Effects of Liquefaction
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Liquefaction Effects
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we will explore the effects of liquefaction. Can anyone tell me what they think liquefaction is?

Is it when the soil turns into a liquid during an earthquake?

Exactly! And when this happens, what kind of consequences might we see?

Buildings might tilt or even fall over, right?

Correct! It's crucial for us as future engineers to understand these effects. Let's remember the acronym 'STABLE' – Settlement, Tilt, Lateral spreading, Boils, and Lifeline damage – to capture the main effects we’ll discuss.

Can you explain sand boils?

Sure! Sand boils occur when water and sand are expelled at the surface during liquefaction, signifying severe soil instability. We'll delve deeper into each effect shortly.

What are lifelines?

Lifelines are critical infrastructure like roads, bridges, and pipelines, which can be damaged due to liquefaction. Understanding this is vital for urban planning in earthquake-prone areas.

In summary, liquefaction can cause settlement, tilting, lateral spreading, boiling, and damage to lifelines. Keep the acronym 'STABLE' in mind as we explore more.
Settlement and Structural Damage
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s talk about ground settlement. What happens when the ground settles suddenly due to liquefaction?

Buildings can sink or crack, right?

Absolutely! Uneven settlement can lead to structural damage. Think about the foundations—what materials might be affected?

Concrete would crack, especially if it's not designed for that kind of movement.

Exactly! Furthermore, let’s recall the effects on tilting. What might cause a building to tilt?

If one side of the foundation loses strength faster than the other.

Correct! It’s crucial to design structures that can handle these conditions. Remember to think about the foundation type and soil engagement. They play critical roles in overall stability.

To sum up, liquefaction causes settlements and can lead to structural tilting, significantly impacting safety and usability.
Lateral Spreading and Surface Effects
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss lateral spreading. Can anyone define it for us?

It’s when the ground moves sideways, right?

Exactly! This can lead to significant horizontal displacement of structures. What kinds of structures do you think are most vulnerable?

Bridges and roads because they rely on firm ground.

Very insightful! Just like the collapse of roadways during events. And what about sand boils? Why are they significant?

They indicate that the soil is unstable and can be dangerous for buildings near them.

Correct! Sand boils show us where the pressure is being released at the surface, a sign of serious issues below. Always assess the area surrounding these boils for safety.

In conclusion, lateral spreading and sand boils are significant indicators of liquefaction effects, requiring careful evaluation to ensure safety.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Liquefaction can lead to severe consequences such as ground settlement, building tilting, and failure of underground utilities. Understanding these effects is crucial for adequate risk assessment and engineering solutions.
Detailed
Effects of Liquefaction
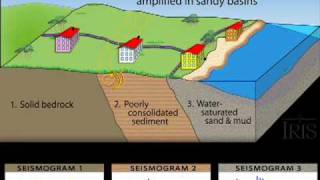
Liquefaction is a phenomenon where saturated, loose soils lose their strength and behave like a fluid under dynamic loads, especially during an earthquake. The effects of liquefaction can be catastrophic:
- Settlement of ground and structures: Buildings may sink unevenly due to the instability of the foundation soil.
- Tilting or overturning of buildings: Structures may not remain vertical and could lead to complete failure if the ground loses strength underneath.
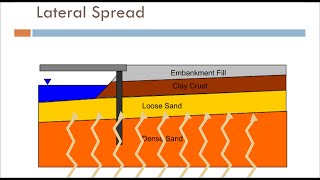
- Lateral spreading and flow failures: Ground movement can occur horizontally, causing significant damage to surface structures.
- Sand boils and ground fissures: Eruptions of sand and water can occur at the surface, leading to further instability.
- Damage to lifelines: Critical infrastructure such as pipelines, roads, and bridges may experience severe damage or failure.
Acknowledging these effects is essential for designing safe structures in seismic zones.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Consequences of Liquefaction
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The consequences of liquefaction can be severe:
- Settlement of ground and structures.
- Tilting or overturning of buildings.
- Lateral spreading and flow failures.
- Sand boils and ground fissures.
- Damage to lifelines (pipelines, roads, bridges).
- Bearing capacity failure.
Detailed Explanation
The effects of liquefaction during an earthquake can lead to significant damage. When liquefaction occurs, the soil loses its strength and stiffness, comparable to how a solid object can turn into a liquid when agitated. This causes the ground and any structures on it to settle or sink. Buildings may tilt or even tip over because of uneven support. Additionally, the phenomenon can cause lateral spreading, where the ground shifts sideways, leading to potential flow failures. Sand boils can appear on the surface, where water and sand mix and erupt, while fissures can crack the ground. Essential infrastructure like pipelines and roads can suffer severe damage, leading to major operational challenges. Lastly, the foundation's ability to support loads can diminish, causing bearing capacity failure.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a wet sponge. When you press down on it, the sponge squishes down and loses its shape. If you let go, it doesn’t immediately regain its form. In a similar way, during an earthquake, liquefaction causes the ground to behave like that sponge, squeezing structures and causing them to settle or collapse. For instance, during the 1964 Niigata earthquake in Japan, many buildings tilted and sand boils erupted, demonstrating the dramatic effects of liquefaction.
Key Concepts
-
Settlement: The process of land or structures sinking due to unstable soil conditions.
-
Lateral spreading: The horizontal displacement of the ground triggered by liquefaction during seismic events.
-
Sand Boils: Surface eruptions of sand and water, indicating excess pore pressure and instability in soil.
-
Lifelines: Critical infrastructure that can suffer serious damage due to liquefaction effects.
Examples & Applications
An example of liquefaction impacts is observed in the port of Anchorage during the 1964 earthquake, where significant ground failures occurred.
Another notable example is the Christchurch earthquakes, where widespread liquefaction led to extensive property and infrastructure damage.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When the ground shakes and the buildings bend, be ready for sand boils—don't let the trouble extend!
Stories
Imagine a city where one day the earth shakes. Underneath, the sandy soil is like a soup, swirling and bubbling. Buildings tilt and streets crack, showing how quickly stability can disappear in a liquefied world.
Memory Tools
Remember 'STABLE': Settlement, Tilt, Affects Lifelines, Boils—these are the key effects of liquefaction.
Acronyms
STABLE
for Settlement
for Tilt
for Affects Lifelines
for Boils
for Liquefaction.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Liquefaction
A phenomenon where saturated, loose soils lose their strength and behave like a liquid during dynamic loading.
- Settlement
The sinking or downward movement of a structure due to the loss of support in the underlying soil.
- Lateral Spreading
The horizontal displacement of soil, which can occur during liquefaction events.
- Sand Boils
Eruptions of sand and water at the ground surface, indicating high pore water pressure during liquefaction.
- Lifelines
Essential infrastructure such as roads, bridges, and pipelines that may be damaged during liquefaction.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
