Basic Signal Processing Operations
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Filtering
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's start with filtering. Filtering is about separating the desired part of the signal from unwanted noise. Can anyone explain why filtering is important?

It's important because it helps improve the quality of the signal, like cleaning up audio.

Exactly! Remember, we use filters to enhance signals in various applications. Think of it as a sieve, allowing only the desired frequencies to pass through. Now, how many types of filters can you name?

Low-pass, high-pass, band-pass, and band-stop filters!

Great job! Those filters help control which frequencies to allow or block. To remember this, think of 'L' for low-pass allowing low frequencies and 'H' for high-pass allowing high frequencies. Can anyone think of an example where filtering is used in everyday technology?

In music players to remove static or background noise!

Exactly! And that’s a perfect segue into our next topic: amplification.
Amplification
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss amplification. Why do we amplify signals?

To make sure they're strong enough for transmission!

Yes, like boosting a radio signal so we can hear it clearly!

Exactly! Amplification is crucial in transmitters. To remember this, just think 'A' for Amplify - we make it bigger! Have you seen amplifiers in use anywhere?

In electric guitars! They make the sound louder!

Great example! Amplifiers are essential in music and communication technologies. Let’s move to modulation now.
Modulation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now we will discuss modulation. Can someone define modulation for us?

It’s putting information onto a carrier wave for transmission.

Exactly! Modulation is key in radio and television communications. Who here can name modulation techniques?

AM and FM!

Well done! To remember this, think 'AM for Amplitude Modulation' - the amplitude varies. And 'FM for Frequency Modulation' - the frequency changes. Why is modulation vital in communications?

It allows signals to travel longer distances without losing quality!

Exactly! Now, moving on to demodulation, which is the reverse of modulation.
Demodulation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Demodulation is how we extract the original signal from a modulated carrier. Why do you think it's so important?

So we can understand the data that was transmitted!

Correct! Without demodulation, we can’t interpret the signals sent. Remember, 'D' for Demodulation is basically 'Decoding' the message. Can anyone give an example of where this happens?

In your radio - it demodulates the signal so you can hear the music!

Perfect example! Finally, let’s look at conversion.
Conversion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

We have two types of conversion: ADC and DAC. What does ADC do?

It converts analog signals into digital format!

Exactly! So we can process them digitally. And DAC?

It converts digital back to analog!

Correct! Think of ADC as 'An Analog to Digital Converter.' This conversion is critical in modern technology. Can anyone tell me how this is used in real life?

In smartphones for audio playback!

Exactly! These conversions make our modern technologies work seamlessly.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore essential signal processing operations that are critical for manipulating and optimizing signals for various applications. Key functions include filtering unwanted components, amplifying signal strength, and converting between analog and digital formats through ADCs and DACs.
Detailed
Basic Signal Processing Operations
Signal processing involves various operations critical for modifying and optimizing signals. This section elaborates on five fundamental operations:
- Filtering: This operation aims to remove unwanted components from a signal. For example, in audio processing, filtering can eliminate background noise, enhancing the quality of the audio signal.
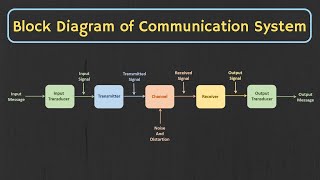
- Amplification: Amplification refers to raising the power level of a signal, making it stronger for transmission or processing. In communication systems, amplifiers are vital to ensure that the signal can travel longer distances.
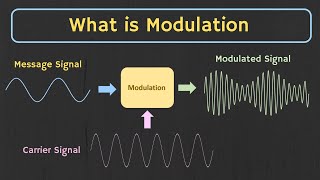
- Modulation: Modulation is the technique of imposing information onto a carrier wave for transmission. This process enables efficient use of bandwidth in communication systems. For instance, AM and FM radio broadcasting utilize modulation to transmit audio signals.
- Demodulation: This operation retrieves the original signal from the modulated carrier signal. It is the reverse process of modulation and is essential for understanding the transmitted information.
- Conversion: This encompasses two primary types:
- ADC (Analog to Digital Converter): Converts an analog signal into a digital format, allowing for digital processing.
- DAC (Digital to Analog Converter): Converts a digital signal back into an analog format, enabling playback through analog devices.
Each of these operations plays a significant role in how signals are processed in both analog and digital formats, paving the way for effective communication and data manipulation.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Filtering
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Filtering: Elimination of unwanted components from a signal.
Detailed Explanation
Filtering is a process used in signal processing to remove unwanted parts from a signal. This can mean eliminating noise or other interference that detracts from the desired signal. Filters can be designed to allow certain frequencies to pass through while blocking others. In technical terms, a low-pass filter allows low-frequency signals to pass while attenuating (reducing the power of) high-frequency signals.
Examples & Analogies
Think of filtering like a coffee filter. When you brew coffee, you want the water to seep through and extract flavors while keeping the coffee grounds from mixing in. Similarly, filters in signal processing allow good signals to pass while blocking unwanted noise.
Amplification
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Amplification: Increasing the signal's power level.
Detailed Explanation
Amplification refers to the process of increasing the strength or power of a signal. This is essential in many applications, such as ensuring that audio signals are loud enough to be heard through speakers. An amplifier takes a weak input signal and increases its amplitude, making it stronger without distorting the original message.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to hear someone whispering in a noisy room. An amplifier is like a microphone and speaker system that takes their quiet voice and makes it loud enough for everyone to hear, ensuring the message is clear.
Modulation
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Modulation: Imposing information on a carrier wave for transmission.
Detailed Explanation
Modulation is a technique used to encode information onto a carrier wave, which is a signal that can travel through various communication mediums. For example, in radio broadcasting, voice or music signals are superimposed on a carrier frequency, enabling the audio to be transmitted over long distances. This helps to effectively use available bandwidth in radio frequencies.
Examples & Analogies
Think of modulation like writing a message on a piece of paper and putting it inside a bottle. The bottle is the carrier wave, and the note inside is the information to be shared. Just as the bottle transports the note across water, modulation allows our information to traverse through the air as radio waves.
Demodulation
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Demodulation: Recovering the original signal from the modulated carrier.
Detailed Explanation
Demodulation is the reverse process of modulation. In this operation, the original information is extracted from the modulated carrier wave. This is a critical step in receiving communicated signals, such as those from radio stations, where it allows the listener to hear the original audio content. Successful demodulation depends on the receiver accurately interpreting the modulation used during transmission.
Examples & Analogies
Think of demodulation as opening a bottle to retrieve the note inside. Once you have the bottle (the carrier wave), you need to carefully remove the note to read the message (the original signal). This step is essential to understand the information being communicated.
Conversion
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Conversion:
○ ADC (Analog to Digital Converter): Converts analog input to digital.
○ DAC (Digital to Analog Converter): Converts digital signal back to analog.
Detailed Explanation
Conversion is a fundamental operation in signal processing that includes two primary processes: Analog-to-Digital Conversion (ADC) and Digital-to-Analog Conversion (DAC). ADC is necessary for transforming real-world analog signals into digital form for processing by computers and digital devices. Conversely, DAC converts digital data back into analog signals so they can be understood by humans, like sound from speakers.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine converting a paper book (analog) into an eBook (digital) using a scanner. The scanner reads the pages (ADC) and digitizes the content. When you want to read it again as a physical book, a printer (DAC) takes the digital file and prints it back onto paper. This visualizes the conversion of signals between analog and digital forms.
Key Concepts
-
Filtering: The elimination of unwanted components from a signal.
-
Amplification: The process of increasing a signal's power level.
-
Modulation: The technique of imposing information on a carrier wave.
-
Demodulation: The recovery of the original signal from the modulated carrier.
-
ADC: Converts analog signals to digital for processing.
-
DAC: Converts digital signals back to analog.
Examples & Applications
Using filters in audio technology to remove noise from recordings.
Employing amplifiers in communication systems to ensure signals reach their destination.
Implementing modulation techniques in radio broadcasting to transmit audio signals effectively.
Using ADC in smartphones to digitize sound for processing and playback.
Applying DAC to convert digital audio files into sound waves through speakers.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Filter out the noise and sound, let the pure signal be found.
Stories
Once upon a time, a shy musician had to amplify her voice to be heard above the crowd. With the magic of amplifiers, her melodies danced through the air, enchanting everyone nearby.
Memory Tools
FAM-DAC: Filtering, Amplification, Modulation, Demodulation, and Conversion for signal processing.
Acronyms
A.M.P. for Amplifier, Modulator, Processor - key tools in signal processing.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Filtering
The process of eliminating unwanted components from a signal.
- Amplification
Increasing the power level of a signal.
- Modulation
Imposing information onto a carrier wave for transmission.
- Demodulation
Recovering the original signal from a modulated carrier.
- ADC (Analog to Digital Converter)
Converts an analog signal into a digital representation.
- DAC (Digital to Analog Converter)
Converts a digital signal back into an analog format.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
