Factors Affecting the Climate of India
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Latitude
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's start by looking at latitude. India is crossed by the Tropic of Cancer. Can anyone tell me how this affects our climate?

I think it means northern India is subtropical and southern India is tropical?

Exactly, Student_1! The latitude essentially divides India into two climatic zones. Remember, 'Tropic = Temperature'. So, subtropical areas are generally more extreme in temperature variation than tropical regions.

What does that mean for the people living in those areas?

Great question, Student_2! The climate influences agricultural practices, lifestyle, and even clothing choices. Warmer tropical areas may have more diverse crops compared to the subtropical north.

So, latitude really sets the stage for climate fundamentals?

Precisely! Latitude is a primary factor in determining the overall climate in India.

In summary, latitude is fundamental in shaping the climatic zones of India, drastically influencing agricultural practices, human habitation, and local economies.
Altitude
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s discuss altitude. How does being higher up in the mountains affect climate?

Higher places are usually colder, right?

Correct, Student_4! In fact, the Himalayas act as a barrier to cold winds from Central Asia, which helps keep northern India warmer. What else can you infer from this?

So, places at higher altitudes like those in the Himalayas would be colder, and maybe have different weather conditions?

Exactly! The altitude leads to lower temperatures and can also affect precipitation. Areas varying in altitude will show diverse climate patterns. Remember, 'high-up = chilly climes'.

Do these altitude changes impact local agriculture too?

Absolutely, Student_2! Different altitudes support various crops and farming practices.

To recap, altitude significantly influences climatic conditions and weather patterns by reducing temperatures and affecting agricultural potential.
Distance from the Sea
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's talk about distance from the sea. How does it play a role in climate?

I think coastal areas are milder compared to places further in?

Correct again, Student_3! Coastal areas like Mumbai and Chennai have a maritime climate, with less temperature variation. What is the opposite of that?

Interior areas experience more extreme weather patterns, right?

Precisely! They experience a continental climate leading to hotter summers and colder winters.

Got it! The sea moderates the temperature near coastlines.

Exactly! To summarize, the distance from the sea causes climate variations, thus being crucial for predicting weather and agricultural outputs.
Relief Features
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s discuss relief features now. How do mountains and hills affect the climate?

Mountains block certain winds, right? Like the Himalayas?

Exactly! The Himalayas intercept cold winds and also trap monsoon winds, leading to heavy rainfall in certain areas. Can anyone think of how much rainfall is influenced by these features?

The Western Ghats shape rainfall in the Western coastal region?

Correct! The Western Ghats influence the distribution of rain, helping lush vegetation grow in regions like Kerala.

So, relief features create distinct climate zones too?

Absolutely right! They shape local climates, affecting ecosystems and agricultural outputs.

In summary, relief features like mountains significantly shape weather patterns and climate zones, affecting rainfall distribution across India.
Wind and Pressure Systems
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let's look at wind and pressure systems. Can anyone explain their significance?

They control weather patterns based on temperature and pressure differences?

Exactly! High pressure over Central Asia during winter pushes air into India. And what about in summer?

Southwest monsoon winds bring heavy rains during summer?

Right! These winds play a crucial role in determining the monsoon. Can anyone tell me why monsoon is important?

It's essential for agriculture in India!

Yes, that's correct! The success of crops heavily relies on the timing and intensity of these winds and the rains they bring.

To summarize, wind and pressure systems influence climate significantly, shaping weather patterns and impacting agriculture.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The climate of India is significantly shaped by latitude, altitude, distance from the sea, relief features, and wind and pressure systems. Each of these factors plays a vital role in determining the temperature, precipitation, and seasonal variations across the country.
Detailed
Factors Affecting the Climate of India
Understanding the climate of India requires an examination of several key factors.
1. Latitude: The Tropic of Cancer divides India into subtropical northern regions and tropical southern regions, affecting temperature and moisture availability.
2. Altitude: The Himalayas serve as a barrier to cold winds from Central Asia, maintaining warmer temperatures in northern India while higher altitudes experience cooler weather.
3. Distance from the Sea: Coastal areas like Mumbai and Chennai enjoy a moderate climate due to their proximity to the sea, whereas interior areas experience more extreme temperatures due to a continental climate.
4. Relief Features: Mountain ranges like the Himalayas block cold winds and influence monsoon patterns, while the Western Ghats play a crucial role in rainfall distribution.
5. Wind and Pressure Systems: The presence of high pressure in Central Asia during winter leads to variable weather patterns, and the southwest monsoon winds are vital for bringing heavy rainfall in summer.
These factors collectively shape the distinct climate patterns observed across India.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Latitude
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Latitude
● The Tropic of Cancer passes through the middle of India.
● Northern India: Subtropical climate
● Southern India: Tropical climate
Detailed Explanation
Latitude plays a crucial role in determining the climate of India. The Tropic of Cancer, an imaginary line located at 23.5 degrees north of the Equator, passes through the middle of India. This positioning affects the temperatures and climate types across the country. Northern India generally experiences a subtropical climate, characterized by hot summers and cold winters. In contrast, southern India, which is closer to the equator, has a tropical climate, marked by warm temperatures year-round and a significant monsoon influence.
Examples & Analogies
Think of latitude like the position of a light bulb in a room. The closer you are to the bulb (the equator), the warmer and brighter it is. Just like in a room, southern India gets more 'light' and warmth compared to northern India.
Altitude
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Altitude
● The Himalayas act as a barrier to cold Central Asian winds, keeping northern India warmer.
● Higher altitudes experience lower temperatures.
Detailed Explanation
Altitude refers to the height above sea level, and it significantly impacts climate. In India, the Himalayas serve as a natural barrier that prevents cold winds from Central Asia from moving into northern India, thereby keeping the region warmer than it would be otherwise. On the other hand, areas at higher altitudes, such as those in the Himalayas themselves, experience lower temperatures as the air gets thinner and less able to hold heat. Consequently, climate varies considerably with altitude.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine climbing a mountain. As you go higher, it gets colder just like how the air on top of a mountain is cooler than at sea level. The Himalayas act like a gigantic blanket for northern India, blocking out the cold from the north.
Distance from the Sea
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Distance from the Sea
● Coastal areas (Mumbai, Chennai) have moderate or maritime climate.
● Interior areas (Delhi, Nagpur) have continental climate with greater extremes.
Detailed Explanation
The proximity to the sea has a substantial effect on the climate of different regions in India. Coastal areas such as Mumbai and Chennai enjoy a maritime climate, which means their weather is generally moderate, with milder temperatures and more humidity throughout the year. In contrast, regions located further inland, like Delhi and Nagpur, experience a continental climate characterized by significant temperature variations; they can have scorching summers and chilly winters compared to their coastal counterparts.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how a beach day often feels cooler than a hot day in the desert. Just like how the ocean breeze keeps beaches moderate, the sea influences the climate around coastal towns in India, while the inland regions feel the heat without the cooling effects of the ocean.
Relief Features
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Relief Features
● The Himalayas block cold winds and trap monsoon winds.
● Western Ghats influence rainfall distribution.
Detailed Explanation
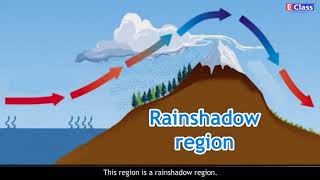
Relief features, or the physical geography of an area, can significantly influence its climate. The great Himalayas act not just as barriers to cold winds but also help in retaining monsoon winds that bring rain. Additionally, the Western Ghats, which run parallel to the western coast, also play a crucial role in attracting and distributing rainfall. Areas on the windward side of these mountains receive heavy rainfall, whereas the leeward side may remain dry, showcasing the impact of topography on climate patterns.
Examples & Analogies
Think about a barrier like a wall in a wind tunnel. The wall blocks some wind and alters how it flows. Similarly, the Himalayas act like walls against cold winds and help 'catch' rain clouds, leading to wet conditions on one side and drier conditions on the other side.
Wind and Pressure Systems
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Wind and Pressure Systems
● Presence of high pressure over Central Asia in winter.
● Southwest monsoon winds in summer bring heavy rainfall.
Detailed Explanation
Wind and pressure systems play a vital role in influencing the climate of India. In winter, a high-pressure system established over Central Asia affects weather patterns, stabilizing conditions in the region. As the seasons change, the southwest monsoon winds emerge in summer, moving in from the Indian Ocean and leading to heavy rainfall across most of the country. This monsoon is the lifeblood for Indian agriculture and significantly shapes the overall climate during this period.
Examples & Analogies
Consider blowing air into a balloon. When the pressure inside the balloon builds up enough, it will pop and send air everywhere. Similarly, the pressure systems in the atmosphere can create wind patterns that result in heavy rains, crucial for replenishing the earth.
Key Concepts
-
Latitude: Influences climate zones through temperature variation.
-
Altitude: Affects temperature and precipitation due to elevation.
-
Distance from Sea: Coastal areas have moderate climates, whereas inland areas experience extremes.
-
Relief Features: Mountains influence rainfall patterns and temperature through obstruction.
-
Wind Systems: Control seasonal and weather changes significantly in India.
Examples & Applications
The Himalayas blocking cold winds keeps northern India warmer.
Mawsynram in Meghalaya receives that highest rainfall due to its orographic features and position.
Coastal cities like Mumbai have less temperature variation due to their maritime climate.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Latitude divides with a line, tropical highs and subtropics incline.
Stories
Once upon a time, high up in the Himalayas, the cold winds couldn't reach the warm valleys, which thrived with life.
Memory Tools
L.A.D.W. - Latitude, Altitude, Distance from Sea, Wind systems for recalling climate factors.
Acronyms
CLIMATE - Climate Layers In Mountains and Terrain Effects, for remembering climatic influences.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Latitude
The geographical coordinate that specifies the north-south position on the Earth’s surface.
- Altitude
The height of an object or point in relation to sea level.
- Maritime Climate
A climate influenced by the proximity to the sea, typically with moderate temperatures.
- Continental Climate
A climate characterized by more extreme temperature differences between summer and winter.
- Relief Features
The physical geography features, such as mountains and valleys, that influence climate.
- Wind and Pressure Systems
Atmospheric pressure conditions and wind movements that impact weather patterns.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
