Introduction to Signal Processing
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Signals
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's begin with the concept of signals. A signal is a function that conveys information about a physical phenomenon. Can anyone tell me the two main types of signals?

Are they analog and digital signals?

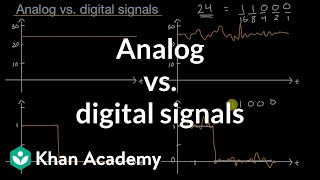
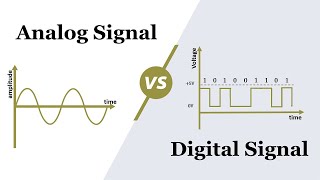
That's correct! Analog signals vary continuously over time, while digital signals take discrete values at specific intervals. Think of analog as a smooth wave and digital as steps. Can someone provide an example?

An audio waveform is an example of an analog signal.

And binary data is an example of a digital signal.

Exactly! Remember: A quick way to recall these is to think 'Analog = Analogous to real-life sounds, while Digital = Digits like 0s and 1s.'

That’s a nice memory aid!

Great! Now, let’s summarize. Signals convey information and can be either analog or digital, depending on their nature.
Applications and Importance
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

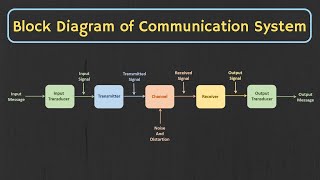
Next, let's focus on the importance of signal processing. It is crucial in communication, audio, video, and even biomedical applications. Can anyone think of how we use signal processing in our daily lives?

Over our phones during calls!

And for streaming music or videos!

Exactly! Signal processing allows us to efficiently transmit, receive, and modify signals, thereby enhancing clarity and removing noise. Remember the acronym C.E.N. – Communication, Enhancement, Noise removal.

C.E.N., that’s a useful way to remember it!

Now, let's summarize this part. Signal processing is fundamental for optimizing communication and ensuring high-quality audio and visuals in various applications.
Key Signal Processing Operations
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

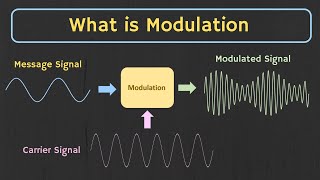
Let’s delve into the basic operations of signal processing like filtering, amplification, modulation, and demodulation. Can someone explain why filtering is important?

It helps eliminate unwanted components from a signal.

Correct! Filtering improves signal quality. Amplification, on the other hand, increases a signal’s power level. Why might we need to amplify a signal?

To ensure it reaches all parts of a system without losing quality!

Exactly! And modulation? What’s its role?

It imposes information on a carrier wave for transmission.

Well done! Modulation is vital for data transmission. Let’s summarize these operations: Filtering removes noise, amplification increases signal power, and modulation helps in sending signals effectively.
Digital vs. Analog Signal Processing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s compare analog and digital signal processing. Who can describe the primary difference between the two?

Analog is continuous while digital is discrete!

Correct! Let's think of hardware. What do we typically use for analog processing?

Resistors and capacitors.

And for digital, we use microprocessors and circuits, right?

Exactly right! Digital processing also offers higher accuracy due to better noise rejection. Remember the mnemonic R.A.F. – Resistors for Analog, Flexibility for Digital!

That's a memorable way to differentiate them!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section introduces the concept of signal processing, which plays a crucial role in various applications like communication and multimedia. It distinguishes between analog and digital signals, emphasizing their importance in modern technology.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
Signal Processing is the field dedicated to analyzing and transforming signals to extract valuable information or optimize them for effective transmission. Signals can be either analog (continuous-time) or digital (discrete-time), with each type possessing distinct characteristics and applications. The significance of signal processing spans numerous domains including communication systems, audio and video technologies, radar, and biomedical devices.
Key Points:
- Signals: Functions conveying information about physical phenomena.
- Analog Signals: Continuously varying signals, like an audio waveform.
- Digital Signals: Discrete-valued signals, such as binary data.
- Essential Operations: Filtering, amplification, modulation, and conversion (both ADC and DAC) are crucial in transforming signals.
- Applications: From mobile phones to medical diagnostics, signal processing forms the backbone of modern electronic systems.
- Importance: Signal processing enables efficient modification, transmission, and reception of signals, while enhancing clarity and removing noise in communication networks.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Signal Processing
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Signal Processing is the analysis and transformation of signals to extract useful information or modify them for efficient transmission.
Detailed Explanation
Signal Processing refers to the techniques used to analyze and modify signals. Signals are essentially various types of data that represent real-world phenomena, such as sound or light. The process includes filtering out unnecessary components or enhancing parts of the signal to make it clearer or more useful. This analysis and transformation can happen in a variety of contexts, such as preparing audio for playback or optimizing data for transmission over a network.
Examples & Analogies
Think of Signal Processing like editing a photo on your phone. Just as you might adjust the brightness, contrast, and colors to make the image clearer and more appealing, signal processing adjusts the data contained in signals to improve its quality and clarity before it is sent or used.
Types of Signals
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Signals can be analog (continuous-time) or digital (discrete-time).
Detailed Explanation
Signals can be categorized into two primary types: analog and digital. An analog signal is a continuous signal that can take any value within a range. It is often represented visually by a smooth curve. In contrast, a digital signal is made up of discrete values represented by binary numbers, such as 0s and 1s. This distinction is crucial because it affects how data is processed, transmitted, and stored.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a smooth, rolling wave at the beach as an analog signal—it flows continuously without breaks. Now picture a series of stepping stones across a stream—this represents a digital signal, where you can only stand on certain specific spots rather than anywhere along the stream.
Applications of Signal Processing
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Signal processing is essential for communication, audio, video, radar, and biomedical applications.
Detailed Explanation
Signal processing is a critical technology that underpins numerous modern applications. In communication systems, it allows for the effective transmission of voice and data, ensuring clarity and reducing interference. In audio and video applications, processing helps improve quality, such as noise reduction in music or enhancing video resolution. Radar systems use signal processing to accurately detect and track objects, while biomedical applications leverage it to interpret signals from medical devices, such as ECG machines to monitor heart activity.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how you use your smartphone to make a call. Signal processing plays a role in ensuring your voice is clear, minimizing background noise, and allowing both you and the other person to hear each other clearly, just like tuning a radio to eliminate static and improve clarity.
Key Concepts
-
Signal Processing: The analysis and transformation of signals.
-
Analog vs Digital Signals: Analog signals are continuous, digital signals are discrete.
-
Applications: Essential for communication, audio, video, and medical technologies.
-
Core Operations: Filtering, amplification, modulation, and demodulation.
Examples & Applications
Audio waveforms are continuous analog signals, while MP3 files represent those sounds as discrete digital signals.
In mobile communication, signal processing helps reduce noise and enhance call clarity.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Analog's like a flowing stream, Digital's steps in a solid team.
Stories
Imagine a librarian (signal) sorting books (information). Analog has books scattered everywhere, while Digital has them neatly shelved in boxes (discrete values).
Memory Tools
C.E.N. for signal processing benefits: Communication, Enhancement, Noise removal.
Acronyms
R.A.F. - Resistors for Analog, Flexibility for Digital.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Signal
A function that conveys information about a physical phenomenon.
- Analog Signal
A signal that varies continuously over time.
- Digital Signal
A signal that takes discrete values at specific time intervals.
- System
A device or algorithm that processes an input signal to produce an output.
- Sampling
Converting a continuous signal into discrete values at regular intervals.
- Quantization
Mapping a large set of input values to a smaller set for digital representation.
- Encoding
Converting quantized values into binary code.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
