Recent Trends and Future Prospects
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Integration with AI and ML
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

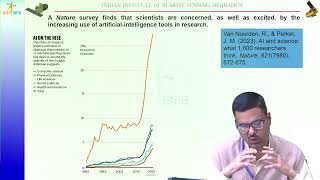
Today, we'll discuss how Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are transforming Geo-Informatics. Can anyone tell me how these technologies might be used?

They can help in image classification, right?

Correct! AI and ML can classify images efficiently, enhancing object detection in remote sensing applications. This is important for urban planning. Can anyone think of other applications?

What about predictive modeling for urban growth?

Exactly! Predictive modeling allows us to anticipate urban expansion, leading to better planning decisions. Remember the acronym 'PIE' for Predictive Imaging Excellence.

So, how do we actually implement this in practical scenarios?

We’ll integrate AI tools within GIS platforms for real-time assessment and analytics. Let’s summarize: AI improves classification and predictive modeling in Geo-Informatics, crucial for effective urban planning.
Cloud-based GIS and Web Mapping
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Moving on, cloud-based GIS platforms like ArcGIS Online are becoming popular. Why do we think they are beneficial?

They can provide access to spatial data from anywhere?

Yes! Accessibility is a major advantage. Furthermore, it allows real-time data streaming. Can anyone give an example of how this could be applied?

During natural disasters, we can access updated maps quickly.

Spot on! Real-time access supports prompt decisions during emergencies. Remember 'SMART' - Streamlining Maps At Real-time Trends. Let's summarize: Cloud-based systems enhance data accessibility and real-time visualization.
Use of UAVs and Drones
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s talk about UAVs and drones. How can they be utilized in Geo-Informatics?

For capturing data quickly, especially in construction projects?

Great answer! Drones facilitate rapid data capture and can create detailed 3D terrain models. What do you think are the benefits of this technology?

They could reduce costs compared to traditional methods!

Right again! Drones offer cost-effective solutions for data gathering. Let's remember 'COST' - Capture Optimized Survey Techniques. In summary, UAVs enhance efficiency and accuracy in Geo-Informatics applications.
Smart Cities and Digital Twins
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, who can explain how Geo-Informatics contributes to smart cities?

It helps in planning and managing urban resources effectively?

Exactly! Additionally, the creation of digital twins allows for monitoring and analyzing city infrastructure in real-time. Can anyone articulate what a digital twin is?

It's a virtual model that represents a physical asset's performance?

Absolutely! Remember the acronym 'VIRTUE' for Virtual Infrastructure Resource for Twin Urban Experiences. In conclusion, smart cities leverage Geo-Informatics for improved resource management through digital twins.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Recent trends in Geo-Informatics emphasize the integration of Artificial Intelligence, cloud-based solutions, and drone technologies. These advancements are shaping the future, particularly in areas like smart cities and digital twins.
Detailed
Recent Trends and Future Prospects
The advancement of Geo-Informatics is increasingly driven by the integration of technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML), which enhance the ability to classify images and predict urban growth effectively. Additionally, cloud-based Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are emerging, enabling real-time data visualization and access through platforms like ArcGIS Online. The adoption of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) and drones is revolutionizing data capture, allowing for rapid construction monitoring and intricate 3D terrain modeling.
Moreover, as urban areas evolve into smart cities, the concept of digital twins—virtual representations of physical assets—is gaining traction, allowing for sophisticated performance analysis and improved urban systems management. This integration of various technologies significantly enhances decision-making processes and offers promising prospects for the future of Geo-Informatics.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Integration with Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Image classification and object detection
• Predictive modeling for urban growth and traffic
Detailed Explanation
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are increasingly being integrated into geo-informatics. This means that computers can help us understand images and data related to geographical features much better than before.
For instance, AI can automatically classify images taken from satellites, identifying different types of land use such as forests, urban areas, or water bodies. Additionally, predictive modeling allows experts to forecast changes in urban areas, such as traffic patterns or how a city might grow in the coming years based on certain strategies or developments.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a city planner who needs to assess the future traffic flow in a growing city. Instead of guessing or manually analyzing each street, they use AI algorithms to analyze vast amounts of data from various sources, such as traffic cameras and GPS data from cell phones, to predict where traffic jams are likely to occur.
Cloud-based GIS and Web Mapping
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Online spatial data platforms (ArcGIS Online, Google Earth Engine)
• Real-time data streaming and visualization
Detailed Explanation
Cloud-based Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and web mapping services have transformed how geo-informatics data is accessed and shared. These platforms allow users to store and analyze geographic data on the cloud instead of relying on local servers. For example, tools like ArcGIS Online and Google Earth Engine enable users to create, analyze, and share maps and spatial data directly through the internet.
This cloud capability supports real-time data updates and dynamic visualization, meaning users can see changes in data as they happen, which is crucial for quick decision-making.
Examples & Analogies
Picture an environmental agency monitoring air quality across a city. With cloud-based GIS, they can access real-time air pollution data collected from various sensors across the city, visualize that data immediately on a map, and share it with the public through an interactive online platform.
Use of UAVs and Drones
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Rapid data capture for construction monitoring
• 3D terrain modeling and volumetric analysis
Detailed Explanation
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) and drones are becoming vital tools in geo-informatics because they can collect data quickly and efficiently. In construction, drones can monitor the progress of projects, capturing images and videos that provide real-time feedback.
Additionally, the use of drones allows for 3D modeling of terrains, which is essential for understanding land structures and planning further developments. This capability also supports volumetric analysis, which assesses the dimensions of a site or material quantities accurately.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a construction company building a new bridge. Instead of sending teams to manually measure the site, they can deploy a drone to fly over the area, capturing detailed 3D images. This not only saves time but also provides precise data that improves the accuracy of their project planning.
Smart Cities and Digital Twins
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Geo-Informatics in IoT-enabled urban systems
• Virtual replication of physical assets for performance analysis
Detailed Explanation
The concept of smart cities involves using technology and data to improve urban living. Geo-informatics plays a critical role here by integrating information from various sources, including Internet of Things (IoT) devices, to manage city services effectively.
Digital twins are another exciting development, where a virtual model of a physical asset (like a building or infrastructure) is created. This model allows city planners to analyze performance and forecast potential issues without impacting the actual physical structure.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a smart city like a high-tech video game. In the game, everything from traffic flow to energy consumption can be monitored and adjusted based on real-time data. A digital twin of a city block might show how adding a new park would affect traffic and pedestrian movements, allowing planners to visualize changes before making real-world decisions.
Key Concepts
-
AI Integration: Enhances classification and predictive modeling in Geo-Informatics.
-
Cloud Technology: Facilitates remote access and real-time data sharing through GIS.
-
UAVs: Provides rapid data capture for monitoring and modeling purposes.
-
Smart Cities: Incorporates Geo-Informatics for enhanced urban management.
-
Digital Twins: Virtual models reflecting the real-time performance of urban assets.
Examples & Applications
AI is utilized in urban planning to predict traffic patterns and manage growth.
Drones capture high-resolution imagery for construction monitoring and land surveys.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Drones in the sky, oh so high, capturing data for you and I!
Stories
Imagine a city where every building has its digital version, allowing planners to watch them grow without any surprises!
Memory Tools
Remember 'G-DAD' for Geo-Informatics: GIS, Drones, AI, Digital twins.
Acronyms
Use 'CLOUD' for benefits of cloud GIS
Connectivity
Live updates
Online access
Universal reach
Data sharing.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
A technology that simulates human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems.
- Machine Learning (ML)
A subset of AI that allows systems to learn from data and improve their performance without explicit programming.
- Cloudbased GIS
Geographic Information Systems hosted on cloud servers, allowing for remote access and real-time data sharing.
- Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs)
Drones used to capture imagery and data over geographical areas without an onboard pilot.
- Digital Twin
A digital replica of a physical entity, used for simulation and analysis.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
