Folded Cascode
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Folded Cascode
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's start our discussion on the Folded Cascode. Can anyone tell me why maintaining a wide output swing is crucial in amplifier design?

I think it allows the amplifier to handle larger signals without distortion.

Exactly! A wider output swing prevents clipping and distortion of the output signal. Now, do we know why PSRR is significant?

It helps to minimize variations in the output due to power supply fluctuations, right?

Correct! This is where the Folded Cascode excelling. This topology efficiently facilitates better PSRR.

Remember, PSRR ensures consistent performance which is vital for precision signal processing.
Operation of Folded Cascode
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's delve into how the Folded Cascode operates. In which configuration do we typically see this topology?

It's usually seen where a common-source stage is followed by a common-gate stage, isn't it?

That's absolutely right! The common-source stage provides voltage gain, while the common-gate stage helps maintain a low output impedance. What does this combination achieve?

It optimizes both gain and output swing.

Perfect! This synergy between stages is fundamental to the success of the Folded Cascode.
Advantages of Folded Cascode
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

What are some key advantages of using the Folded Cascode in amplifier design?

It has a wider output swing and better PSRR.

Also, isn't it great for improving the overall gain efficiency?

Yes! It effectively utilizes headroom in IC design, allowing for higher performance in limited space.

Keep these advantages in mind when designing circuits, as they can lead to significant performance improvements.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The Folded Cascode is a significant topology in MOSFET amplifiers known for maximizing output swing while maintaining high performance metrics. With its configuration, it achieves better PSRR and makes it suitable for various applications, especially in high-frequency circuits.
Detailed
Folded Cascode
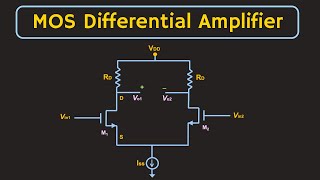
The Folded Cascode configuration is an advanced amplifier topology that enhances the output swing while providing superior power supply rejection ratio (PSRR). In essence, it combines the benefits of both common-source and common-gate amplifiers, allowing for greater flexibility in circuit designs. The folded cascode approach improves signal integrity, which is crucial in high-frequency applications, by ensuring that the output voltage maintains its desired level even when faced with fluctuations in power supply. This section explores the characteristics, advantages, and applications of the Folded Cascode in practice.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Folded Cascode
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Benefits:
- Wider output swing
- Better PSRR
Detailed Explanation
The folded cascode is a type of amplifier configuration used primarily in operational amplifiers. This configuration offers a variety of advantages, the most notable being a wider output swing, which allows the output voltage to range more significantly without clipping. Additionally, it provides improved Power Supply Rejection Ratio (PSRR), meaning it can maintain performance even with variations in the supply voltage.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a flexible bridge that can swaying gently with wind—this flexibility represents the wider output swing of the folded cascode amplifier, adjusting to changes in load or input without collapsing. Similarly, just like a well-constructed bridge can handle the pressure of passing vehicles without falling apart, a good folded cascode design can handle fluctuations in the power supply without degrading its performance.
Key Concepts
-
Folded Cascode: A combined amplifier topology that leverages common-source and common-gate stages for improved performance.
-
Output Swing: The range of output voltage an amplifier can provide without distortion.
-
Power Supply Rejection Ratio: Vital for maintaining output stability amidst supply voltage variations.
Examples & Applications
A Folded Cascode can be used in high-frequency applications where maintaining signal integrity is crucial.
In operational amplifiers, a Folded Cascode stage enhances both gain and PSRR, making them ideal for precision amplification.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Folded Cascode, it takes its stride, with swing and PSRR, right by its side!
Stories
Imagine an engineer named Carl, building a bridge (the Folded Cascode) that connects two cities (common-source & common-gate), allowing cars (signals) to travel smoothly without hitting bumps (distortion) or being affected by the weather (power variations).
Memory Tools
To remember 'Folded Cascode', think of 'F-C' for 'Flexibility & Consistency' in output swing and stability.
Acronyms
PSRR – Provides Stable Results amidst fluctuations.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Folded Cascode
An amplifier topology that combines the functionalities of common-source and common-gate configurations to provide higher output swing and improved PSRR.
- Output Swing
The maximum range of output voltage that an amplifier can provide without distortion.
- Power Supply Rejection Ratio (PSRR)
A measure of how well a circuit rejects changes in its supply voltage and maintains output stability.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
