Summary
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Signal Processing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

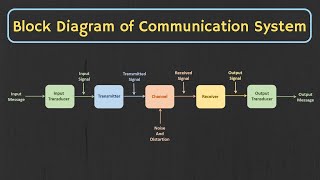
Signal processing is a foundational component of many electronic systems. Can anyone explain what signal processing involves?

Is it just the analysis of signals?

Exactly! Signal processing involves analyzing and transforming signals to extract useful information or modify them for better transmission. It plays a critical role in communication systems.

So, what types of signals do we usually deal with?

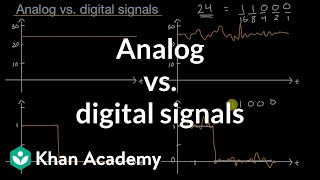
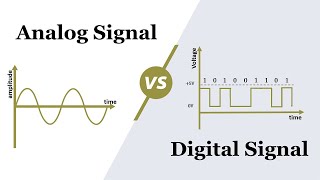
Great question! We primarily deal with **analog signals**, which are continuous, and **digital signals**, which are discrete. Remember the acronym ADC: Analog to Digital Conversion, which highlights one of the key transitions we see in signal processing.

What makes digital signal processing more advantageous than analog?

DSP is preferred due to its high accuracy, programmability, and resistance to noise. In contrast, analog systems can be affected by interference, making DSP significantly more reliable.

So, where exactly is signal processing used?

Signal processing is utilized across various fields including mobile communications, medical diagnostics, and multimedia systems. It’s remarkable how these concepts apply to technology in our everyday lives!

To summarize, signal processing is key for modern technology, where digital systems provide significant advantages in clarity and efficiency.
Core DSP Processes
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s dive into core processes like sampling, filtering, and modulation. Can anyone explain what sampling is?

Isn’t it about converting continuous signals into discrete ones?

Correct! Sampling is the process of converting analog signals to a digital form by taking measurements at regular intervals. This is crucial for digital processing.

And what about filtering?

Filtering refers to removing unwanted components from a signal. Think of it as cleaning the signal for clearer communication. A simple way to remember filtering is to think of a coffee filter— it removes the grounds, just as signal filtering removes noise.

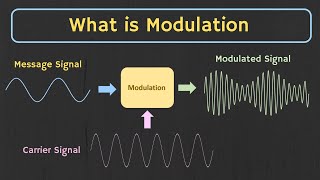
What role does modulation play?

Modulation is key for imposing information on a carrier wave for transmission. It enables effective signal communication over distances, and in digital processing, it ensures that the signal retains its integrity despite being sent through various mediums.

Summarize all these terms for us!

Sure! We discussed **sampling**, which converts signals, **filtering**, which cleans them up, and **modulation**, which helps transmit information. These processes form the backbone of digital signal processing and are essential for the application of these technologies.
Applications of Signal Processing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s explore applications. Who can name some areas where signal processing is used?

Medical imaging and communications, right?

Absolutely! Applications like **ECG** monitoring in medical devices, **modems**, and even in multimedia systems such as audio and video streaming utilize signal processing.

What does that tell us about its importance?

It underscores that signal processing is essential for not just transmitting data effectively, but also for enhancing clarity and quality in various forms. Remember: everyday technologies like smartphones heavily rely on these principles.

We can see how it connects to so many aspects of our lives!

Exactly! So to recap, signal processing is vital for modern electronics, facilitating digitization for clarity, efficiency, and a broad range of applications from communications to healthcare.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section emphasizes the core concepts of signal processing, highlighting the differences between analog and digital signals. It notes the foundational role of digital signal processing in various applications, illustrating its benefits such as accuracy and programmability.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
Signal processing is a critical aspect of modern electronics, serving as the backbone for various communication systems. In this section, we differentiate between two primary types of signals: analog and digital. Analog signals are characterized by their continuous nature, while digital signals are defined by their sampled and quantized states. The significance of digital signal processing (DSP) is underscored through its capabilities for accuracy, flexibility, and programmability. Core signal processing operations such as sampling, filtering, modulation, and conversion are integral to the functionality of DSP. The applications of these principles range extensively from mobile communication networks to medical diagnostics and multimedia systems, showcasing the profound impact of signal processing in our technology-driven world.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Role of Signal Processing
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Signal processing plays a foundational role in modern electronics and communication.
Detailed Explanation
Signal processing is a crucial area in electronics and communications. It involves analyzing and manipulating signals to improve the quality of communication and information transmission. Think of signal processing as the backbone that supports various technological applications we rely on today, such as mobile phones and the internet.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you're listening to your favorite song on the radio. The music travels through the air as an analog signal. Signal processing is what helps ensure that you hear the song clearly, without static or interruptions. It’s the technology making sure that your listening experience is smooth and enjoyable.
Types of Signals
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Analog signals are continuous; digital signals are sampled and quantized.
Detailed Explanation
Signals can be classified into two major types: analog and digital. Analog signals are continuous, meaning they can take on an infinite number of values, similar to a smooth wave. Digital signals, on the other hand, are discrete and are created by sampling the analog signal at specific intervals and quantizing those samples into defined values, often represented in binary form (0s and 1s). This distinction is important because it impacts how signals are processed and transmitted.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a dimmer light switch (analog signal) versus a simple on/off switch (digital signal). The dimmer allows you to adjust the brightness smoothly, while the on/off switch simply flips between two states. This illustrates the difference between continuous and discrete signals.
Advantages of Digital Signal Processing
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Digital signal processing is favored due to accuracy, programmability, and flexibility.
Detailed Explanation
Digital signal processing (DSP) offers several advantages over analog processing. Because digital signals are processed mathematically, they can achieve higher accuracy and are less susceptible to noise interference. Additionally, DSP systems can be programmed to perform various tasks, which grants them flexibility to adapt and evolve according to new requirements. This adaptability makes digital processing a preferred method in modern technology.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a versatile Swiss Army knife that can transform into different tools (like scissors, screwdriver, etc.) as needed. Digital signal processors work similarly, allowing for various operations to be performed on the same digital signal without needing hardware changes.
Core Processes in Signal Processing
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Core processes include sampling, filtering, modulation, and conversion.
Detailed Explanation
Signal processing involves several core operations: Sampling (capturing signal values at intervals), Filtering (removing unwanted frequencies), Modulation (modifying signals to transmit information), and Conversion (changing signals between analog and digital formats). These processes ensure that signals are not only captured accurately but also transmitted in a way that maximizes communication quality.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a filter on a coffee maker. Just as it removes the bitter grounds while allowing the rich flavor to pass through, filtering in signal processing eliminates unwanted noise from the desired signal, ensuring clarity in communication.
Applications of Signal Processing
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Applications range from mobile communication to medical diagnostics and multimedia systems.
Detailed Explanation
Signal processing techniques are widely used in various fields, including mobile communication, where they enhance voice quality and data transmission speeds; in medical diagnostics, where processed signals from devices help in imaging and monitoring health; and in multimedia systems, where audio and video signals are compressed and transmitted efficiently. This broad range highlights the importance of signal processing in daily life.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how you stream a movie online. Signal processing is what compresses the video for faster streaming and later decompresses it for high-quality viewing, ensuring you enjoy uninterrupted entertainment regardless of your internet speed.
Key Concepts
-
Signal Processing: Analyzing and transforming signals.
-
Analog vs Digital: Continuous vs Discrete.
-
Core DSP Processes: Sampling, filtering, modulation, and conversion.
-
Applications: Medical devices, communication systems, multimedia.
Examples & Applications
An example of an analog signal is a temperature reading measured continuously over time, while a digital signal example is a temperature reading taken every hour and represented in binary format.
Mobile phones use digital signal processing to filter out background noise, ensuring clearer calls.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Analog signals flow and glide, while digital ones choose a side.
Stories
Imagine two friends, Anna (analog) and Dave (digital). Anna loves playing piano continuously, while Dave programs music on his computer, taking breaks between notes. This is how they represent audio signals.
Memory Tools
To remember DSP concepts: A - Analog, S - Sampling, F - Filtering, M - Modulation.
Acronyms
DSP
Digital Signal Processing focuses on **D**iscreteness
**S**ampling
and **P**rocessing.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Signal Processing
The analysis and transformation of signals to extract useful information or modify them for efficient transmission.
- Analog Signal
A continuous signal that varies over time, such as an audio waveform.
- Digital Signal
A discrete signal that takes specific values at defined intervals, like binary data.
- Sampling
The conversion of a continuous signal into discrete values at regular intervals.
- Filtering
The elimination of unwanted components from a signal to enhance clarity.
- Modulation
The process of imposing information on a carrier wave for transmission.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
