Classification of Rainfall Data
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Time Scale Classification of Rainfall Data
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to explore how we can classify rainfall data based on time scales. We can look at it hourly, daily, monthly, or annually. Can anyone tell me why it's important to consider different time scales in rainfall data?

I think it helps in observing trends over time?

Exactly! By analyzing different time frames, we can identify patterns, like seasonal changes in rainfall. For instance, monthly data may show us how rainfall peaks during the monsoon.

But what about hourly data?

Good question! Hourly data can provide insights into sudden rain events, which are important for flood forecasting. So, remember the acronym ‘TIME’ to recall the types: T for Time scale, I for Individual hours, M for Monthly trends, and E for Annual totals.

So, using ‘TIME’ helps organize this information!

Yes! To summarize, different time scales help us adapt our strategies to manage water resources effectively.
Spatial Scale Classification
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let's discuss spatial scale. Rainfall data classification also involves point and areal rainfall. Can anyone explain the difference?

Point rainfall is like data from a single rain gauge, right?

Correct! While areal rainfall gives an average over a larger area, which is crucial for hydrological modeling. Remember the acronym ‘SPACE’: S for Spatial classification, P for Point data, A for Areal averages, C for Coverage, and E for Estimations.

Why would we use areal rainfall instead of point data?

Great question! Areal rainfall provides a better estimate for large-scale applications like irrigation planning, as it considers variations across the entire area.

So it helps us get a more comprehensive view of rainfall?

Exactly! To wrap up, understanding these classifications is essential for effective water resource management.
Format of Rainfall Data
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let's dive into how we can classify rainfall data based on its format. What are the two main types of data formats we might encounter?

Raw data and processed data?

Exactly! Raw data comes directly from rain gauges, while processed data includes summaries and trends that we've analyzed. Can anyone tell me why processed data is important?

It makes it easier to interpret and relay information, right?

Exactly! Processed data allows stakeholders to make decisions based on clear, accessible information. As a memory aid, think of 'FARM' for Formats: F for Formats, A for Analysis of raw, R for Resulting data processing, and M for Management decisions.

So, we need both formats to effectively manage rainfall data?

Yes! In summary, understanding the different formats helps us effectively communicate rainfall data to various audiences.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses the classification of rainfall data in terms of time scales (hourly, daily, monthly, annual), spatial scales (point vs. areal rainfall), and data formats (raw vs. processed). Understanding these classifications is essential for analyzing rainfall patterns and making informed decisions in water resource management.
Detailed
The classification of rainfall data is pivotal for understanding and operating within India's complex hydrological systems. Rainfall data can be categorized into three main types:
- Time Scale: Rainfall can be evaluated over different periods, including hourly, daily, monthly, and annual data, which helps in identifying patterns and trends in precipitation.
- Spatial Scale: This involves distinguishing between point rainfall (data collected at a specific location) and areal rainfall (average rainfall over a larger area), which is especially valuable in hydrological modeling.
- Format: Rainfall data appears in two major formats: raw data, which is collected directly from measuring instruments, and processed data, which includes statistical summaries and trends that aid in data interpretation.
This classification framework supports effective planning, decision-making, and management of water resources, ensuring that they meet the agricultural, domestic, and energy generation needs across India.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Time Scale Classification
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Rainfall data can be classified based on:
• Time Scale:
- Hourly, daily, monthly, annual
Detailed Explanation
Rainfall data is categorized according to the time over which precipitation is measured or aggregated. This classification includes:
- Hourly: Data that shows rainfall amounts measured every hour. It's useful for understanding short-term weather patterns.
- Daily: Total rainfall measured each day. This helps in analyzing daily weather conditions and planning accordingly.
- Monthly: The total rainfall summed up for each month. This format is useful for assessing seasonal patterns in rainfall.
- Annual: Aggregate data for the entire year, helping to evaluate long-term trends in precipitation.
Examples & Analogies
Think of rainfall data like the reports you receive from a fitness tracker. Just like it shows your activity over different periods (hourly steps, daily exercise, monthly summaries, and yearly progress), rainfall data provides insights over varying timeframes, helping you understand patterns.
Spatial Scale Classification
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Spatial Scale:
- Point rainfall vs areal rainfall
Detailed Explanation
This classification is about where the rainfall data is collected and how representative it is. It includes:
- Point Rainfall: This represents rainfall measured at a specific point using a rain gauge. It gives precise information for that exact location but may not represent surrounding areas.
- Areal Rainfall: This represents the average rainfall over a larger area, such as a district or a watershed, usually calculated using multiple rain gauge measurements. It's useful for understanding how rainfall affects broader regions, especially in agricultural planning.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine using a single thermometer to measure temperature in your room (point measurement) versus averaging temperatures from several thermometers placed around your neighborhood to understand the overall climate (areal measurement). This analogy highlights the difference in scope provided by each measurement type.
Format Classification
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Format:
- Raw data (from rain gauges)
- Processed data (statistical summaries, trends)
Detailed Explanation
The format classification of rainfall data indicates how the data has been presented or processed:
- Raw Data: This is the unprocessed data received directly from rain gauges, showing actual measurements, without any alterations or interpretations. It’s essential for detailed assessments but can be overwhelming without context.
- Processed Data: This includes data that have been summarized or analyzed to show trends and statistical information, making it easier for users to draw meaningful conclusions. Examples include monthly averages or annual totals, which provide insights without needing to sift through all the raw data.
Examples & Analogies
Consider watching a raw video of a sports game that shows every detail and moment, versus reading a post-game summary that highlights the key plays and scores. Just as the summary condenses information for easier understanding, processed data simplifies complex information for practical use.
Key Concepts
-
Time Scale: Classification of rainfall data based on intervals such as hourly, daily, monthly, and annual, critical for recognizing trends.
-
Spatial Scale: Differentiating rainfall data between point measurements and areal averages, essential for effective resource management.
-
Raw Data: Unprocessed data directly collected from rain gauges, essential for primary analysis.
-
Processed Data: Data that has undergone statistical analysis to provide clearer insights for decision-making.
Examples & Applications
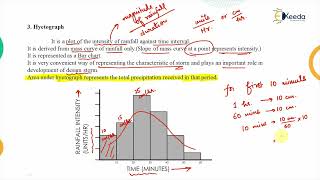
An example of time scale classification may involve plotting daily rainfall over a monsoon season to appreciate trends in precipitation.
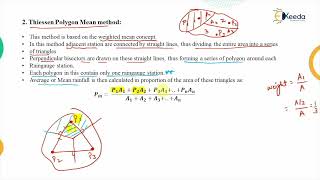
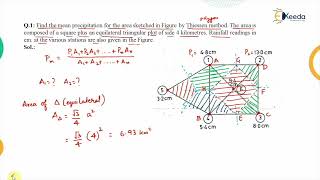
An example of spatial scale can be demonstrated through comparing point rainfall measurements from various rain gauges against the average rainfall calculated for a large catchment area.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
For rainfall data, time flies, measure hourly, daily, monthly, and finally raise our eyes!
Stories
Once, in a land where rainfall was plentiful, a wise old man classified it over time and space, helping crops flourish and rivers race.
Memory Tools
‘SPACE’ helps us remember: Spatial classification, Point data, Areal averages, Coverage, Estimations.
Acronyms
‘TIME’ stands for
Time scale
Individual hours
Monthly trends
and Epic annual totals.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Time Scale
The intervals at which rainfall data is collected and analyzed, including hourly, daily, monthly, and annual periods.
- Spatial Scale
The geographical context of rainfall data, distinguishing between point rainfall (specific location) and areal rainfall (average over a larger area).
- Raw Data
Data collected directly from rain measurement instruments, unprocessed and unfiltered.
- Processed Data
Statistical summaries, trends, or analyses derived from raw data for easier interpretation.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
