Key Terms
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Conductors and Insulators
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, let's discuss conductors and insulators. Can anyone tell me what a conductor is?

Isn't it a material that allows electricity to flow through it?

Exactly! Good conductors include metals like copper and aluminium. What about insulators? Who can give me an example?

Rubber and plastic are insulators, right?

That's right! Remember the acronym 'C-P' for Conductors are 'Copper' and 'Plastic' is for Insulators. Now, can liquids also conduct electricity?

I think some of them can. Like salt water, right?

Exactly! Today we’ll explore how liquids can conduct electricity and the chemical changes that occur.
Testing Liquid Conductivity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's move to testing liquid conductivity. Who can explain how we can test if a liquid is a good conductor or not?

We can use a tester, right? With a light bulb?

Yes! When we dip the tester's ends into the liquid, if the bulb glows, the liquid is a good conductor. What liquids would you like to test?

Let's try lemon juice and vinegar!

Great choices! Remember, if the bulb glows, we classify that liquid as a good conductor.
Chemical Effects of Electric Current
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

As we explore the chemical effects of electric currents, can anyone tell me what happens when current passes through a conducting solution?

I think it creates bubbles or gas, right?

Exactly! Gas bubbles form at the electrodes. This is one of the signs of a chemical reaction. What else might we observe?

Maybe a color change in the liquid?

Yes! Both gas formation and color changes show that a chemical reaction is taking place, which is significant when we talk about electrolysis.
Introduction to Electroplating
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s discuss electroplating. Who knows what it is?

It's when one metal gets coated with another metal using electricity!

Very good! Electroplating is widely used to enhance metals. For example, why do you think we electroplate objects?

To make them shiny and protect them from rust?

Exactly! Excellent! Remember, electroplating ensures durability and aesthetic appeal of the objects.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore the distinction between good and poor conductors of electricity, the chemical effects of electric current in solutions, and specific concepts like electroplating and the behavior of various liquids when exposed to electric currents.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of Key Terms
This section introduces key terms related to the chemical effects of electric current, emphasizing the different types of conductivity in materials. Conductors are defined as materials that allow electric currents to flow easily, such as metals like copper and aluminium, while insulators, including rubber and plastic, do not facilitate electric flow.
Conductivity in Liquids
The text emphasizes the investigation of liquids as conductors of electricity. It contrasts pure water, which is a poor conductor, with saline or acid solutions that do conduct electricity due to dissolved ions.
Chemical Effects of Electric Current
Significantly, the section discusses the chemical reactions generated when electric currents pass through conducting solutions, leading to phenomena such as gas production, changes in color, and electroplating. The importance of distinguishing between strong and weak conductors is highlighted, emphasizing practical applications such as testing different liquids with a simple electrical tester aligned with a compass needle.
Moreover, the practice of electroplating is introduced, explaining how one metal can be deposited onto another via electrical processes, showcasing practical applications in industry and everyday objects, reinforcing the concept of chemical transformation initiated by electric currents.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Good Conductors of Electricity
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Some liquids are good conductors of electricity and some are poor conductors.
Detailed Explanation
Good conductors are materials that easily allow electric current to pass through them. In the context of liquids, some substances like lemon juice and vinegar conduct electricity well, while others, like distilled water, do not conduct electricity effectively without additional substances (like salt) dissolved in them.
Examples & Analogies
Think of good conductors as highways where cars (electric current) can travel quickly. Just like a highway with no traffic can allow cars to move freely, good conductors allow electric current to flow easily. On the other hand, poor conductors are like narrow or congested roads, which slow down or block the cars from passing.
Chemical Effects of Electric Currents
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The passage of an electric current through a conducting liquid causes chemical reactions.
Detailed Explanation
When electricity flows through a conducting solution, it can cause various chemical changes. These effects include the production of gas bubbles, color changes, and the deposition of solid materials. For instance, if you pass current through a solution of saltwater, the current can cause chlorine gas to form at one electrode and hydrogen gas at the other.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a baking soda solution reacting to electricity like bubbling dough that rises when yeast is added. When you put electricity into the solution, it's similar to adding yeast to the dough, making it react in noticeable ways, like bubbling and changing.
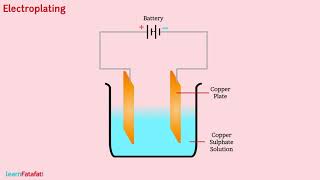
Electroplating
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The process of depositing a layer of any desired metal on another material, by means of electricity, is called electroplating.
Detailed Explanation
Electroplating is a technique used to coat a material with a thin layer of metal. This process uses electric current to move metal ions from a solution onto the surface of an object. This is commonly used to enhance the appearance of items like jewelry or to protect metal surfaces from corrosion.
Examples & Analogies
Think of electroplating like decorating a cake. The cake itself represents a less expensive material, and the icing represents the costly metal layer. Just as icing gives a cake a nice appearance and flavor, electroplating gives cheaper materials a shiny and attractive finish.
Key Concepts
-
Conductors vs Insulators: Materials that allow electricity vs those that do not.
-
Liquids as Conductors: Certain liquids, especially with ions, can conduct electricity.
-
Chemical Changes: Electrical currents can produce gas, color changes, and deposits.
-
Importance of Electroplating: It enhances the physical properties of metals.
Examples & Applications
Testing the conductivity of lemon juice, which glows a bulb, showing it's a good conductor.
Electroplating gold over silver jewelry to give an attractive finish.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Metals are bright, conductors of light; rubber holds tight, keeps currents from flight.
Stories
Once there was a shiny copper wire who wanted to share its current with water, but pure water was shy and kept the current inside.
Memory Tools
C-L-A for Conductors: Copper, Lemon juice, Acids.
Acronyms
LED
Light Emitting Diode
illuminating our world.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Electrode
A conductive material that allows electricity to enter or leave a medium.
- Electroplating
The process of depositing a layer of any desired metal on another material using electricity.
- Good Conductor
A material that efficiently allows electric current to flow through it.
- LED
Light Emitting Diode; a device that emits light when electric current flows through it.
- Poor Conductor
A material that does not efficiently allow electric current to flow through it.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
