Project Management in Hardware System Development
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Project Management in Hardware Development
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll discuss the importance of project management in hardware system development. Can anyone tell me what project management is?

It’s a way to manage projects to meet certain goals.

Exactly! It helps ensure that we meet cost, quality, and timeline objectives. Why do you think that’s important?

So we can deliver products on time and within budget.

Right! And it also aligns teams, resources, and risks. Let’s remember this with the acronym ACRONYM: Align, Control, Risk, Organize, Network, Yield, Manage. What does each word remind you of?

It reminds me of all the aspects necessary for a successful project!

Great! Let’s summarize: Project management in hardware development is essential for aligning resources, ensuring quality, and meeting objectives.
Hardware Development Lifecycle
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's explore the phases of the Hardware Development Lifecycle, or HDLC. Can anyone name one of the phases?

Requirements gathering?

Correct! In that phase, we define what the system must do. What’s the next phase?

System design?

Exactly! Planning architecture, components, and interfaces is vital here. Can anyone remember the mnemonic to help us with these phases?

I think it’s R-S-I-V-D?

Yes, ‘Rushing Students Inclined Vital Discussions’ can help you recall Requirements, System design, Implementation, Validation, and Deployment. Well done! In summary, the HDLC includes several essential phases, all interlinked.
Key Project Management Principles
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s discuss key project management principles. Who can name one?

Scope definition!

Correct! Clear scope helps identify deliverables. Can anyone explain why time management is important?

Because we need to create schedules and keep the project on track.

Exactly! Think of time management as having a roadmap for our project. Let’s try to remember them as: S-T-R-C-P. What does that stand for?

Scope, Time, Resource, Communication, and Planning!

Fantastic! These principles guide successful project management. Let's recap: scope definition, time management, resource allocation, risk management, communication, and quality assurance are essential.
Risk Management in Hardware Projects
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, we will look at risk management. Can you name a common risk in hardware projects?

Component lead times?

Yes! That’s a significant risk. What could we do to mitigate this risk?

We could have backup suppliers.

Exactly! What about the concept of a risk register? Do you remember what it is?

It’s a document to track and rank risks?

Great job! Remember the mnemonic ‘R-R-M-V’ for Register, Rank, Mitigate, Validate. Summing up, understanding risks and having strategies are crucial components of project management.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore the significance of project management in hardware system development, detailing the hardware development lifecycle, key project management principles, planning tools, budget management, risk management, team dynamics, and modern methodologies. Understanding these components is crucial for aligning resources and ensuring project success.
Detailed
Project Management in Hardware System Development
Introduction
Project management plays a critical role in hardware system development, which is a complex, multidisciplinary effort involving electrical, mechanical, and software domains. Effective project management ensures that objectives related to cost, quality, and timelines are achieved through proper planning, execution, monitoring, and control.
The Hardware Development Lifecycle (HDLC)
The HDLC consists of several phases: 'Requirements Gathering', 'System Design', 'Implementation', 'Integration & Testing', 'Validation & Certification', and 'Deployment & Release'. Each phase is essential for systematic progress and successful project outcomes.
Key Project Management Principles
Principles such as 'Scope Definition', 'Time Management', 'Resource Allocation', 'Risk Management', and 'Communication' are vital in guiding project execution and aligning teams for effective delivery.
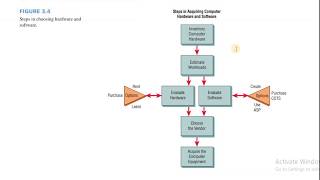
Project Planning Tools
Tools like 'Gantt Charts', 'PERT/CPM Charts', 'Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)', and 'Kanban Boards' help visualize timelines, track tasks, and manage dependencies effectively.
Budget and Cost Management
Understanding different cost categories, including design, prototyping, components, testing, and the contingency budget, is crucial for maintaining budget control and preventing overruns.
Risk Management in Hardware Projects
Identifying risks, such as long lead times, design errors, and vendor issues, and applying mitigation strategies, ensures projects stay on track despite challenges.
Team and Stakeholder Management
Clear roles and responsibilities are outlined for team members, including project managers, engineers, and stakeholders. Communication and coordination among these roles are vital for project success.
Agile and Hybrid Methodologies
The section explores various methodologies in hardware projects: traditional waterfall, agile, and hybrid approaches, highlighting the increasing popularity of hybrid models in embedded systems development.
Project Monitoring and Control
Techniques such as milestone reviews, earned value management, and key performance indicators are essential for monitoring project progress and ensuring it remains aligned with objectives.
Documentation and Deliverables
Various documents, including the project charter, schematics, test plans, and design history file, are crucial for maintaining project clarity and regulatory compliance.
Summary of Key Concepts
Effective project management in hardware development is fundamental to delivering high-quality products on time and within budget. Employing structured tools and strategies for risk, resource, and communications enables a smoother project execution process.
Youtube Videos
Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Project Management in Hardware Development
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Hardware system development involves complex, multidisciplinary efforts across electrical, mechanical, and software domains.
- Project management ensures that cost, quality, and time objectives are met through effective planning, execution, monitoring, and control.
- It aligns teams, resources, and risks to achieve successful system delivery.
Detailed Explanation
In the introduction, we learn that developing hardware systems isn't straightforward; it merges multiple fields like electrical engineering, mechanical engineering, and software development. Project management plays a crucial role in bringing all these different elements together. It helps to manage costs, maintaining quality, and completing projects on time through planning and tracking activities. By coordinating teams, managing resources, and being aware of risks, project management enables successful delivery of hardware systems.
Examples & Analogies
Think of project management as the conductor of an orchestra. Each musician (representing different domains like electrical, mechanical, and software engineers) plays their part, but without the conductor, the performance might be chaotic. The conductor ensures that everyone plays in harmony, stays on schedule, and contributes to a successful musical piece, much like project management in hardware development.
The Hardware Development Lifecycle (HDLC)
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Phase Description
1. Requirements Gathering: Define what the system must do (functional & non-functional)
2. System Design: Plan architecture, components, interfaces
3. Implementation: Develop schematics, PCB layout, firmware, mechanical parts
4. Integration & Testing: Assemble and verify hardware system functionality
5. Validation & Certification: Ensure system meets standards and stakeholder needs
6. Deployment & Release: Market and support lifecycle maintenance
Detailed Explanation
The Hardware Development Lifecycle (HDLC) outlines the steps taken in developing hardware systems. First, during 'Requirements Gathering', teams clarify what the hardware must accomplish. Then, in 'System Design', they sketch out the architecture and components needed. 'Implementation' follows, where actual schematics and physical parts are created. After assembling the components, 'Integration & Testing' happens to ensure everything works together properly. Next is 'Validation & Certification', which checks if the system meets necessary standards. Finally, during 'Deployment & Release', the system is launched and ongoing support is organized.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine building a car. First, you need to gather requirements like its size and features (Requirements Gathering). Then, you design the car's structure (System Design), and build it (Implementation). After putting it together and checking if it runs (Integration & Testing), you ensure it meets safety standards (Validation & Certification). Finally, you sell the car and provide service when needed (Deployment & Release). This sequence helps ensure a well-functioning final product.
Key Project Management Principles
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Principle Application
- Scope Definition: Identify deliverables and system boundaries clearly
- Time Management: Create schedules, Gantt charts, and milestones
- Resource Allocation: Assign people, tools, and budgets appropriately
- Risk Management: Anticipate and mitigate technical, timeline, or supply risks
- Communication: Establish status reports, meetings, and stakeholder updates
- Quality Assurance: Define processes to meet performance, safety, and reliability goals
Detailed Explanation
This section discusses vital principles crucial to effective project management in hardware development. 'Scope Definition' refers to clearly outlining what the project will deliver. 'Time Management' entails setting timelines and milestones to track progress. 'Resource Allocation' ensures the right people and tools are assigned effectively. 'Risk Management' involves identifying potential risks and planning how to address them. Effective 'Communication' keeps all stakeholders informed through reports and meetings. Finally, 'Quality Assurance' focuses on making sure that the product meets necessary performance and safety standards.
Examples & Analogies
Think of these principles as the foundational rules of a sports team. Just as a team defines its goals (scope), creates a game plan and practice schedule (time management), assigns players to specific positions (resource allocation), prepares for potential challenges (risk management), communicates strategies (communication), and strives for peak performance (quality assurance), a hardware development project relies on these principles to achieve success.
Project Planning Tools
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Tool Use
- Gantt Charts: Visualize project timeline and dependencies
- PERT/CPM Charts: Analyze project flow and critical paths
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS): Decompose the project into manageable parts
- Kanban Boards: Track tasks visually (e.g., Trello, Jira)
- RACI Matrix: Define roles: Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed
Detailed Explanation
Project planning tools enhance managing projects effectively. Gantt Charts help visualize timelines and show how tasks overlap. PERT/CPM Charts are utilized to analyze the flow of a project and identify critical tasks that could delay the entire project. The Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) helps break down the project into smaller, more manageable components. Kanban Boards facilitate task tracking visually, while the RACI Matrix clarifies roles within the project, ensuring everyone knows their responsibilities.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a chef planning a big wedding feast. They might create a timeline (Gantt Chart) to understand when each dish needs to be prepared. They would identify critical milestones like when to start cooking the main dish (PERT/CPM Chart). They can break down the preparations, listing all ingredients and steps needed for each dish (WBS). They might use a visual board to track tasks—like who is responsible for salads and desserts (Kanban Board). Finally, they clarify who manages which part of the feast to avoid confusion (RACI Matrix).
Key Concepts
-
Project Management: The application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to project activities.
-
HDLC: A series of phases necessary for developing hardware systems.
-
Risk Management: Proactive identification and mitigation of risks in project workflows.
-
Budget Management: Planning and control of project finances.
Examples & Applications
Using Gantt charts to visualize project schedules during the implementation phase.
Creating a risk register to track potential risks such as supply chain delays.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To manage our project with ease, we follow the steps, as it pleases. Define, design, build, test, deploy, in managing projects, we find joy!
Stories
Imagine a ship captain managing a fleet. They chart courses, assign roles, and anticipate storms, ensuring a safe and successful voyage, much like project managers navigate through phases and risks.
Memory Tools
Remember ‘S-T-R-C-P’ for Scope, Time, Resource, Communication, Planning in project principles.
Acronyms
ACRONYM
Align
Control
Risk
Organize
Network
Yield
Manage.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- HDLC
Hardware Development Lifecycle; phases of progression in hardware system development.
- Project Charter
Document that defines project objectives, scope, and stakeholders.
- Gantt Chart
Visual tool for scheduling project tasks over time.
- Risk Register
Document that tracks identified risks and their status.
- Earned Value Management (EVM)
Technique to measure project performance and progress.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
