Applications of Jet Grouting
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Jet Grouting
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're exploring jet grouting, a technique that enhances soil properties. Can anyone describe what jet grouting involves?

Is it about injecting something into the soil?

Exactly! Jet grouting involves injecting a cement mixture at high pressure to strengthen and stabilize the soil. Does anyone know why this is particularly useful?

To prevent soil liquefaction during earthquakes?

Great point! Jet grouting helps mitigate liquefaction risks, a crucial factor in seismic zones. Remember, J.E.T - Justify Enhanced Treatment!

What kind of structures can benefit from this?

Excellent question! It’s widely used for underpinning foundations, especially in soft or liquefiable soils.

So, it can be used in cities where construction must be quiet?

Exactly! Jet grouting is ideal for urban environments because it's low in noise and vibration. Let's summarize: Jet grouting increases soil strength, mitigates liquefaction, and is ideal for urban construction.
Jet Grouting Mechanics
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s dive into how jet grouting actually works. Who can summarize the process?

We drill holes, right?

Correct! After drilling holes, a high-pressure jet mixes cement into the soil to replace it. Why is that important?

It mixes the soil and makes it stronger?

Yes! The jet erodes the old soil and replaces it with a stronger mixture. Remember: E.R.O.D.E - Enhance by Replacing Old Dirt Effectively.

What about the spacing of the columns?

Great question! The spacing and diameter of the jet-grouted columns depend on factors like load and environment. Summarizing: Jet grouting involves drilling, high-pressure injection, and effective re-stabilization of soft soils.
Practical Applications of Jet Grouting
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s discuss some practical applications of jet grouting. Anyone know of any case studies?

What about using it under bridges for stability?

Exactly! Jet grouting was used to support existing infrastructure during earthquakes by mitigating movements. Can you think of any others?

The dam project for liquefaction prevention?

Yes! The Beydag dam project used jet grouting to stabilize liquefiable soils, enhancing its seismic resistance. Let’s remember: J.E.T. - Just Every Treatment necessary for stability in construction!

So it helps in both new construction and supporting existing structures?

Absolutely! It’s versatile and crucial in modern engineering. To summarize, jet grouting is used for stability in various applications, notably in construction near seismic zones.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses the applications of jet grouting, emphasizing its effectiveness in mitigating liquefaction and providing stability to soft soils. It examines case studies demonstrating its use in infrastructure projects and the operational mechanics behind the method.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
Jet grouting is a cutting-edge method in ground improvement with three primary applications: underpinning or excavation support, stabilization of liquefiable soils, and groundwater or pollution control. The process begins by drilling small-diameter holes into the ground, followed by the injection of a high-pressure fluid that erodes existing soil and replaces it with a cement mixture. Studies have shown that this method is effective in limiting the risk of liquefaction during seismic events and in enhancing the bearing capacity of foundations.
The section includes various case studies, such as the use of jet grouting for stabilization under embankments and in construction along highways. These applications highlight the technology's flexibility in urban settings where traditional methods may be disruptive and its importance for seismic resilience in infrastructure. Overall, jet grouting proves essential for improving soil strength and controlling groundwater in construction projects.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Jet Grouting Applications
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Applications of the jet grouting system fall into three broad categories: underpinning or excavation support, stabilization of soft or liquefiable soils, groundwater or pollution control.
Detailed Explanation
Jet grouting is a versatile technique used in geotechnical engineering across three main areas: 1) As an underpinning method for existing structures and excavation sites, ensuring stability during construction. 2) To strengthen soft or liquefiable soils, enhancing their ability to withstand forces such as earthquakes. 3) To control groundwater or prevent pollution, maintaining soil integrity and protecting the environment.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a tall building being constructed on soft ground. Without proper support, the structure could sink or tilt. Jet grouting acts like a strong foundation of solid rock, enveloping the soft soil to stabilize it, ensuring the building stands firm. Additionally, if pollutants threaten to seep into the ground, jet grouting can seal off the contaminated area, similar to wrapping a delicate item in bubble wrap to prevent damage.
The Jet Grouting Process
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
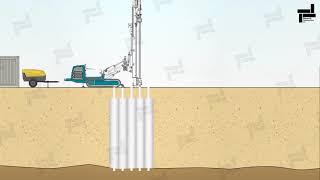
The method consists of soil injection of a mixed fluid at high pressure forming jets that erode and replace the existing soil with the injection mixture. In general this method begins by drilling small-diameter holes (90-150 mm) up to the final injection depth.
Detailed Explanation
Jet grouting works by injecting a specially mixed fluid—usually a combination of water and cement or other binding agents—into the soil at high pressure. This process begins with drilling small holes into the ground, typically between 90 to 150 mm in diameter, down to the desired depth. When the mixture is injected, it creates jets that erode and replace the surrounding soil, filling in gaps and stabilizing the ground effectively.
Examples & Analogies
Think of using a high-pressure water hose to clean a dirty surface. The water ejects dirt and debris while potentially applying a coat of sealant to protect the surface underneath. Similarly, jet grouting cleans and replaces unstable soil with strong, cohesive material, securing the foundation for whatever is built above.
Use in Earthquake Mitigation
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Cooke (2000) studied the use of jet grouting under an embankment slope at existing highway bridges to mitigate the risk of earthquake-induced liquefaction damage. The jet-grouted zone helped to limit movements of the abutment by containing and limiting the shear deformations that occurred in the liquefiable soils under the embankment that were softened due to the development of excess pore water pressures during shaking.
Detailed Explanation
In regions prone to earthquakes, soils can become liquefied, which increases the risk of structural damage. Jet grouting can address this issue effectively. For example, Cooke's research found that jet grouting applied under highway embankments helped stabilize structures by creating a solid zone that countered the movement and softening of surrounding soils during seismic events. This stabilization is critical for maintaining integrity during an earthquake.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a sponge soaked with water. When you shake it, it becomes squishy and loses its shape. This is like liquefaction in soil. Jet grouting acts like a strong layer, giving the sponge (or soil) structure, so it doesn’t lose form when pressure or shaking is applied, thus protecting the bridge above.
Supporting Foundations with Jet Grouting
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The performance of a jet-grouted zone is highly dependent on its strength. The strength assumed for the jet grouted material was high and resulted in no material failure during shaking.
Detailed Explanation
The effectiveness of jet grouting largely relies on the strength of the injected material. If the jet-grouted area is strong enough, it can withstand the shake of an earthquake without failing. This stability is crucial for the safety of structures above the ground, ensuring that they remain upright and secure during and after seismic activities.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a sturdy bridge made of tough materials compared to a flimsy bridge made of plastic. The strong bridge can handle heavy loads and shaking, while the weak one cannot. Similarly, a strong jet-grouting material supports buildings effectively, preventing structural failures.
Reducing Liquefaction Potential
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Geotechnical News (2008) reported from Olgun (2003), the soils were improved to increase bearing support for shallow foundations and to reduce liquefaction potential of the sand layers.
Detailed Explanation
Jet grouting is also employed to enhance the bearing capacity of shallow foundations, particularly in areas with sandy soils susceptible to liquefaction. By injecting grout into these layers, the ground is improved, making it stronger and more stable against liquefaction during events like earthquakes. This process ensures that constructions sit on solid ground, significantly reducing the risks of sinking or tilting.
Examples & Analogies
If you're building a sandcastle at the beach, you know that wet sand holds together better than dry sand. Jet grouting works similarly to saturating the sand with water and packing it tightly, creating a more stable base for the foundation of a building.
Key Concepts
-
Jet Grouting: A technique for soil improvement that utilizes high-pressure cement injection.
-
Liquefaction Risk Mitigation: Reducing the risk of soil liquefaction during seismic events.
-
Underpinning Foundations: Strengthening existing foundations with injected soil mixtures.
Examples & Applications
In the Beydag dam project, jet grouting was instrumental in stabilizing liquefiable soils beneath the structure.
Jet grouting has been effectively used under embankments to limit shear deformations during earthquakes.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Jet grouting makes soil tight, keeps it strong when the quake takes flight.
Stories
Imagine a shaken building, with its soft soil failing; then, jet grouting arrives like a superhero to fix the grounding.
Memory Tools
J.E.T. - Justifying Enhanced Treatment for earth stabilization.
Acronyms
JET
Jetting
Eroding
Tightening.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Jet Grouting
A soil improvement method involving the injection of high-pressure fluids to stabilize and strengthen soils.
- Soil Liquefaction
A phenomenon where saturated soil substantially loses strength due to applied stress, often occurring during earthquakes.
- Underpinning
A method of strengthening an existing foundation by adding support.
- Cement Mixture
A combination of cement, water, and sometimes aggregates used for the injection in jet grouting.
- Groundwater Control
The management of groundwater levels to maintain stability and reduce the risk of liquefaction.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
