Halloysite Mineral
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Structure of Halloysite
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will discuss halloysite mineral, which is fascinating because it shares a similar structure to kaolinite but contains interlayer water. Can anyone tell me what we mean by a two-layer sheet mineral?

Isn't it that it has two types of sheets stacked together?

And those sheets are held together differently than in other clays, right?

Exactly! Halloysite has a two-layer structure, formed by stacking layers of silica and gibbsite sheets. However, unlike kaolinite, halloysite is unique because it has water in between these layers, affecting how it reacts to changes in moisture.

So, does that water make halloysite expand or contract?

Yes, it's significant in that regard. It can expand when wet and contract when dry. Remember the abbreviation 'H2O' stands for water that plays a vital role in halloysite's behavior.
Properties of Halloysite
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s dive deeper into how the water influences halloysite’s properties. Can anyone name some properties of halloysite?

I think it can swell up, right?

Yes, and it probably makes it more plastic, which is useful in pottery!

Great points! The presence of water indeed affects its plasticity and behavior during drying and wetting cycles, which can be critical in applications like ceramics and agriculture.

And what about its stability? How does it hold up compared to kaolinite?

While kaolinite maintains a stable structure without considerable expansion, halloysite's interlayer water means it can absorb moisture from the environment, making it less stable in some cases. Remembering the effects of water can be crucial. Let's remember this concept through the saying, 'Water is the key to halloysite’s flexibility!'
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Halloysite minerals have a structure similar to kaolinite, showcasing a two-layer sheet, but they differ in containing water between these sheets. This feature affects their properties including swelling and shrinking behavior.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
Halloysite is a two-layer sheet mineral, structurally akin to kaolinite yet distinguished by the significant presence of water situated between the individual sheets. This crucial property sets halloysite apart, influencing its behavior in various environmental conditions. Unlike kaolinite, halloysite exhibits a degree of plasticity and reactivity due to the interlayer water, affecting its applications and interactions in soil. The discussion of halloysite not only adds to our understanding of clay minerals but also emphasizes the broader implications in soil chemistry and agriculture, thus underlining its significance in environmental studies.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Basic Structure of Halloysite
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
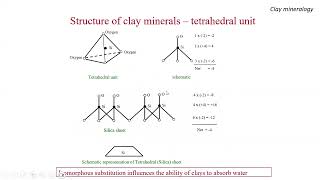
The basic unit is also a two-layer sheet similar to that of kaolinite except for the presence of water between the sheets.
Detailed Explanation
Halloysite is similar to kaolinite in that it has a two-layer sheet structure. However, a key difference is that halloysite contains water molecules that are positioned between these sheets. This water affects the mineral's properties, making it more unique compared to kaolinite.
Examples & Analogies
Think of halloysite like a sandwich with two layers of bread (the sheets) and some mayonnaise or filling (the water) in between. Just like the filling changes the sandwich's taste and texture, the water makes halloysite behave differently compared to kaolinite.
Comparison with Other Clay Minerals
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Montmorillonite and illite clay minerals are the most common. A basic three-layer sheet unit is formed by keeping one silica sheet each on the top and at the bottom of a gibbsite sheet. These units are stacked to form a lattice as shown.
Detailed Explanation
Montmorillonite and illite are other common clay minerals that differ structurally from halloysite. Montmorillonite consists of three-layer units, with a silica sheet sandwiched between two gibbsite sheets. This structure affects its properties, such as its ability to absorb water and expand. In contrast, halloysite, with its two-layer structure containing water, behaves differently, especially in terms of swelling.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine building a sandwich but with three layers instead of two. The top and bottom layers are plain bread (silica sheets) while the filling is different in each sandwich (gibbsite sheets). This extra layer can make it thicker and change how it holds onto moisture, similar to how montmorillonite behaves when exposed to water.
Properties of Halloysite
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Halloysite's ability to hold water between layers allows it to remain stable under various conditions.
Detailed Explanation
The presence of water in halloysite plays a crucial role in maintaining its stability. Unlike other clay minerals that may expand or shrink significantly when wet or dry, halloysite can effectively manage the moisture between its layers without undergoing major changes in structure. This makes halloysite advantageous in certain applications, such as pottery or ceramics, where stability is key.
Examples & Analogies
Consider halloysite like a well-insulated water bottle. It keeps the liquid inside without spilling or becoming overly warm or cool. Similarly, halloysite's structure helps it maintain its properties without significant changes, making it reliable in various environments.
Key Concepts
-
Two-layer sheet structure: Halloysite has layers consisting of silica and gibbsite each containing water between them, which influences its physical properties.
-
Plasticity: The water content between layers affects halloysite's plastic behavior, making it suitable for various applications.
Examples & Applications
Halloysite is used in ceramics because of its plasticity, which allows for shaping and forming into various products.
In agriculture, halloysite's ability to retain moisture can aid soil in areas prone to drought.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Halloysite spreads like a sponge, keeping crops alive in a grunge.
Stories
Imagine halloysite as a cozy blanket with water, wrapping plants snugly to help them survive.
Memory Tools
H2O = Halloysite's Helpful Water - think about how it affects properties.
Acronyms
H2O
Halloysite’s Two-layered Oasis where water resides.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Halloysite
A clay mineral that consists of a two-layer structure and incorporates water between its sheets.
- Twolayer sheet mineral
A type of mineral composed of two stacked layers, typically involving a silica sheet and a gibbsite sheet.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
