Categories of Compaction Grouting
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Compaction Grouting
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're going to talk about compaction grouting and its significance in ground improvement. Who can tell me what compaction grouting involves?

Is it about injecting grout into the soil to make it more stable?

Exactly! Compaction grouting involves injecting a stiff grout that displaces soil but doesn’t permeate into it. Think of it like inflating a balloon—you expand it while keeping the outside intact. This solidifies the ground beneath.

What are some scenarios we use this method in?

Great question! We use it under existing structures, in urban areas where noise and vibration must be minimal, and in narrow spaces.

How do we do that practically?

We use injection pipes set up on the foundation. The injection process happens stepwise, lifting pipes between 0.3 and 1.5 meters each time to treat the full soil thickness!

Can it really help with liquefaction?

Yes! It effectively increases soil density and mitigates liquefaction potential, making it a vital technique in geotechnical engineering. Let's summarize today's key points: compaction grouting is a displacement-based technique ideal for improving soil stability in sensitive environments.
Execution of Compaction Grouting
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand what compaction grouting is, let's discuss how it's executed. Can anyone describe how the injection works?

Is it a bottom-up method where you inject from the bottom of the structure?

Exactly! Injection starts from the foundation and pushes the soil outward. We raise the injection pipes incrementally to cover the entire soil layer effectively.

What are the target results of this process?

The aim is to stabilize the soil by increasing its density and bearing capacity while controlling potential local settlements. This is especially important in built-up areas.

How do we ensure the process is effective?

Post-treatment monitoring is crucial. We look at parameters like the Soil Penetration Test (SPT) resistance to gauge improvement. Can anyone recall why sandy soils are ideal for this technique?

Because they have fewer fines, making them easier to compact, right?

Exactly right! Excellent summary, everyone. Remember, effective compaction grouting relies on precision and the right soil conditions.
Case Studies and Effectiveness
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's take a look at some real-world applications. Can anyone give me an example where compaction grouting was successfully implemented?

I remember hearing about improvements made at an airport runway.

Correct! Case studies, such as those presented by Orense, highlight significant improvements in SPT resistance, especially in sandy environments, which helped mitigate liquefaction risks.

Were there any other cases involving existing structures?

Yes, one case involved a manufacturing plant where careful injection techniques were crucial due to the existing infrastructure. The results showed increased structural stability after treatment.

That sounds impressive! So, what's the takeaway from these examples?

The takeaway is that compaction grouting can effectively enhance the strength and stability of liquefiable lands, making it essential for structural integrity in at-risk areas. Remember, understanding the context of application makes this technique effective.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Compaction grouting is a technique used to enhance soil stability and density, primarily in urban or sensitive environments. The process involves injecting a stiff grout to displace and compact surrounding soil, with specific methods tailored for existing structures and urban areas.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
Compaction grouting is a crucial method in ground improvement, particularly beneficial for enhancing the stability of liquefiable soils. This technique focuses on solidifying the earth by introducing a stiff grout mixture that does not permeate existing soil, leading to an increase in soil density and supporting structures above. Key categories of compaction grouting include treatments conducted under existing structures, in urban areas, or in narrow zones, all of which emphasize minimal disruption. The implementation involves a bottom-up injection process where pipes are inserted into the foundation and grout is injected incrementally, enhancing pressure and density. Historical case studies demonstrate its effectiveness, especially in sandy soils, reinforcing structural integrity and reducing liquefaction risks.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Compaction Grouting
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
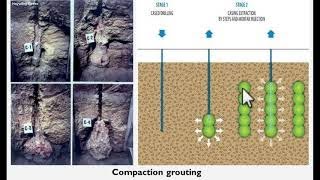
Compaction grouting is a soil injection with low workability cement paste that remains homogeneous without entering the soil pores. The cement mass extends, soil is moved and finally compacted. The liquefaction improvement using compaction grouting divides into the following categories:
(a) Treatment under existing structures;
(b) Treatment in urban areas with low levels of vibration and noise;
(c) Treatment in narrow areas.
Detailed Explanation
Compaction grouting involves injecting a specially formulated cement-based grout into the soil. This grout does not seep into the small voids of the soil but rather displaces it, thereby compacting the surrounding material. The technique is categorized based on where it is applied: under existing structures, in urban settings with minimal disturbance, and in confined spaces.
Examples & Analogies
Think of compaction grouting like using a balloon. When you blow into a balloon, you’re not just filling it up; the air pushes against the balloon's walls, causing them to stretch and compact the surrounding material. Similarly, when grout is injected into the soil, it pushes on and compresses the nearby soil.
Injection Process of Compaction Grouting
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The execution of compaction by injection technology using bottom-up method takes place as follows. In the first stage, injection pipes set up on the foundation soil of the existing or future foundations using drilling machines. The injection process begins. Mixture injected through the pipes pushes the surrounding soil; then the injection pipes raises about 0.3-1.5 m and the process renews. The 'in steps' injection process continues until the whole thickness of the soil layer is treated.
Detailed Explanation
The injection process occurs in a series of steps. Initially, pipes are inserted into the soil where grout will be injected. As grout is injected, it expands and moves the surrounding soil, which compacts it. After a certain volume of grout has been injected, the pipes are raised slightly and the process continues, ensuring that every layer of soil is treated systematically.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to fill a layered cake with cream by injecting it from the bottom. You would push the cream in, then lift the syringe slightly to inject the next layer. This systematic approach ensures that the cream fills every layer effectively, just like the compaction grouting method fills and compacts each layer of soil.
Objectives of Compaction Grouting
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The primary purpose of compaction grouting is to increase the density of soft, loose or disturbed soil, typically for settlement control, structural re-leveling, increasing the soil’s bearing capacity, and mitigation of liquefaction potential.
Detailed Explanation
Compaction grouting aims to make soil denser and stronger, which is crucial for areas that experience settling or where structures need additional support. The technique enhances the soil's ability to support structures and reduces the risk of liquefaction during geological events such as earthquakes.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it as reinforcing a sponge. When you press a sponge down (compaction grouting), it becomes denser and can hold more weight. In the same way, compacting soil under a building means it can better withstand the weight of the structure above it.
Effectiveness and Case Studies
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Compaction grouting was capable of producing the improvement in SPT resistance required to mitigate liquefaction risk. The method of construction, whether 'bottom-up', 'top-down' or combination of the two, affected the level of effectiveness and the resulting ground heave.
Detailed Explanation
Research has shown that the method of compaction grouting can significantly improve the strength of the soil against liquefaction. However, the effectiveness can vary depending on the specific technique used and the soil conditions. Methods may include different approaches to injecting grout that can lead to different outcomes in terms of ground stability.
Examples & Analogies
Picture different ways of packing a suitcase: laying clothes flat or rolling them up. Each method has its strengths, just like the different compaction grouting methods have specific benefits based on the situation.
Key Concepts
-
Stiff Grout Injection: A non-permeating method that raises soil density.
-
Liquefaction Mitigation: Crown grouting helps reduce the risk of soil liquefaction during seismic events.
-
Urban Application: Compaction grouting is ideal for working within urban constraints to maintain structure stability.
Examples & Applications
A manufacturing plant was successfully stabilized using a bottom-up injection method to prevent foundation settling.
An airport runway underwent compaction grouting to improve soil density and mitigate liquefaction potential.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Grout goes in, soil is pushed, compaction done, stability's rushed.
Stories
Imagine a beleaguered city where the ground beneath is sinking. A grouting team swoops in, injecting stiff mixtures that raise the ground back, ensuring buildings stand tall again.
Memory Tools
Remember the four 'I's of compaction grouting: Injection, Increase, Integrity, Improvement.
Acronyms
COMP
Compaction On Minimal disturbance Project.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Compaction Grouting
A soil improvement technique involving the injection of a stiff grout to increase soil density without permeating existing soil.
- Liquidity
The ability of soil to behave like a liquid under stress, which poses risks during seismic activity.
- Soil Penetration Test (SPT)
A field test to determine the geotechnical properties of soil, commonly used to assess soil density.
- Grout Bulb Mass
The volume of grout that expands and displaces the surrounding soil during the compaction grouting process.
- BottomUp Method
An injection technique in compaction grouting where grout is injected from the base upward to treat soil layers incrementally.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
