Professional Skills and Software Tools in Geo-Informatics
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Essential Software Platforms in Geo-Informatics
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's begin our session by discussing the essential software tools in Geo-Informatics. Software like ArcGIS and QGIS are popular GIS platforms. Can anyone explain why GIS is important?

GIS helps us visualize and analyze spatial data effectively, right?

Exactly, Student_1! It allows us to see patterns and relationships within the geographic context. Now, what about remote sensing software? Why do you think we need it?

Isn't it used to analyze satellite images and get data about the Earth without touching it?

Correct! Software like ERDAS Imagine and ENVI play a crucial role in that. Can anyone list a specific application of remote sensing?

Environmental monitoring, like tracking deforestation through satellite images!

Right again! Environmental monitoring is a great example. Overall, understanding these tools is essential for handling geographic data effectively.
Key Skills for Civil Engineers in Geo-Informatics
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s move on to the skills needed for civil engineers using these tools. Why do you think managing spatial databases is critical?

Because data accuracy is important for proper analysis, right?

Exactly! Managing data accurately is key to making informed decisions. What are some other skills that come to mind?

Digitizing and editing spatial features must be important too!

Great point! Digitizing allows us to create up-to-date representations of the data we need. What about interpreting satellite imagery?

That helps us understand land-use changes over time!

Precisely! All these skills build a solid foundation for effective use of Geo-Informatics in engineering projects.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore key software tools such as GIS, remote sensing, photogrammetry, and LiDAR applications alongside essential skills for civil engineers, including spatial database management and satellite imagery interpretation. Understanding these components is crucial for effective engagement in Geo-Informatics in an engineering context.
Detailed
Overview
In the realm of Geo-Informatics, proficiency in various software platforms and skillsets is critical for civil engineers. This section details the essential software tools used to manage, analyze, and visualize geographic data, alongside the professional skills required for effective application.
Essential Software Platforms
- GIS Software: Tools such as ArcGIS, QGIS, and MapInfo are integral for geospatial analysis and visualization. These platforms allow users to handle spatial data effectively, making informed decisions based on geographic patterns.
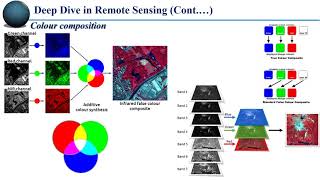
- Remote Sensing Software: Tools including ERDAS Imagine and ENVI are vital for interpreting satellite imagery and analyzing data acquired from remote sensing technologies.
- 3D Modeling and Photogrammetry: Software like Agisoft Metashape and Pix4D is necessary for creating detailed 3D models through image processing techniques.
- LiDAR Processing Tools: Tools such as LAStools and Global Mapper aid in processing point cloud data generated from LiDAR technology.
- Programming and Scripting: Familiarity with programming languages like Python (utilizing libraries such as GDAL, Rasterio, and GeoPandas) and R for spatial analysis enhances automation and data manipulation capabilities.
Key Skills for Civil Engineers
To effectively leverage these tools, civil engineers must develop a range of skills, including:
- Managing spatial databases and handling attribute tables.
- Digitizing spatial features and conducting spatial queries.
- Interpreting complex satellite imagery and applying coordinate transformations for precise location services.
- Automating geospatial processes through programming.
In summary, mastering software tools and essential skills empowers civil engineers to contribute substantially to projects relying on spatial data.
Youtube Videos

![What is MSc Geoinformatics course? – [Hindi] – Quick Support](https://img.youtube.com/vi/QC6cEfNk1aQ/mqdefault.jpg)







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Essential Software Platforms
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- GIS Software: ArcGIS, QGIS (open source), MapInfo, GRASS GIS
- Remote Sensing Software: ERDAS Imagine, ENVI, SNAP
- Photogrammetry & 3D Modeling: Agisoft Metashape, Pix4D, Autodesk ReCap
- LiDAR Processing Tools: LAStools, Global Mapper, CloudCompare
- Programming and Scripting: Python (with libraries like GDAL, Rasterio, GeoPandas), R (for spatial analysis)
Detailed Explanation
This chunk outlines the essential software platforms used in Geo-Informatics. GIS software such as ArcGIS and QGIS are fundamental for mapping and visualizing data. Remote sensing software like ERDAS Imagine and ENVI allows for analysis of satellite imagery. For creating 3D models and photogrammetry, tools such as Agisoft Metashape are employed. LiDAR processing is facilitated by tools like LAStools and Global Mapper, which help in dealing with point cloud data from LiDAR sensors. Furthermore, programming languages like Python and R are important for automating tasks, conducting analyses, and managing geospatial data.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the software tools as a toolbox for a carpenter. Just as a carpenter uses various tools for cutting, measuring, and joining wood, Geo-Informatics professionals use different software tools for mapping, analyzing, and visualizing spatial data.
Key Skills for Civil Engineers
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Handling spatial databases and attribute tables
- Digitizing and editing spatial features
- Conducting spatial queries and overlays
- Interpreting satellite imagery
- Working with coordinate transformations and projections
- Automating tasks using Python or ModelBuilder in ArcGIS
Detailed Explanation
This chunk lists key skills that civil engineers should possess when working with Geo-Informatics. These skills include the ability to manage spatial databases, which involves storing and organizing geospatial data effectively. Engineers need to digitize and edit spatial features, ensuring accuracy in their maps. Conducting spatial queries allows them to extract specific information from a dataset. Interpreting satellite imagery is crucial for understanding land use and environmental changes. Additionally, understanding coordinate systems is vital for accurate mapping and analysis. Finally, automation skills with programming languages like Python help streamline repetitive tasks, making processes more efficient.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a chef in a kitchen. Just as a chef needs to know how to use a variety of kitchen tools and understand recipes to create delicious dishes, civil engineers must learn diverse skills and tools to effectively use Geo-Informatics in their projects.
Key Concepts
-
GIS Tools: Essential for visualization and analysis of spatial data.
-
Remote Sensing: Critical for acquiring data without physical contact.
-
Photogrammetry: Important for deriving measurements from images.
-
LiDAR: Used for high-resolution mapping and modeling.
-
Programming & Scripting: Enhances data handling and automation capabilities.
Examples & Applications
Using ArcGIS for urban planning to visualize land use.
Employing ENVI to analyze changes in forest cover over decades.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
GIS is the way to see, maps and data come together in harmony.
Stories
Imagine a city planner using ArcGIS to design roads, finding the fastest routes for traffic. While at the same time, remote sensors detect pollution, aiding urban health.
Memory Tools
GIRP - Gather, Interpret, Represent, Present for GIS skills.
Acronyms
PRISM - Programming, Remote Sensing, Image Processing, Spatial Management.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- GIS Software
Geographic Information System software used for storing, analyzing, and visualizing spatial data.
- Remote Sensing Software
Tools used to analyze data collected from satellites and other aerial platforms without physical contact.
- Photogrammetry
Technique for measuring positions and extracting information about physical objects from photographs.
- LiDAR
Light Detection and Ranging technology that measures distances using laser light to create high-resolution maps of the environment.
- Programming and Scripting
Using coding languages to automate tasks and manipulate spatial data.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
