Electricity
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Electricity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’re diving into electricity. It’s a fundamental part of our daily lives. Can someone tell me what electricity is?

Isn't it just the power we use to turn on lights and appliances?

Exactly! Electricity is a controllable form of energy used in many applications. Remember the acronym 'POWER' — P for practical uses, O for omnipresence in homes, W for work, E for energy flow, and R for revolutionizing life.

So, it’s a form of energy we can use wherever we need it?

Yes, indeed! Now, how does it flow? Can anyone explain how electricity travels in a circuit?
Electric Circuits
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Electricity flows through a closed path known as a circuit. Can anyone tell me what a closed circuit is?

It's when the path for electricity is complete, allowing current to flow.

Great! And what factors can control the current?

I think resistance is one of them, right?

Exactly, resistance opposes current, while voltage drives it. Remember 'Ohm's Law' — V = I x R, where V is voltage, I is current, and R is resistance.
Heating Effects of Electric Current
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

As we discuss electricity, let’s talk about its heating effects. Who can explain what happens when current flows through a resistor?

It gets warm, right? That’s how heaters work!

Exactly! This heating effect can be very useful. Think about 'HEAT' — H for heating, E for efficiency, A for applications like toasters, and T for technology.

So, this heat is actually useful in daily appliances?

Yes, and understanding it helps us use electricity wisely. Let's wrap up with what we’ve learned today.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This chapter explores the fundamental concepts of electricity, including its nature, how it flows through circuits, and the factors that influence electric current. Additionally, it delves into the heating effects of electric current and their practical applications.
Detailed
CHAPTER Electricity
Electricity is a pivotal energy source in contemporary society, facilitating convenience across diverse applications in homes, schools, hospitals, and industries. This chapter addresses key questions surrounding electricity: What is electricity? How does it traverse an electric circuit? What factors manage its flow? By the end of this chapter, readers will have a deeper understanding of electric current and its thermal effects, essential for recognizing electricity's significance in everyday life.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Importance of Electricity
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Electricity has an important place in modern society.
Detailed Explanation
Electricity is a crucial part of our everyday lives. It powers homes, schools, hospitals, and industries, making it essential for performing a multitude of tasks. Without electricity, many of the conveniences we enjoy today, such as lighting, heating, and using electronic devices, would be impossible.
Examples & Analogies
Think of electricity as the lifeblood of modern civilization, much like how water is essential for life. Without a reliable water supply, daily activities like drinking, cooking, and bathing would be disrupted, just as they would without electricity for our devices and routines.
Uses of Electricity
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
It is a controllable and convenient form of energy for a variety of uses in homes, schools, hospitals, industries, and so on.
Detailed Explanation
Electricity is versatile; it can be used for lighting, heating, powering appliances, and operating machinery. In homes, it lights up our rooms and heats our food. In schools, it aids in teaching through audio-visual aids. Hospitals rely on it for medical equipment to save lives. Industries depend on it for manufacturing and production processes.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine how difficult our lives would be without electricity in these various settings. Picture trying to study in a dark room or going to a hospital without any electricity to operate essential machines—they would be nearly impossible without this vital energy source.
Fundamental Questions about Electricity
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
What constitutes electricity? How does it flow in an electric circuit? What are the factors that control or regulate the current through an electric circuit?
Detailed Explanation
The study of electricity begins with basic questions about its nature and behavior. Electricity consists of the flow of electric charge, commonly through materials. In an electric circuit, it flows when there is a complete path. Various factors, such as resistance, voltage, and current, determine how effectively electricity moves through the circuit.
Examples & Analogies
Just like water flowing through pipes, electricity flows through wires. If a pipe is narrow (high resistance), less water flows. Similarly, in a circuit, resistance can limit how much electricity flows. Understanding these principles helps in designing effective electrical systems.
Heating Effect of Electric Current
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
We shall also discuss the heating effect of electric current and its applications.
Detailed Explanation
The heating effect of electric current refers to the heat produced when current flows through a conductor due to resistance. This is utilized in many applications, such as in electric heaters and ovens where heat is needed to cook food or provide warmth.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how a toaster works. When you turn it on, electricity flows through a wire, and as it encounters resistance, the wire heats up and toasts the bread. This is a practical illustration of the heating effect of electric current in action.
Key Concepts
-
Electricity: A versatile form of energy used widely in modern society.
-
Electric Circuit: A closed pathway for electricity to flow.
-
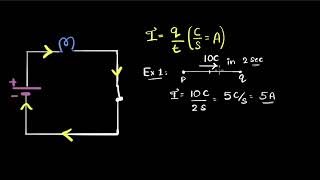
Current: The rate of flow of electric charge.
-
Resistance: A property that hinders current flow.
-
Voltage: The driving force behind the movement of current.
Examples & Applications
When you turn on a light switch, electricity flows through the circuit to produce light.
Electric heaters use the heating effect of current to warm up a room.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Electricity, so bright and keen, controls our lives like a magic scene.
Stories
Imagine a tiny road with cars (electrons) traveling at different speeds (current) while facing bumps (resistance) on their way. The bumps slow them down, which is how we control energy use!
Memory Tools
Remember 'PRIV' to recall key concepts: P for Power, R for Resistance, I for Current, and V for Voltage.
Acronyms
To remember the flow in a circuit, think 'CARS'
for Circuit
for Alternating
for Resistance
and S for Supply.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Electricity
A controllable form of energy that is used for various applications in everyday life.
- Electric Circuit
A closed loop through which electric current can flow.
- Current
The flow of electric charge through a conductor.
- Resistance
The opposition to the flow of electric current, measured in Ohms.
- Voltage
The electric potential difference that drives current through a circuit, measured in Volts.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
