifies the signal?

Absolutely! Systems can be devices or algorithms that manipulate signals for various purposes. Remember, a system is essential for transforming signals from one form to another.

So systems can also include things like an equalizer in audio processing?

Exactly right! An equalizer changes the frequency balance of audio signals, showcasing how systems can serve many functions. Great example!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Key Definitions offers an overview of critical terms used in signal processing. It differentiates between analog and digital signals, introduces the notion of systems, and explains important processes like sampling and quantization, foundational to understanding signal transformation and analysis.
Detailed
Key Definitions
Signal processing is a field that deals with analyzing and transforming signals to glean information or enhance transmission. In this section, key concepts are introduced that are fundamental to signal processing. A 'signal' is a function that represents information about a physical phenomenon, and they are categorized into analog and digital types.
Key Terms:
- Signal: A representation of a physical phenomenon that conveys information.
- Analog Signal: A continuous signal that varies over time, like an audio waveform.
- Digital Signal: A discrete representation of a signal taken at specific intervals, often represented in binary code.
- System: Refers to either a device or an algorithm that processes an input signal to produce an output signal.
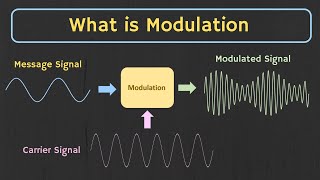
- Sampling: The process of converting a continuous signal into discrete values at consistent intervals
- Quantization: The technique of mapping a large range of values to a smaller set in digital representation.
- Encoding: Refers to the conversion of quantized values into binary format.
Each of these definitions plays a crucial role in understanding how signals are manipulated and within what framework signal processing operates. The knowledge of these concepts is essential for delving into more complex topics in signal processing.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Signal
Chapter 1 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Signal: A function that conveys information about a physical phenomenon.
Detailed Explanation
A signal is essentially a way to represent information or data that describes a physical condition or event. This can include sounds, lights, or any measurable aspect in nature. Essentially, if there is something in the environment that can be measured, it can be thought of as a signal.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a signal like a song being played on a radio. The song conveys information (music, lyrics) that communicates feelings and ideas. Just as the song represents the artist's creativity, a signal represents information about a specific physical event.
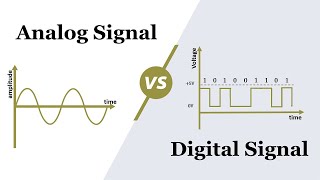
Analog Signal
Chapter 2 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Analog Signal: Varies continuously over time (e.g., audio waveform).
Detailed Explanation
An analog signal is a type of signal that changes continuously over time. This means its value can take any value within a range, creating a smooth waveform. For example, if you look at a sound wave from a musical instrument, the sound wave is plotted as a continuous curve that corresponds to the changes in sound intensity over time.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a dimmer switch for lights. If you slowly increase the light intensity from off to bright, you can visualize an analog signal's smooth transition, which represents varying levels of light as the switch is adjusted.
Digital Signal
Chapter 3 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Digital Signal: Takes discrete values at specific time intervals (e.g., binary data).
Detailed Explanation
In contrast to analog signals, digital signals represent information by taking discrete values. This means that at specific moments in time, the signal will take on a particular value, often represented in binary (0s and 1s). Digital signals are widely used in computers and digital systems because they are less susceptible to noise and distortion.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a staircase. Each step on the staircase represents a discrete value. Just like you can only stand on the steps, not between them, a digital signal can only take specific values at set intervals, akin to those 'steps.'
System
Chapter 4 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
System: A device or algorithm that processes an input signal to produce an output.
Detailed Explanation
A system in signal processing is responsible for taking an input signal, processing it in some way, and then producing an output signal. Systems can be physical devices like radios or algorithms such as software that manipulates audio or images. They play a crucial role in shaping how we interact with signals.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a coffee machine as a system: it takes in coffee grounds and water (input signal), processes them by brewing (the algorithm), and outputs a freshly brewed cup of coffee (output signal). Just like how the coffee machine transforms inputs into a desired beverage, signal processing systems transform information into a usable format.
Sampling
Chapter 5 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Sampling: Converting a continuous signal into discrete values at regular intervals.
Detailed Explanation
Sampling is the process of converting a continuous signal (like an analog signal) into a digital signal by taking measurements at regular intervals. Each of these measurements represents the value of the continuous signal at that specific time, transforming it into discrete data points.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine taking a photograph. If you were to capture a continuous image of a landscape, you would need to take 'samples' at specific intervals in time. Each snapshot would represent a moment in that landscape, similar to how sampling captures points of a continuous signal.
Quantization
Chapter 6 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Quantization: Mapping a large set of input values to a smaller set (for digital representation).
Detailed Explanation
Quantization is the process of mapping a continuous range of values to a finite set of values, which is essential for creating digital representations of signals. During this process, the continuous values are assigned to discrete values, which may lead to some loss of information but is necessary for storage and processing in digital forms.
Examples & Analogies
Think of quantization like creating a color palette for an artist. A full rainbow of colors (analog values) may be too complex to reproduce fully, so the artist selects a limited number of colors (quantized values) that best represent the desired image, achieving a balance between detail and simplicity.
Encoding
Chapter 7 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Encoding: Converting quantized values into binary code.
Detailed Explanation
Encoding is the final step in preparing quantized values for digital systems, where these values are transformed into binary code that computers can read and process. Each quantized value is translated into a series of 0s and 1s. This allows for easier storage, transmission, and processing of the data.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a secret code system where each letter is represented by a number: A=1, B=2, C=3, etc. When you encode a word, you replace each letter with its corresponding number. This encoding makes it easier to keep track of words in a data system, just as encoding is used to process numerical data in computers.
Key Concepts
-
Signal: A fundamental concept representing information.
-
Analog Signal: Continuous in nature, representing real-world phenomena.
-
Digital Signal: Discrete representation critical for digital technology.
-
System: Essential for signal processing, transforms or processes signals.
-
Sampling: Key process for converting analog to digital.
-
Quantization: Reduces the range of a signal for digital use.
-
Encoding: Transforms quantized values into a binary format.
Examples & Applications
A sound wave as an analog signal reflects continuous changes in air pressure due to sound.
Digital signals can be represented as series of zeros and ones, such as in a binary file for music.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Signals convey, in forms they sway, analog flows, digital shows!
Stories
Imagine you’re a signal traveling on a journey. As an analog wave, you glide endlessly, but if you turn into a digital signal, you leap from point to point! That’s the difference between traveling freely and stepping carefully!
Memory Tools
Remember A for Analog (Always flows), D for Digital (Discrete jumps).
Acronyms
S.A.Q.E. - Signal, Analog, Quantization, Encoding.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Signal
A function that conveys information about a physical phenomenon.
- Analog Signal
A signal that varies continuously over time.
- Digital Signal
A signal that takes discrete values at specific time intervals.
- System
A device or algorithm processing an input signal to produce an output.
- Sampling
The process of converting a continuous signal into discrete values at regular intervals.
- Quantization
Mapping a large set of input values to a smaller set for digital representation.
- Encoding
The conversion of quantized values into binary code.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
