Advanced Topics in IC Packaging
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
3D IC Packaging
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will learn about 3D IC packaging. Can anyone tell me what they think it is?

Is it when circuits are stacked on top of each other to save space?

Exactly! 3D IC packaging allows for greater integration in a smaller footprint. What are some benefits you can think of?

Maybe it helps with speed and reduces power consumption?

Correct! The use of Through-Silicon Vias, or TSVs, enables faster signal transmission. Can anyone remember what TSVs do?

They create vertical connections between stacked ICs!

Right again! So, what applications might we find for 3D IC packaging?

Mobile devices and GPUs!

Great responses! In summary, 3D IC packaging enhances performance and miniaturization, making it vital for modern devices.
Fan-Out Wafer-Level Packaging (FOWLP)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's discuss Fan-Out Wafer-Level Packaging, or FOWLP. Can anyone describe what makes this method unique?

It spreads the electrical connections out for better compactness?

Correct! FOWLP allows for thinner packages with high interconnect density. What do you think are its benefits?

It should help with thermal conductivity, right?

Exactly! This also helps in reducing manufacturing costs due to automation capabilities. What can you think of its applications?

I believe it's used in mobile devices and IoT?

Spot on! So, as a group, let's summarize: FOWLP offers advanced packaging that's smaller, efficient, and cost-effective.
Advanced Materials in IC Packaging
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dive into advanced materials in IC packaging. Why do you think materials choice is crucial in this field?

Different materials help with heat and strength, right?

Absolutely! Materials like ceramic and organic substrates play vital roles. Can anyone give me an example of high-performance materials?

Graphene-based or carbon nanotube materials for thermal management?

Well said! These materials significantly improve thermal conductivity. Moreover, flexible substrates are becoming popular in wearable tech too. Why is flexibility important?

Because they need to fit on clothing and be comfortable!

Exactly! As we summarize, advanced materials in IC packaging are essential for ensuring performance, reliability, and application-specific requirements.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses the evolving landscape of IC packaging technologies, highlighting advanced materials, techniques, and trends that address the growing demand for smaller, faster semiconductor devices. Key topics include 3D ICs, FOWLP, and the significance of advanced substrates and thermal management solutions.
Detailed
Advanced Topics in IC Packaging
IC packaging technologies are rapidly evolving to meet the increasing demands for smaller, faster semiconductor devices. This section explores emerging trends in IC packaging that focus on higher performance, compact form factors, and reliable connections.
3D IC Packaging
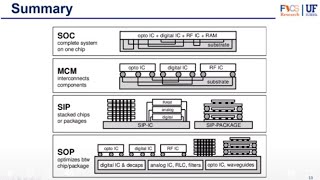
One major trend is 3D IC packaging, where multiple integrated circuits (ICs) are stacked to create a three-dimensional package. This approach enhances integration and minimizes space.
- Through-Silicon Vias (TSVs) create vertical connections through the silicon die, improving signal speed while reducing power consumption.
- Applications include GPUs, high-performance computing, and IoT devices.
Fan-Out Wafer-Level Packaging (FOWLP)
Another advanced technique is Fan-Out Wafer-Level Packaging (FOWLP), characterized by spreading out electrical connections over a larger area to create a thinner package without sacrificing performance.
- Benefits include improved thermal conductivity and manufacturing cost reductions.
- Commonly utilized in mobile devices and high-performance memory.
Advanced Materials and Thermal Management
The section also emphasizes the importance of advanced substrates, such as ceramic and organic materials, in enhancing thermal management, signal integrity, and mechanical strength.
- Recent innovations include Thermal Interface Materials (TIMs) and lead-free solder for high-power applications.
- Flexible and stretchable packaging technologies are also introduced to accommodate innovative designs in electronics, especially for wearable devices.
In summary, as the semiconductor industry continues to innovate, understanding these advanced IC packaging topics is essential for developing the next generation of high-performance electronic devices.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Advanced Topics in IC Packaging
Chapter 1 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
As the demand for smaller, faster, and more efficient semiconductor devices continues to grow, IC packaging technologies must evolve to meet these challenges. Advanced IC packaging techniques aim to address the need for higher performance, compact form factors, and reliable connections while enabling miniaturization, higher integration, and enhanced functionality in complex systems.
This chapter explores emerging trends in IC packaging technologies, as well as advanced materials and techniques used to meet the evolving needs of the semiconductor industry. We will discuss 3D packaging, fan-out wafer-level packaging (FOWLP), advanced substrates, and innovative materials that are shaping the future of IC packaging.
Detailed Explanation
This section introduces the concept of IC packaging, which refers to the methods used to enclose integrated circuits. It highlights the growing demand for smaller and more efficient devices, which pushes the need for advancements in packaging technologies. The section notes that modern packaging techniques are designed to provide better performance, compactness, and reliability for increasingly complex semiconductor devices.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to fit a powerful laptop into a small bag – the packaging needs to be smart to fit everything neatly while ensuring it remains functional. Just like a well-thought-out bag design can accommodate various items efficiently, advanced IC packaging techniques are designed to fit more components into smaller spaces without sacrificing their capabilities.
Emerging Trends in IC Packaging Technologies
Chapter 2 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Several new packaging techniques are being developed to address the challenges posed by increasingly complex and powerful ICs. These technologies aim to improve thermal management, signal integrity, power delivery, and interconnect density while reducing overall package size.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk discusses how new packaging methods are evolving to tackle the challenges that come with modern, complex integrated circuits. It emphasizes critical aspects such as managing heat (thermal management), maintaining the quality of signal transmission (signal integrity), ensuring power is efficiently delivered, and maximizing the number of connections in a limited area (interconnect density). These advancements help in achieving smaller and more efficient packaging solutions.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like organizing a closet. If you have more items than space, you must find ways to fit everything neatly while keeping it accessible. The advancements in IC packaging are like using clever organizers to make the most out of every inch, ensuring all components fit well and function optimally.
3D IC Packaging
Chapter 3 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
3D IC packaging involves stacking multiple ICs on top of each other to create a three-dimensional package. This technology allows for higher integration and smaller footprints, making it ideal for applications where space is limited.
Detailed Explanation
3D IC packaging is a technique where multiple integrated circuits are stacked vertically, optimizing space and improving performance. By using Through-Silicon Vias (TSVs) — vertical connections that facilitate communication between the stacked ICs — the overall size of the package is minimized while maintaining functionality and speed. This method is particularly useful in devices requiring compact structures, like smartphones.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a multi-layered cake; each layer represents a different function of the ICs. Instead of spreading everything out on a large table (2D), stacking the layers allows the cake to remain appealing and functional while taking up much less space — just like 3D packaging does with integrated circuits.
Fan-Out Wafer-Level Packaging (FOWLP)
Chapter 4 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Fan-out wafer-level packaging (FOWLP) is an advanced packaging technique where the IC is placed in a reconstituted wafer and the electrical connections are “fanned out” to a larger area. This provides a smaller, thinner package compared to traditional packaging methods while maintaining high interconnect density.
Detailed Explanation
FOWLP is a modern IC packaging method that enhances the integration density and thermal performance while significantly reducing the size of the package. The technique involves placing the IC in a reconstituted wafer with connections spread out (fanned) over a larger area, allowing for a thinner package without compromising on performance. This makes it particularly advantageous for devices in need of compact and efficient designs.
Examples & Analogies
Think about a smartphone’s circuit board like a bustling town with lots of streets (connections). FOWLP allows for many streets to accommodate increased traffic (more connections) without widening the entire town’s footprint, thus making it more efficient and functional in a smaller area.
Advanced Substrates
Chapter 5 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The substrate is the foundation of the IC package, providing electrical connections and mechanical support. Advanced substrates offer improved thermal conductivity, signal integrity, and mechanical stability, enabling the performance of modern ICs.
Detailed Explanation
Advanced substrates serve as the base for integrated circuits, playing a crucial role in holding the components together and conducting electrical signals efficiently. Different types of substrates, such as ceramic, organic, and flexible substrates, are designed for various applications depending on the requirements of heat management, signal integrity, and flexibility. For instance, ceramic substrates are ideal for high-power applications due to their thermal properties, while flexible substrates are used for wearable technology.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the substrate as the foundation of a house; just as a strong foundation supports the entire structure and keeps it stable, advanced substrates support and enhance the performance of electronic devices, ensuring they operate reliably and effectively.
Thermal Interface Materials (TIMs)
Chapter 6 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Effective thermal management is crucial for ensuring that high-performance ICs remain within safe operating temperatures. Thermal interface materials (TIMs) improve the thermal conductivity between the IC and heat sink, ensuring effective heat dissipation.
Detailed Explanation
Thermal Interface Materials (TIMs) play a significant role in managing heat in high-performance integrated circuits. They are used to enhance the heat transfer between the ICs and heat sinks, preventing overheating and ensuring optimal operating temperatures. Innovations in TIMs, like graphene and carbon nanotube materials, significantly boost heat dissipation capabilities compared to traditional materials, maintaining performance and reliability in advanced circuits.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a person sweating on a hot day trying to cool down. TIMs function like a cooling cloth that absorbs and spreads heat away from the body, helping stay cool — similarly, TIMs absorb heat from ICs, preventing them from becoming too hot and maintaining their efficiency.
Advanced Solder Materials
Chapter 7 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
As ICs become more complex, the materials used for interconnects and soldering must be advanced to handle higher power levels and reduce the risk of failure due to thermal cycling and electromigration.
Detailed Explanation
With the rise in complexity of integrated circuits, the materials used for soldering must evolve to withstand higher power levels and thermal changes. Traditional solder materials are being replaced by more advanced options like lead-free solder and copper bumps, which provide lower resistance and improved heat conductivity. These advancements are essential to ensure reliability and performance in high-power applications.
Examples & Analogies
Think of solder as the glue that holds together important connections in an electrical circuit. Just like you would use a stronger glue to hold heavier items, advanced solder materials are designed to support the increased demands of modern ICs, making them more robust and reliable.
Key Concepts
-
3D IC Packaging: A method to stack multiple ICs to reduce size and improve performance.
-
Fan-Out Wafer-Level Packaging: A technique that allows high interconnect density in a thinner format.
-
Advanced Materials: Includes substrates and TIMs that enhance performance, reliability, and assembly processes.
-
Flexible Packaging: Specially designed materials that cater to wearable and stretchable electronics.
Examples & Applications
Example 1: In mobile devices, 3D IC packaging is crucial for integrating multiple functionalities in a compact form factor.
Example 2: FOWLP is used in many IoT applications, providing a balance between size and performance.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Stack it high, don't be shy, 3D ICs reach for the sky!
Stories
Imagine a city where buildings (ICs) grow upward (3D), connecting through secret tunnels (TSVs) for quick transport (signals).
Memory Tools
FOWLP - Forgetting Overly Wide Layers of Packaging.
Acronyms
TIM - Thermal Interface Materials, to remember as 'Temperature Is Managed.'
Flash Cards
Glossary
- 3D IC Packaging
A packaging technique that involves stacking multiple integrated circuits on top of each other to enhance integration and save space.
- ThroughSilicon Vias (TSVs)
Vertical interconnects that pass through the silicon die to facilitate electrical connections between stacked ICs.
- FanOut WaferLevel Packaging (FOWLP)
An advanced packaging method that spreads electrical connections to create a thinner package while maintaining high interconnect density.
- Thermal Interface Materials (TIMs)
Materials that improve thermal conductivity between ICs and heat sinks, promoting effective heat dissipation.
- LeadFree Solder
Solder alloys that do not contain lead, often used in IC packaging to meet environmental regulations.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
