Profit Maximisation
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Profit Maximization Definition
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we will talk about profit maximization. Can anyone tell me what profit is?

Isn't profit just what you earn after subtracting costs?

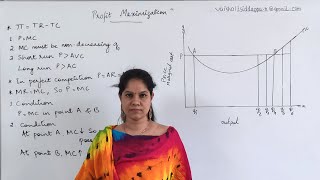
Exactly! Profit, denoted by π, is calculated as total revenue (TR) minus total cost (TC). So what do you think total revenue is?

It's the money made from selling goods, right?

Yes! In a perfectly competitive market, it’s the price times the quantity sold. Now, can anyone summarize how we express profit mathematically?

Profit equals total revenue minus total costs: π = TR - TC.

Well done! Let’s move on to discuss the conditions for profit maximization.
Conditions for Profit Maximization
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To maximize profit, certain conditions need to be met. Does anyone know what the first condition is?

Is it that price has to equal marginal cost?

Exactly, we call this Condition 1: for maximum profit, P must equal MC. Why do you think that’s important?

It means the revenue from selling one more unit is just covering the cost of making that unit?

Correct! Now, can anyone identify Condition 2?

It's about marginal cost not decreasing at the profit-maximizing level?

Exactly! Non-decreasing marginal cost at q0 ensures that raising production won't decrease profitability. Now, let’s talk about the third condition.
Short-run vs Long-run Conditions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

In the short run, we said the price must be greater than AVC. What happens if it’s not?

The firm wouldn't want to produce at all?

Exactly! If p < AVC, the firm will shut down in the short run. How about in the long run?

Is it about the price needing to be greater than average cost?

Yes! If p < AC in the long run, the firm will exit the market. What can we conclude about these conditions for a firm’s sustainability?

It’s essential for the price to cover costs in the long run to stay competitive.

Exactly right! The conditions dictate whether a firm can sustain its operations. Let’s summarize.
Graphical Representation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's look at a graphical representation of profit maximization. Why do you think graphs are useful here?

They help visualize how costs and revenues interact!

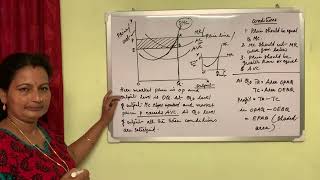
Exactly! We usually plot total revenue, total cost, and the point where they intersect shows maximum profit. Can anyone tell me what shape these curves might take?

TR curves usually slope upwards and TC curves slope up too, but at a different rate?

Correct! This indicates how profits are initially growing before they start to taper off. By analyzing these curves, firms can make informed production choices!

So the area between TR and TC represents profit?

Exactly! The larger the area, the greater the profit. Great conclusions today!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section discusses how firms determine the optimal quantity of output to produce for maximum profitability, emphasizing the conditions of profit maximization in both the short and long run within a perfectly competitive market.
Detailed
In this section, we explore the concept of profit maximization within the framework of a perfectly competitive market. A firm aims to optimize its operations to maximize profit (π), which is defined as total revenue (TR) minus total cost (TC). The first step in identifying the quantity at which profit is maximized (denoted as q0) is understanding three essential conditions:
- The price (p) must equal marginal cost (MC) indicating that the firm produces where the additional cost of producing one more unit is equal to the price at which it can sell that unit.
- The marginal cost should be non-decreasing at q0, meaning it cannot fall as output increases.
- In the short run, the price must exceed the average variable cost (p > AVC), and in the long run, the price must be greater than the average cost (p > AC).
By maintaining these relationships, a firm can ensure it is maximizing its profitability within the constraints of market conditions.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Profit
Chapter 1 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A firm produces and sells a certain amount of a good. The firm’s profit, denoted by π, is defined to be the difference between its total revenue (TR) and its total cost of production (TC). In other words, π = TR – TC. Clearly, the gap between TR and TC is the firm’s earnings net of costs.
Detailed Explanation
Profit is essentially what a firm earns after accounting for all its costs. To calculate profit, firms look at their total revenue, which is what they make from selling their goods, and subtract the total costs they incur to produce those goods. Thus, profit can be thought of as the leftover money after expenses are paid.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine running a lemonade stand. You sell lemonade for $1 a cup. If you sell 100 cups, your total revenue is $100. If your costs for lemons, sugar, and cups amount to $40, your profit is $100 (revenue) - $40 (costs) = $60. This leftover $60 is your profit.
Maximizing Profit
Chapter 2 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A firm wishes to maximise its profit. The firm would like to identify the quantity q at which its profits are maximum. By definition, then, at any quantity other than q₀, the firm’s profits are less than at q₀. The critical question is: how do we identify q₀?
Detailed Explanation
To maximize profit, a firm needs to find the exact amount of goods (quantity q₀) it should produce. If the firm produces less or more than this quantity, its profits will not be as high as they could be. The firm thus seeks to determine q₀ by analyzing its profits at different levels of production.
Examples & Analogies
Think about baking cookies. If you bake 12 cookies, you might find your profits are high. But if you bake only 6, you lose potential sales; if you bake 24, you might waste ingredients and time if you can't sell them all. The goal is to find that sweet spot of 12 cookies where you maximize your profit.
Conditions for Maximum Profit
Chapter 3 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
For profits to be maximum, three conditions must hold at q₀: 1. The price, p, must equal MC; 2. Marginal cost must be non-decreasing at q₀; 3. For the firm to continue to produce, in the short run, price must be greater than the average variable cost (p > AVC); in the long run, price must be greater than the average cost (p > AC).
Detailed Explanation
These three conditions ensure that the firm is not only covering its costs but also maximizing its profit. The first condition means the price of the product equals the cost to make one additional unit (marginal cost). The second condition implies that costs shouldn't be going down as more is produced (otherwise, producing more would still be profitable). The final conditions ensure that the firm is not losing money in the short and long run.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a pizza shop. If they sell a pizza for $15, and it costs $10 to make, they're in profit. But they also need to ensure that as they make more pizzas, the cost does not keep dropping unexpectedly (which could provide false indicators), and they must earn more than their costs overall, ensuring sustainable business.
Condition 1: Price Equals Marginal Cost
Chapter 4 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Profits are the difference between total revenue and total cost. Both total revenue and total cost increase as output increases. Notice that as long as the change in total revenue is greater than the change in total cost, profits will continue to increase. Therefore, we can conclude that as long as marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost, profits are increasing. It follows that for profits to be maximum, marginal revenue should equal marginal cost. In other words, profits are maximum at the level of output (which we have called q₀) for which MR = MC.
Detailed Explanation
To maximize profits, the additional revenue from selling one more unit (marginal revenue, MR) must equal the additional cost of producing that unit (marginal cost, MC). If MR is higher than MC, it indicates that the firm can increase profits by producing more. Conversely, if MR is lower, the firm is losing profits and should decrease production.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a coffee shop. If selling one additional cup of coffee earns them an extra $5 (MR), but it costs them $4 to make that cup (MC), they're better off making that extra cup, as they're still profiting by $1. The shop should continue this until MR equals MC for optimal profit.
Condition 2: Non-decreasing Marginal Cost
Chapter 5 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Consider the second condition that must hold when the profit-maximizing output level is positive. The marginal cost curve cannot slope downwards at the profit-maximising output level. This means that if marginal cost is still falling, then the firm has room to increase output and potentially increase profits. Thus, if the marginal cost curve slopes downward at a certain output level, it cannot be at the profit-maximizing point.
Detailed Explanation
If the marginal cost is decreasing as output increases, this means the firm can still produce more at a lower cost, which contradicts the notion of maximizing profit because they haven’t reached their full earning potential. For profit maximization, the marginal cost curve must trend upwards or at least plateau, indicating that firms are fully utilizing their capacity.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a car factory. If the cost to produce more cars decreases as production ramps up, the factory can keep producing. If they hit a point where producing one more car costs more than it did for the last while still making a profit, they’ve reached a peak of their optimal output and must not go beyond it.
Condition 3: Price Relative to Average Costs
Chapter 6 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Consider the third condition that must hold when the profit-maximising output level is positive. In the short run, the price must be higher than the average variable cost (p > AVC); in the long run, the price must be higher than the average cost (p > AC).
Detailed Explanation
This condition ensures that the firm's revenue from selling goods is enough to cover not only its marginal costs but also its average costs. Specifically, in the short run, firms should at least cover variable costs to keep operating. In the long run, firms should cover all costs, including fixed and variable costs.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a bakery that sells bread. If the price of a loaf is $3 but the variable costs (like flour and water) are $2, the bakery is covering its production costs and making a profit. However, if the price drops below $2, they'll stop baking bread as they cannot cover their ingredient costs, and in the long term, if they cannot cover all costs, they'll shut down.
Key Concepts
-
Profit Maximization: The process of increasing the difference between total revenue and total costs.
-
Conditions for Profit Maximization: The three key conditions that must be met for a firm to maximize its profits.
-
Short-run and Long-run: Distinctions that identify different operational strategies and outcomes based on time.
-
Graphical Analysis: The use of graphs to visualize and analyze revenue and cost relationships for decision-making.
Examples & Applications
A bakery sells 200 cakes at a price of Rs 100 each, making a total revenue (TR) of Rs 20,000. After calculating the costs, if the total cost (TC) is Rs 15,000, the profit is Rs 5,000.
A farmer breaks even with a total revenue of rs 30,000 and total costs of rs 30,000, indicating no profit or loss.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To maximize, let profits rise, Revenue beats cost - that's no surprise.
Stories
Imagine a baker who discovers if he lowers costs while maintaining sales price, his profits rise significantly. This baker learns to balance revenue and costs to keep the business thriving.
Memory Tools
Use 'PRIME' to remember: Profit, Revenue, Inputs, Marginal, Equal - for analyzing profit maximization.
Acronyms
Remember ‘P-MAC’ for Profit Maximization
Price = Marginal Cost
Average Costs must be covered.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Profit (π)
The difference between total revenue (TR) and total cost (TC).
- Total Revenue (TR)
The total income a firm earns from selling its goods, calculated as price times quantity sold.
- Total Cost (TC)
The total expense incurred by a firm in producing goods.
- Marginal Cost (MC)
The additional cost incurred from producing one more unit of a good.
- Average Variable Cost (AVC)
The variable costs per unit of output produced.
- Average Cost (AC)
The total cost per unit of output produced, including both fixed and variable costs.
- Perfect Competition
A market structure with many buyers and sellers producing homogenous products where no single consumer or producer can influence the market price.
- Shut Down Point
The point where the firm's revenue is not sufficient to cover its variable costs, leading to a halt in production in the short run.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
