Advanced Materials in IC Packaging
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Advanced Substrates
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to discuss advanced substrates in IC packaging. Can anyone tell me what a substrate does in an IC package?

Isn't it the base that helps connect the IC electrically and support it physically?

Exactly! Substrates provide both electrical connections and mechanical support. Now, we can categorize them into three types: ceramic, organic, and flexible. Let's start with ceramic substrates. Why are they often preferred for high-power applications?

Because they have high thermal conductivity and can resist high temperatures!

That's right! For example, aluminum oxide and aluminum nitride are popular ceramic materials. Now, who can explain the advantages of organic substrates?

They are usually lower in cost and have recently improved signal integrity and interconnect densities.

Great! Lastly, flexible substrates are important for which types of devices?

Wearable devices and anything that needs to bend or fit into curved shapes!

Exactly! Flexible substrates allow for innovative applications in flexible electronics. To summarize, advanced substrates include ceramic, known for thermal properties, organic for cost-effectiveness, and flexible for adaptability.
Thermal Interface Materials
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's move on to thermal interface materials, or TIMs. Why do you think TIMs are crucial in high-performance ICs?

They help with heat dissipation, so the IC doesn't overheat during operation.

Correct! Effective thermal management is essential for maintaining performance. What types of advanced TIMs are emerging?

I've heard about graphene and carbon nanotubes. They are said to have better thermal conductivity.

Exactly! These materials can significantly improve heat dissipation. Additionally, there are phase change materials, or PCMs. Can anyone explain how they work?

PCMs absorb heat when they change from solid to liquid, providing cooling when needed.

Well explained! So, to wrap up, TIMs, including advanced materials like graphene and PCMs, are vital for thermal management in high-performance ICs.
Advanced Solder Materials
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss advanced solder materials. What challenges are driving the need for enhanced solder materials in ICs?

With ICs becoming more complex, we need materials that can handle higher power levels and resist things like thermal cycling.

Exactly! That brings us to lead-free solder, which is now required due to regulations like RoHS. Can anyone name some common lead-free solder alloys?

I think tin-silver-copper alloys are popular.

That's right! And there’s ongoing research into even better alternatives. What about copper bumps? Why are they gaining popularity?

Because they have lower resistance and better thermal conductivity compared to gold bumps!

Exactly! In summary, as IC technology becomes more advanced, the need for enhanced solder materials like lead-free alloys and copper bumps continues to grow.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The content delves into various advanced materials necessary for modern IC packaging, including advanced substrates like ceramics and organics, innovative thermal interface materials for efficient heat management, and advanced solder materials that address increased power and reliability challenges in packaging technology.
Detailed
Advanced Materials in IC Packaging
Introduction
The advancements in semiconductor devices necessitate innovative materials in IC packaging. These materials must effectively handle thermal management, signal integrity, mechanical strength, and moisture resistance to meet the rising demands of performance and reliability.
Key Areas of Focus
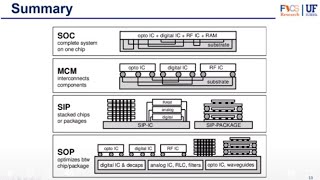
1. Advanced Substrates
Substrates serve as the foundation of IC packages and are vital for electrical connections and mechanical support. They are key in ensuring enhanced performance, and their types include:
- Ceramic Substrates: Such as Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3) and Aluminum Nitride (AlN), are favored in high-power applications due to superior thermal conductivity and high-temperature resistance.
- Organic Substrates: Materials like Polyimide and FR4 are cost-effective, with recent advancements improving signal integrity and interconnect density.
- Flexible Substrates: Essential for wearable and flexible electronics, these polymer-based substrates are lightweight and adaptable to curved surfaces.
2. Thermal Interface Materials (TIMs)
Effective heat management using TIMs is essential to keep high-performance ICs at safe operating temperatures. Notable TIMs include:
- Advanced TIMs: Emerging materials like graphene and carbon nanotubes show increased thermal conductivity compared to traditional epoxy or metal-based TIMs.
- Phase Change Materials (PCMs): These materials provide passive cooling during phase transitions, suitable for high-power ICs in mobile and power applications.
3. Advanced Solder Materials
The evolution of solder materials is critical as IC complexities increase. Key advancements include:
- Lead-Free Solder: Complying with regulations like RoHS, alloys like tin-silver-copper (SAC) are becoming standard, while researchers explore alternatives for better performance.
- Copper Bumps: Utilized in flip-chip packaging due to their lower resistance and superior thermal conductivity as compared to gold bumps.
Conclusion
The exploration of advanced materials in IC packaging is vital for meeting complex and rigorous performance demands. Whether through new substrates, TIMs, or solder innovations, these materials play a crucial role in the future of semiconductor technology.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Importance of Materials
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The development of new materials is crucial to meeting the performance and reliability demands of modern semiconductor devices. These materials are designed to address challenges such as thermal management, signal integrity, mechanical strength, and moisture resistance.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk emphasizes the significance of advanced materials in IC packaging. As technology evolves, semiconductor devices require materials that can handle increased performance needs, especially regarding heat management and connection reliability. Efficient thermal management ensures that devices do not overheat, which could lead to failures, while signal integrity ensures that the electronic signals transmitted within the device maintain their accuracy.
Examples & Analogies
Think of this like a high-performance sports car. Just as the car needs high-quality components to withstand high speeds and intense heat, semiconductor devices require advanced materials to function optimally in demanding environments.
Advanced Substrates
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The substrate is the foundation of the IC package, providing electrical connections and mechanical support. Advanced substrates offer improved thermal conductivity, signal integrity, and mechanical stability, enabling the performance of modern ICs.
● Ceramic Substrates: Ceramic materials such as aluminum oxide (Al2O3) and aluminum nitride (AlN) are commonly used in high-power applications due to their superior thermal conductivity and high-temperature resistance.
● Organic Substrates: Polyimide and FR4 (flame retardant 4) are widely used for lower-cost applications. Recent advancements in organic materials allow for better signal integrity and higher-density interconnects.
● Flexible Substrates: For wearable devices, flexible electronics, and bending applications, flexible substrates made from polymer-based materials are gaining popularity due to their lightweight nature and ability to be conformed to curved surfaces.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk highlights different types of advanced substrates used in IC packaging. Each substrate type serves a unique purpose based on application needs. Ceramic substrates excel in high-power scenarios due to their ability to conduct heat effectively and endure higher temperatures. Organic substrates are cost-effective yet provide strong technical performance. Flexible substrates are designed for modern applications where devices must conform to varying shapes, like wearables.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the different types of shoes we wear: sturdy boots are suitable for hiking (like ceramic substrates for high power), sneakers are great for comfort and everyday use (like organic substrates), and flexible sandals are perfect for warm weather (like flexible substrates for wearables). Each type of shoe serves its specific need, similar to how each substrate type supports various IC applications.
Thermal Interface Materials (TIMs)
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Effective thermal management is crucial for ensuring that high-performance ICs remain within safe operating temperatures. Thermal interface materials (TIMs) improve the thermal conductivity between the IC and heat sink, ensuring effective heat dissipation.
● Advanced TIMs: Graphene-based and carbon nanotube materials are emerging as highly efficient thermal conductors that can significantly improve heat dissipation compared to traditional epoxy or metal-based TIMs.
● Phase Change Materials (PCMs): PCMs absorb heat during the transition from solid to liquid, providing passive cooling in high-power ICs. These materials are being explored for use in mobile devices and power electronics.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk describes the role of thermal interface materials which are essential for effective heat escape from ICs. Advanced TIMs such as graphene enhance heat transfer more than standard materials, ensuring devices can operate at high performance without overheating. Phase change materials offer passive cool-down solutions by changing state when temperature rises, ideal for modern electronics like smartphones that generate significant heat.
Examples & Analogies
Think of TIMs like the coolant in a car. Just as coolant circulates to prevent the engine from overheating, TIMs facilitate heat movement away from the semiconductor components, ensuring they remain operational and safe, especially during heavy use.
Advanced Solder Materials
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
As ICs become more complex, the materials used for interconnects and soldering must be advanced to handle higher power levels and reduce the risk of failure due to thermal cycling and electromigration.
● Lead-Free Solder: With environmental regulations like RoHS, lead-free solder alloys such as tin-silver-copper (SAC) are used in IC packaging. However, there is ongoing research into alternative solder materials with lower melting points and improved strength.
● Copper Bumps: Copper bumps are increasingly being used in flip-chip packaging for their lower resistance and better thermal conductivity compared to traditional gold bumps.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk focuses on solder materials essential for IC connections. As semiconductor devices get more intricate, they need solder materials that can withstand more heat without failing. Lead-free options are now standard due to safety regulations, while copper bumps are becoming popular owing to their efficiency in transferring heat compared to older materials.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a bridge supporting heavier vehicles; as the cars become larger and more powerful, the materials used in the bridge's construction must be stronger and more resilient. Similarly, as ICs advance, the solder materials performing connections must also evolve to meet the increasing demands.
Key Concepts
-
Advanced Substrates: Vital for support and connectivity, including ceramic, organic, and flexible types.
-
Thermal Interface Materials: Essential for heat management, including advanced polymers and phase change materials.
-
Lead-Free Solder: Environmental compliance leads to the use of new alloys for improved performance.
-
Copper Bumps: Offer better conductivity than traditional gold bumps in flip-chip technologies.
Examples & Applications
Ceramic substrates like Aluminium Oxide (Al2O3) are used in high-power applications due to their thermal stability.
Graphene is being researched as an advanced thermal interface material due to its high thermal conductivity.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Substrates, oh they help us bond, with materials strong and beyond.
Stories
Once there was a thermal manager who wished to keep ICs cool. He used TIMs so well that he could rule without heat's downfall.
Memory Tools
COP - Copper = Outstanding Properties (for copper bumps).
Acronyms
STC - Substrate Types
Ceramic
Thermal
and Copper.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Advanced Substrates
Materials that provide the foundation for IC packages, such as ceramic, organic, and flexible materials.
- Thermal Interface Materials (TIMs)
Materials that enhance heat transfer between the IC and its heat sink to manage temperature effectively.
- LeadFree Solder
Solder alloy products that do not contain lead, complying with environmental regulations.
- Phase Change Materials (PCMs)
Materials that absorb heat during phase transitions to provide passive cooling.
- Copper Bumps
Interconnects made from copper, used in flip-chip packaging for their superior conductivity.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
