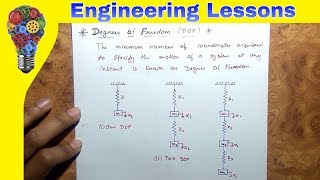
Definition of Free Vibration
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Free Vibration
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are focusing on free vibration. Can anyone tell me what free vibration means?

Isn't it when something vibrates without any external forces?

Exactly! Free vibration occurs after an initial disturbance when external forces are absent. It's crucial for understanding how our structures behave during earthquakes.

So, it's like when you flick a swing and it keeps going by itself?

That's a perfect analogy! The swing vibrates freely after you give it that initial push. This is similar to how a mass-spring system oscillates.
Mass-Spring Systems
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

In a mass-spring system, what are the components we need to consider?

There's the mass, which can move in one direction, and a spring, right?

Correct! The mass-movement is limited to one direction and the spring's stiffness is key to how it oscillates.

What happens if we add damping?

Great question! Damping would absorb energy, reducing the amplitude of vibrations over time, but that's a topic for later. For now, let's focus on these ideal, undamped systems.
Understanding Natural Frequency
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

What do we mean by 'natural frequency' in free vibration?

I think it's how fast the system vibrates naturally without any help.

Exactly! It's determined by the mass and stiffness of the system. The formula is ω_n = √(k/m).

So, if we increased the mass, would the natural frequency decrease?

Yes, that's correct! More mass means less natural frequency, causing slower vibrations.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In the context of a Single Degree of Freedom (SDOF) system, free vibration describes how the system oscillates freely, typically involving a mass-spring arrangement. This concept serves as a cornerstone for understanding more complex vibration scenarios, especially in structural dynamics and earthquake engineering.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of Free Vibration
Free vibration represents the motion of a mechanical system without the influence of external forces, occurring after an initial disturbance. In the case of a Single Degree of Freedom (SDOF) system, this typically involves a mass-spring configuration that oscillates freely. Key aspects include:
- Natural Motion: Free vibration happens naturally when the system is displaced and released.
- Dynamic Behavior: The behavior of the system can be analyzed through its parameters such as mass (m), stiffness (k), and natural frequency (C9_n).
- Significance in Engineering: Understanding free vibrations is crucial in structural dynamics, specifically for assessing responses in buildings during seismic events and designing for resilience against such disturbances.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Understanding Free Vibration
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Free vibration refers to the motion of a mechanical system when it is allowed to vibrate naturally without the influence of external forces after an initial disturbance.
Detailed Explanation
Free vibration is a type of oscillation that occurs when a mechanical system moves independently after being set into motion. It does not have any external disturbances acting on it, allowing it to vibrate in its natural state. Think of it like pushing a swing - once you let go, it swings back and forth freely without any additional pushes.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a child on a swing at a playground. When pushed, the swing moves and continues swinging back and forth without any further intervention. As long as there aren’t any external forces acting on it, like wind or someone jumping onto it, the swing will continue its motion in a predictable rhythm.
Mass-Spring System
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
For a SDOF system, this typically involves a mass-spring system set into motion and allowed to oscillate freely.
Detailed Explanation
In a Single Degree of Freedom (SDOF) system, free vibration is often modeled as a mass attached to a spring. When the mass is displaced from its equilibrium position and then released, it begins to oscillate. The spring provides the restoring force that pulls the mass back towards its original position, causing it to move back and forth. This is a fundamental concept in vibration analysis as it simplifies many complex vibrational behaviors into a single framework.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a rubber band. When you stretch it and then let it go, it snaps back to its original position. If you pull it just slightly and let it go, it can oscillate back and forth. In a similar way, a mass on a spring will vibrate back and forth once disturbed.
Key Concepts
-
Free Vibration: The natural motion of a system after an initial disturbance without external forces.
-
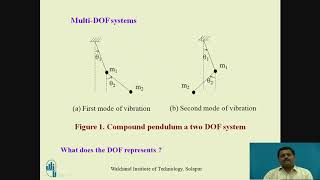
Single Degree of Freedom (SDOF): Simplified systems that oscillate in one direction, crucial for analyzing vibrations.
-
Natural Frequency: The frequency at which an SDOF system vibrates freely, determined by mass and stiffness.
Examples & Applications
A weight suspended from a spring, when pulled down and released, will oscillate up and down in free vibration.
A tuning fork vibrating after being struck and producing a musical tone is an example of free vibration.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When the system's free and clear, it vibrates with a cheer!
Stories
Imagine a swing that's been pushed. After you let go, it rocks back and forth freely, illustrating free vibration.
Memory Tools
Remember 'F-M-V' for Free Vibration: 'Free' stands for no forces, 'Mass' for the object's mass, and 'Vibration' for its oscillations.
Acronyms
SDOF stands for Single Degree of Freedom - think of it as 'Single Direction'.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Free Vibration
The motion of a system allowed to oscillate naturally after being displaced without external forces acting on it.
- Single Degree of Freedom (SDOF)
A system characterized by a single mass moving in one direction, commonly analyzed in vibration studies.
- Natural Frequency (ωₙ)
The frequency at which a system oscillates freely, determined by its mass and stiffness.
- MassSpring System
A simple mechanical system consisting of a mass attached to a spring, used to study free vibration.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
