Gain-Bandwidth Product (GBW)
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Gain-Bandwidth Product
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into the Gain-Bandwidth Product, or GBW, which is essential for evaluating amplifier performance. Can anyone tell me why understanding GBW might be important?

Isn't it because it helps in balancing gain and bandwidth?

Exactly! The GBW shows how an amplifier's gain decreases as the frequency increases. So what is the formula for GBW?

It's the product of the voltage gain and the -3dB bandwidth, right?

That's correct! Remember it as GBW = |A_V0| × f_{-3dB}. Let’s remember that as 'Gain over Bandwidth'.

Does this mean if we increase the gain, we have to sacrifice the bandwidth?

Precisely! Understanding this trade-off is crucial for designing effective amplifiers. Good job!

In summary, GBW is a key metric that summarizes the relationship between gain and bandwidth in amplifiers.
Evaluating GBW in Circuit Design
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand the concept of GBW, how do we apply this in circuit design?

We can use it to select components that meet our specifications!

Exactly! For instance, if we want an amplifier with a high gain, we need to choose components carefully to ensure we still meet the necessary bandwidth requirements.

What if we want a wide bandwidth, though?

Then you'd likely have to settle for a lower gain. It’s all about compromise! GBW helps us make informed decisions about these trade-offs.

Let's summarize: GBW not only showcases the trade-off between gain and bandwidth but also guides us in selecting the right components for our designs.
Practical Implications of GBW
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To wrap up, let's discuss some real-world applications where GBW plays a crucial role. Can anyone think of an example?

In audio amplifiers? They often need a specific balance of gain and bandwidth.

Excellent point! Audio amplifiers need to amplify signals without distorting them, hence the importance of managing GBW.

And in RF applications too, right? They need to maintain quality across higher frequencies.

Correct! RF amplifiers benefit from a high GBW to maintain signal integrity at various frequencies.

In summary, GBW is vital not just in theory but in practical applications, shaping the design choices engineers make in various domains.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore the concept of Gain-Bandwidth Product (GBW), a key metric that reflects the trade-off between gain and frequency response in amplifiers. By understanding GBW, engineers can design circuits that meet their desired specifications by effectively managing gain and bandwidth.
Detailed
Gain-Bandwidth Product (GBW)
The Gain-Bandwidth Product (GBW) is defined mathematically as the product of the voltage gain (
|A_V0|) of an amplifier at a specific frequency and its -3dB bandwidth (f_{-3dB}). The formula used to express this relationship is:
\[ GBW = |A_{V0}| \times f_{-3dB} \]
This crucial parameter helps designers understand the limitations and capabilities of amplifiers, indicating how gain and bandwidth interact. An increase in voltage gain typically results in a decrease in bandwidth, and vice versa. This trade-off is essential for optimizing amplifier designs in practical applications. Understanding the GBW allows engineers to select appropriate circuits based on their requirements, ensuring reliability and efficiency in signal processing.
Youtube Videos

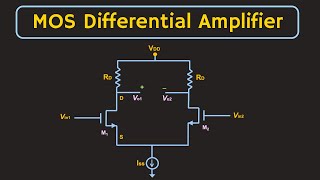
Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Gain-Bandwidth Product (GBW)
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The Gain-Bandwidth Product (GBW) is defined as:
\[ GBW = |A_{V0}| × f_{-3dB} \]
Detailed Explanation
The Gain-Bandwidth Product (GBW) is a crucial metric in amplifier design. It represents the trade-off between the amplification factor (gain) and the frequency response of the amplifier. Here, |A_{V0}| refers to the voltage gain at DC (or low frequencies), and f_{-3dB} is the frequency at which the output power of the amplifier drops to half its maximum value (known as the -3dB point).
This means that as you increase the gain of an amplifier, the bandwidth (the range of frequencies over which the amplifier can operate effectively) decreases, and vice versa. The GBW remains constant for a given amplifier, indicating that if you want higher gain, you'll have to accept a lower bandwidth.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a highway that allows for two lanes of traffic (high gain) but has a speed limit that cars cannot exceed (bandwidth). If you remove some of the lanes to allow fast cars (increase gain), the overall capacity of the highway (the effective use of bandwidth) may diminish. In this analogy, maintaining a consistent flow of traffic (the GBW) means balancing the number of cars (gain) allowed and their speed (frequency response).
Key Concepts
-
Gain-Bandwidth Product (GBW): A product of voltage gain and -3dB bandwidth that shows the trade-off between these two characteristics in an amplifier.
-
Trade-off: The balance between gain and bandwidth, where boosting one typically reduces the other.
Examples & Applications
An amplifier designed for audio applications may prioritize a bandwidth sufficient to cover the human audio spectrum (20 Hz to 20 kHz) while needing a decent voltage gain for effective sound amplification.
In a radio frequency (RF) application, an amplifier might be required to operate at high frequencies effectively, thus necessitating a higher GBW to prevent signal degradation.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Gain up high, Bandwidth low; to balance out, this we know.
Stories
Imagine a diver who can only dive deep for a limited time; if he focuses on going deeper (gain), he risks taking longer breaks (bandwidth).
Memory Tools
Giant Bandwidth Wonders: GBW stands for Gain-Bandwidth Product.
Acronyms
G B W
Great Balance Wants – in amplifier design
we always need to balance gain and bandwidth.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- GainBandwidth Product (GBW)
A measure of the trade-off between the gain of an amplifier and its bandwidth, calculated as the product of voltage gain and -3dB bandwidth.
- 3dB Bandwidth
The frequency range over which the amplifier maintains its gain within 3 decibels of its maximum value.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
