Estimating Wind Loads of a Building
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Wind Load Estimation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to focus on estimating wind loads acting on buildings, especially during cyclones. Can anyone tell me why it's crucial to estimate wind loads?

To ensure that buildings can withstand severe weather conditions?

Exactly! Now, what types of factors do you think influence these estimates?

Wind speed, building height, and shape could play a role.

Right! We'll see how Bernoulli's equation helps us in this estimation. Remember: BE for Bernoulli's Equation!
Applying Bernoulli's Equation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's apply Bernoulli's equation. Who remembers the basic form of Bernoulli's equation?

Pressure energy plus kinetic energy plus potential energy equals a constant?

Correct! In our case, we'll focus on how pressure changes with wind speed. Can someone give me an example?

If the wind speed is 250 km/h, we can calculate pressure differences affecting buildings.

That's right! The formula involves translating wind speed into pressure.
Control Volume Concept
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss control volumes. What do we mean by a control volume in fluid mechanics?

It's the space used to analyze fluid flow around a certain boundary?

Precisely! And how does that apply when estimating wind loads?

We can track how wind enters and leaves the control volume to estimate forces.

Exactly! You'll notice how crucial it is for calculating changes in momentum in our wind load scenarios.
Practical Example of Wind Load Calculation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's analyze a real-life example. Given a cyclonic wind speed of 250 km/h, how would you approach calculating the lift force on a building roof?

We would start with the pressure difference created by that wind speed.

Correct! What is the formula you would use here?

We can use P = 0.5 * ρ * V^2 to calculate dynamic pressure.

Good! This is how we calculate forces acting on structures and ensure they are designed safely.
Summary and Review
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we covered how to estimate wind loads using Bernoulli's equation and control volumes. Can someone summarize what we've learned?

We learned about the importance of wind load estimation, especially during cyclones.

Great! And what key equations did we focus on?

Bernoulli's equation and mass conservation equations.

Exactly! Always remember these principles when dealing with wind load estimations in engineering.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, the process of estimating the wind loads acting on buildings is explored, with real-life examples, particularly considering cyclones. It emphasizes applying Bernoulli’s equations, control volume analysis, and the importance of understanding pressure variations due to wind speeds in structural engineering.
Detailed
Estimating Wind Loads of a Building
This section delves into the critical task of estimating wind loads acting on buildings, especially under extreme weather conditions such as cyclones. The importance of understanding wind loads is emphasized, showcasing how wind speeds of up to 250 km/h can significantly impact structural integrity. The discussion is anchored around Bernoulli's equation, which is instrumental in calculating pressure differences and resulting forces on structures.
By employing real-life scenarios, such as estimating wind uplift at an airport affected by cyclonic winds, readers are introduced to practical applications of fluid mechanics principles. Control volume concepts and streamline analyses further clarify how these calculations are made. Key parameters, like atmospheric pressure and velocity, are translated into lift forces that structures must be designed to withstand. Furthermore, the chapter discusses foundational equations of mass conservation and momentum in relation to wind load calculations, underscoring the relationship between fluid dynamics principles and civil engineering applications.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Wind Load Estimation
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
As we start with a real life example problems, today let us start with a real life problems like estimating the wind loads of a building where the cyclone effect is more disasters.
Detailed Explanation
Estimating wind loads involves analyzing how strong winds, particularly during cyclones, can affect buildings. Wind loads are crucial for designing safe structures, especially in areas prone to severe weather. In this example, we are focusing on the necessity of understanding these loads to prevent structural failures during cyclones.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a kite being flown on a windy day. If the wind gets too strong, the kite can be pulled from your hands and may even get damaged. Similarly, buildings must be designed to resist the pull of the wind to avoid damage or collapse.
Computing Pressure Differences at Wind Speeds
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
For example, if you look at this, the airport locations in Bhubaneswar and the cyclonic speed of the 250 kilometer per hours you can compute it what will be the pressure difference between the off stream in off area as well as the inside the airport.
Detailed Explanation
When cyclonic winds reach speeds of 250 km/h, the pressure outside a building can be quite different from the pressure inside. This pressure differential can cause roofs to lift off buildings. Understanding and calculating this difference is critical for engineers when designing buildings that can withstand such forces.
Examples & Analogies
Think of blowing up a balloon. As you blow air into it, the inside pressure builds up. If the balloon gets too much air, the pressure could push outwards and pop the balloon. For buildings, if the pressure inside is significantly lower than the pressure outside during a storm, it can lead to catastrophic failure.
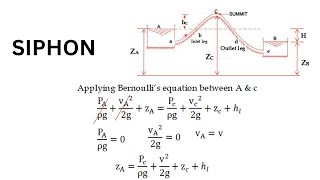
Applying Bernoulli’s Equation
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
And that pressure difference will uplift these the roof of this aircraft airport system. So the basically what I am to try to say that if you look at these problems which look it is very complex, but with help of the control volume concept and the drawing the streamlines we have then if you apply the Bernoulli’s equations you can solve these problems to estimate what could be the wind loads when you have a cyclonic speed 250 kilometer per hours passing through this type of civil engineering structures.
Detailed Explanation
Bernoulli’s equation relates pressure, velocity, and height within a flowing fluid. When applied to our wind load problem, it allows engineers to calculate expected pressures exerted by wind on structures. By visualizing airflow as streamlines, they can understand how wind behaves and how it influences the pressures on buildings.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how a car’s windows can feel pushed out when driving fast. The swift motion of air creates low pressure inside the car as compared to the outside. Similarly, buildings must contend with the pressures created by wind flowing around them.
Calculating Lift Force from Wind Pressure
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
P = Atmospheric pressure at 50 m height
P = 100725.8 N/m2
V = 250 Kmph (Design Wind Load)
= 69.44 m/s
Lift Force= ρ * A * V² / 2 = 25317.26 N = 25.3 KN.
Detailed Explanation
In calculating wind loads, we convert wind speed into a lift force using the formula: Lift Force = 0.5 * ρ * A * V², where ρ is air density, A is the area exposed to the wind, and V is the wind velocity. Substituting the values helps us determine the force acting on a structure due to wind.
Examples & Analogies
Picture how an airplane wing generates lift. As air flows faster over the wing, it creates lower pressure on top, lifting the plane. Buildings experience similar forces from wind, needing careful design to ensure they can 'resist' this lift.
Understanding the Control Volume Concept
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
And if you look at this way, it is quite easy to compute the wind load estimations, but we should know exactly how to apply the Bernoulli’s equations and what are the assumptions are there.
Detailed Explanation
The control volume concept simplifies the analysis of fluid flows by examining a defined volume through which fluid passes. It allows engineers to apply conservation laws (mass, momentum, and energy) effectively. Understanding the assumptions behind the Bernoulli equation, such as steady flow and incompressibility, is key to using it correctly.
Examples & Analogies
Visualize a container full of water with holes at different heights. The water flows out of the holes at different speeds. By focusing on a specific section of the container (a control volume), we can analyze how the water flows without having to account for the entire container, making the problem easier to understand.
Key Concepts
-
Pressure Difference: Understanding the difference in pressure across surfaces can aid in determining lift forces.
-
Bernoulli's Principle: It establishes the relationship between velocity and pressure in fluid flows.
-
Wind Load Calculation: Essential for structural engineering to ensure buildings can withstand wind forces.
Examples & Applications
Estimating the pressure difference for a roof of an airport under a cyclonic wind speed of 250 km/h.
Using Bernoulli's equation to assess the lift force on structural components affected by wind.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When the wind does blow, lets find out the flow; with Bernoulli we'll find out, just watch as it goes!
Stories
Imagine a tall building standing strong against a storm, its engineers using Bernoulli's principle to ensure it withstands the wind's oppressive force.
Memory Tools
Remember 'PLANE': Pressure, Lift, Area, Number (of factors), Estimate - to calculate wind load.
Acronyms
M.E.W.L. – Mass, Energy, Wind load, Lift - key concepts in assessing wind forces.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Bernoulli's Equation
A principle of fluid dynamics that describes the conservation of energy in flowing fluids.
- Control Volume
A defined volume in a flow field through which fluid can flow in and out, allowing for analysis of mass and momentum.
- Wind Load
The force exerted by the wind on a structure.
- Cyclone
A severe weather pattern characterized by strong winds and low pressure, often causing significant damage.
- Dynamic Pressure
The pressure exerted by a fluid in motion, calculated as 0.5 times the fluid density times the velocity squared.
- Lift Force
The upward force experienced by an object due to pressure differences in a fluid environment.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
