Rainfall Data Collection Agencies
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Rainfall Data Collection
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to discuss the agencies involved in collecting rainfall data in India. Can anyone name a major agency responsible for this?

Isn't it the India Meteorological Department or IMD?

Exactly! The IMD is the primary agency. It plays a critical role in meteorological data collection. What other agencies can you think of?

I remember hearing about the Central Water Commission.

Good! The CWC also collects and analyzes rainfall data. It's vital for managing water resources. Now, let's summarize—what agencies have we mentioned?

IMD and CWC.

Correct! Additionally, there's the State Meteorological Departments and CGWB. Let's keep those in mind as we explore more.
Instruments for Rainfall Measurement
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let's dive into the instruments used for rainfall data collection. What types of gauges do you think we might use?

I think there are non-recording and recording gauges?

Absolutely right! Non-recording gauges, like the Symons Rain Gauge, are often used for manual observations, whereas recording instruments provide ongoing data. Can you think of any examples of recording gauges?

What about the tipping bucket gauge?

Yes! The tipping bucket gauge is a common example. It automatically records the amount of rain. What other types do you remember?

There's also the weighing bucket gauge.

Correct! These instruments help us obtain accurate rainfall measurements, which are essential for data analysis.
Importance of Rainfall Data
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Why do you think collecting accurate rainfall data is important?

It helps with irrigation and agricultural planning, right?

Exactly! Precise rainfall data helps in planning for irrigation and water supply. Any other applications?

It also helps in disaster management, like predicting floods.

Spot on! Accurate rainfall data indeed aids in disaster preparedness and management. Can we list some other areas where this data is crucial?

Hydroelectric power generation, I suppose.

Right again! Overall, understanding rainfall data helps in planning and managing water resources effectively.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Rainfall data in India is collected by multiple agencies including the India Meteorological Department, the Central Water Commission, and various state departments. These organizations utilize different types of rain gauges, from non-recording to recording instruments, to ensure accurate data collection.
Detailed
Rainfall Data Collection Agencies
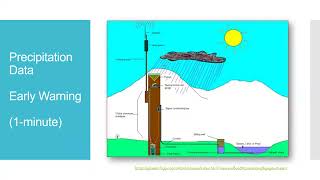
Rainfall data is crucial for managing water resources in India, and several agencies play a role in its collection and maintenance. The primary agency involved is the India Meteorological Department (IMD), which spearheads efforts to monitor and analyze rainfall patterns across the country. Other important agencies include the Central Water Commission (CWC), State Meteorological and Irrigation Departments, Central Ground Water Board (CGWB), as well as various Agricultural Universities and Research Institutes.
Instruments Used for Rainfall Data Collection:
Agencies employ a range of instruments to gather rainfall data:
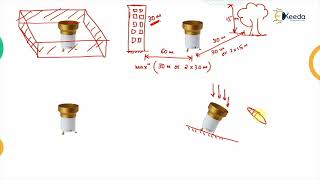
- Non-recording Rain Gauges such as the Symons Rain Gauge, widely used by the IMD.
- Recording Rain Gauges, which provide continuous data, including:
- Tipping bucket gauge
- Weighing bucket gauge
- Float-type gauge
These instruments are essential for generating accurate rainfall measurements, which can then be analyzed for effective water resource management.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Rainfall Data Collection
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Rainfall data in India is collected and maintained by several agencies:
- India Meteorological Department (IMD) – primary agency.
- Central Water Commission (CWC)
- State Meteorological and Irrigation Departments
- Central Ground Water Board (CGWB)
- Agricultural Universities and Research Institutes
Detailed Explanation
In India, the responsibility for collecting and managing rainfall data falls to various agencies. Each agency has a specific role:
- The India Meteorological Department (IMD) is the main agency, tasked with monitoring weather patterns and collecting precipitation data nationwide.
- The Central Water Commission (CWC) focuses on managing the country's water resources and ensuring sustainable usage.
- State Meteorological and Irrigation Departments work at the state level to monitor local weather and rainfall conditions.
- The Central Ground Water Board plays a crucial role in managing groundwater resources, which often depend on rainfall.
- Lastly, Agricultural Universities and Research Institutes conduct studies and perform research to support agricultural practices and policies based on rainfall data.
Examples & Analogies
Think of these agencies like a team of specialists in a city that monitors the weather: the IMD is like the city's weather center providing forecasts, while the CWC focuses on water bodies, similar to a city's water management department. Each plays a distinct but cooperative role in ensuring that the entire area is well-informed about rainfall and water resources.
Instruments Used for Rainfall Data Collection
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Instruments Used:
- Non-recording Rain Gauges
- Symons Rain Gauge (widely used by IMD)
- Recording Rain Gauges
- Tipping bucket gauge
- Weighing bucket gauge
- Float-type gauge
Detailed Explanation
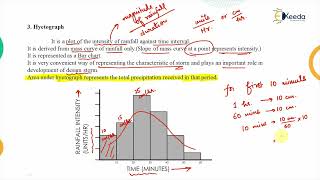
Rainfall data collection involves various types of instruments. Non-recording rain gauges, such as the Symons rain gauge, are traditionally used to collect rainfall by manually measuring the amount collected over a period.
- In contrast, recording rain gauges automate this process. There are several types:
- The tipping bucket gauge measures rainfall by tipping a bucket after a set amount of water collects, recording each tip.
- The weighing bucket gauge weighs the water collected, providing continuous data.
- Float-type gauges use a float that rises with the water level to measure rainfall continuously. Each type of gauge has its strengths and applications based on the need for accuracy and data logging.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a chef measuring ingredients for a recipe. A non-recording rain gauge is like a traditional measuring cup where you pour until you see the right amount. In comparison, the recording rain gauges are like a digital scale that continuously logs how much of an ingredient you have. This way, you get precise measurements without needing to keep checking manually.
Key Concepts
-
Rainfall Data Collection Agencies: Organizations such as the IMD and CWC responsible for collecting and analyzing rainfall data.
-
Types of Rain Gauges: Different instruments like non-recording and recording gauges are used to measure rainfall.
Examples & Applications
The India Meteorological Department (IMD) uses the Symons Rain Gauge to manually record rainfall, while the Tipping Bucket Gauge provides continuous automatic measurements.
The Central Water Commission (CWC) collaborates with various state departments to collect and interpret rainfall data for effective resource management.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
IMD and CWC, collecting data with glee; Symons and buckets, measuring rain, for water's gain!
Stories
Once in India, the IMD and CWC worked together to ensure no drop was missed; they measured rain with Symons gauges and tipping buckets to nourish land and prevent drought.
Memory Tools
Remember 'IMD's Reliable Rain Gathering' for the agencies involved.
Acronyms
IMD
Indian Meteorology Dominance
the lead in rain data collection.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- India Meteorological Department (IMD)
The primary agency responsible for meteorological data collection and analysis in India.
- Central Water Commission (CWC)
An agency tasked with coordinating water resource development and conservation in India.
- Symons Rain Gauge
A type of non-recording rain gauge widely used by the IMD.
- Tipping Bucket Gauge
A recording rain gauge that measures rainfall automatically by tipping a bucket when a specific amount of water is collected.
- Weighing Bucket Gauge
A type of recording rain gauge that measures rainfall by weighing the collected water.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
