Kaolinite Mineral
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Clay Minerals
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will dive into clay minerals, particularly focusing on kaolinite. Can anyone tell me why clay minerals are significant in soil science?

I think they affect soil properties, like fertility and drainage.

Exactly! Clay minerals, especially silicates, play a crucial role in soil functionality. Now, what do we know about the structure of these minerals?

They have tetrahedral and octahedral units, right?

Correct! These units combine to create sheets that stack to form various clay minerals. Remember, the basic units of clay minerals contribute to high surface area, influencing properties like water retention.
Understanding Kaolinite
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s take a closer look at kaolinite. It's formed by stacking a gibbsite sheet on a silica sheet. Who can describe what this means structurally?

It means there are two layers, one from gibbsite and one from silica.

Exactly! And these are held together by hydrogen bonds. Why is this important for kaolinite's stability?

Because strong bonds prevent water from entering, meaning it won’t expand much.

Good point! This characteristic makes kaolinite quite unique compared to other clay types, such as montmorillonite, which can swell. Let's recap before we move on.
Applications and Implications of Kaolinite
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

What do you think makes kaolinite so abundant in certain deposits?

Its stable structure might make it resistant to weathering?

Precisely! Its stability contributes to its prevalence in residual deposits. Does anyone know the applications of kaolinite in industries?

I read it’s used in ceramics and paper production.

That's right! Its properties make kaolinite very useful. As we finish this session, what’s a key takeaway about kaolinite?

Kaolinite is stable, has low water absorption, and is used in many products!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The kaolinite mineral consists of a two-layer structural unit featuring a silica sheet stacked on a gibbsite sheet. Its structure provides stability and resistance to water penetration, making it the most abundant component of residual clay deposits.
Detailed
Kaolinite Mineral
Kaolinite is a type of clay mineral characterized by its unique two-layer structural unit, formed by the stacking of a gibbsite sheet over a silica sheet. This arrangement ensures that the bonds holding these units together, predominantly hydrogen bonds, are strong enough to prevent water entry into the lattice structure. As a result, kaolinite exhibits stability and very limited expansion when subjected to water saturation, distinguishing it from other clay minerals like montmorillonite which can swell significantly. Furthermore, kaolinite is noted for being the most abundant constituent of residual clay deposits, highlighting its geological significance.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Structure of Kaolinite
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
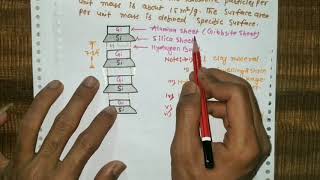
The basic kaolinite unit is a two-layer unit that is formed by stacking a gibbsite sheet on a silica sheet.
Detailed Explanation
Kaolinite consists of a basic structural unit where a gibbsite sheet (which contains aluminum and hydroxyl) is placed on top of a silica sheet (which contains silicon and oxygen). This combination creates a two-layer structure. Understanding this layering is essential because it defines how kaolinite behaves and interacts with water.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a sandwich where the gibbsite sheet is the filling and the silica sheet is the bread. The way these components are stacked creates a structure that, just like a sandwich, holds everything together and gives it a specific shape.
Bonding and Stability
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
These basic units are then stacked one on top of the other to form a lattice of the mineral. The units are held together by hydrogen bonds. The strong bonding does not permit water to enter the lattice. Thus, kaolinite minerals are stable and do not expand under saturation.
Detailed Explanation
The kaolinite units stack together to form a complex lattice structure, held tightly by hydrogen bonds. These bonds are strong enough to prevent water from entering between the layers. Consequently, kaolinite does not swell when it gets wet, making it stable in various environmental conditions. This property is significant for soil and construction applications.
Examples & Analogies
Think of kaolinite like a tightly packed suitcase where all items inside are stacked together with no space left for additional items (like water). Just as the suitcase remains the same size no matter how wet it gets outside, kaolinite retains its form without expanding when it absorbs moisture.
Prevalence of Kaolinite
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Kaolinite is the most abundant constituent of residual clay deposits.
Detailed Explanation
Kaolinite is widely found in clay deposits that form from weathered rocks over time. Its abundance among clay minerals means it plays a crucial role in many soil types, influencing their texture and fertility. This prominence also makes it important for various industrial applications, including ceramics and paper production.
Examples & Analogies
If you think of clay minerals as different types of fruits in a basket, kaolinite would be the banana, the most common and recognizable option. Just like bananas are often used in many recipes because of their availability, kaolinite is frequently utilized in different industries because of its widespread presence.
Key Concepts
-
Two-layer structure: Kaolinite has a two-layer structural unit formed by gibbsite and silica sheets.
-
Stability: Thanks to hydrogen bonding, kaolinite is stable and does not swell significantly.
-
Geological Significance: Kaolinite is the most abundant component of residual clay deposits.
Examples & Applications
Kaolinite is widely used in the ceramic industry due to its stability when fired at high temperatures.
In paper production, kaolinite acts as a filler, improving the smoothness and brightness of paper.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Layers of two, strong and true, kaolinite sticks like super glue.
Stories
Imagine a stable kingdom where two towers, one of gibbsite and one of silica, stood proudly, bonded by the strongest of friendships, never letting a flood affect their strength.
Memory Tools
G-S (Gibbsite - Silica) is all you need to remember for kaolinite’s structure.
Acronyms
K.S. (Kaolinite Stability) – Keep in mind how stability prevents swelling.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Kaolinite
A clay mineral formed from stacked gibbsite and silica sheets, characterized by stability and low expansion.
- Silicate
A mineral primarily composed of silicon and oxygen, forming the basis for clay structures.
- Hydrogen Bonds
Weak bonds that hold layers of kaolinite together, preventing water entry.
- Layer Structure
The arrangement of silica and gibbsite sheets in kaolinite forming its mineral lattice.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
