Southwest Monsoon Season – June to September
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to the Southwest Monsoon
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will dive into the Southwest Monsoon Season, which occurs from June to September. Can anyone tell me what happens during this season?

I think it rains a lot during this time!

Exactly! The Southwest Monsoon brings heavy rainfall to most parts of India. This is largely due to winds that come from the Indian Ocean. Can anyone remember the two branches of these winds?

There’s the Arabian Sea branch and the Bay of Bengal branch!

Perfect! Both branches significantly influence the rainfall patterns across India. To remember these, think of **A-B-C**: **A**rabian, **B**ay, and **C**louds for the rain.
Impact of Topography on Rainfall
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's discuss how topography plays a role in the monsoon rains. Particularly, how do you think the Western Ghats affect rainfall?

Maybe the mountains make it rain more?

Great thinking! The Western Ghats cause **orographic rainfall**. This means that as moist air rises over the mountains, it cools and releases rain. Can anyone recall what we call this process?

Orographic rainfall!

Right! That concept is key when studying monsoons. Just remember, as the saying goes: 'Mountains lift, skies give!'
Significance of the Southwest Monsoon
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, why do we need to understand the Southwest Monsoon, especially in terms of its impact on agriculture?

Because many farmers depend on the rain for their crops!

Exactly! The monsoon is crucial for agriculture since a majority of Indian farmers rely on monsoon rains for irrigation. However, what happens if there is a monsoon failure?

That could lead to droughts and crop failures, right?

Yes, and it's a significant concern for the economy. To help remember, think of 'Rain means Grain.' If farmers want a good harvest, timely monsoon rains are essential!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
During the Southwest Monsoon Season, the country experiences substantial rainfall, primarily affected by two branches of monsoon winds: the Arabian Sea branch and the Bay of Bengal branch. The region's topography, especially the Western Ghats, significantly influences rainfall distribution through orographic rainfall.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
The Southwest Monsoon Season stretches from June to September and is a critical period in India’s climatic calendar. The season commences with the onset of monsoon winds originating from the Indian Ocean, which gives rise to heavy rainfall across most parts of the country. This season is notably divided into two main branches: the Arabian Sea branch and the Bay of Bengal branch.
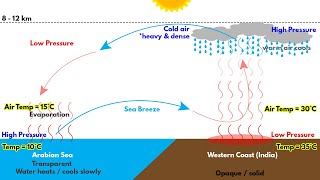
The Arabian Sea branch primarily affects the western coast, bringing substantial rains to states like Kerala and Maharashtra, while the Bay of Bengal branch influences the eastern regions, impacting states such as Odisha and West Bengal.
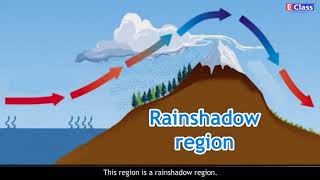
A significant aspect of the monsoon phenomenon is the orographic rainfall experienced along the Western Ghats. As moist air ascends over these mountains, it cools and condenses, resulting in heavy precipitation on the windward side. The intricate relationship between these wind patterns and the region's topography is crucial in determining rainfall distribution during this season. Understanding the dynamics of the Southwest Monsoon is essential due to its significant impact on agriculture, water supply, and local economies.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Onset of Monsoon Winds
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Onset of monsoon winds from the Indian Ocean.
Detailed Explanation
The southwest monsoon season marks the arrival of monsoon winds, which originate from the Indian Ocean. These winds are crucial for bringing rainfall to various parts of India. The onset typically begins around June and continues until September, representing a significant time for agriculture and water supply across the country.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a giant sponge soaking up water. When the winds blow from the Indian Ocean, they carry a lot of moisture, similar to how a sponge holds water. When the winds reach the land, they release this moisture, leading to heavy rain, just like a sponge spilling out the collected water.
Heavy Rainfall in Most Parts
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Causes heavy rainfall in most parts.
Detailed Explanation
The southwest monsoon is responsible for heavy rainfall across most regions of India. The amount of rainfall varies by location, but overall, it is a vital season for agricultural activities as it replenishes groundwater and supports crop growth. The precipitation also affects rivers, lakes, and other water bodies, ensuring they are filled for the dry months that follow.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the monsoon as a generous friend who shares water from their overflowing well. Just like how crops thrive with this fresh water, farmers depend on the monsoon rains to grow the food we eat, making the season an essential part of the agricultural calendar.
Branches of Monsoon
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Divided into:
○ Arabian Sea branch
○ Bay of Bengal branch
Detailed Explanation
The southwest monsoon is divided into two main branches: the Arabian Sea branch and the Bay of Bengal branch. The Arabian Sea branch enters India from the west and brings rain to states like Maharashtra and Gujarat. Meanwhile, the Bay of Bengal branch enters from the east and affects regions like Odisha and West Bengal. Together, these branches ensure that rainfall is distributed across diverse areas, although some regions may receive more rainfall than others.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of the two branches as two rivers flowing from different directions towards the same destination. Just like a river brings life and sustenance to the land it flows through, both branches of the monsoon are essential for providing the much-needed water to different parts of India.
Orographic Rainfall along the Western Ghats
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Orographic rainfall along the Western Ghats.
Detailed Explanation
Orographic rainfall occurs when moist air is forced to rise over the Western Ghats, a mountain range located along India's west coast. As the air rises, it cools and condenses, resulting in significant rainfall on the windward side of the mountains. This phenomenon explains why regions like Kerala and Karnataka receive abundant rainfall, while the leeward side may experience drier conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a car driving up a hill on a hot day. As the car climbs, the air gets cooler, causing condensation on the windshield. Similarly, the air moving over the Western Ghats cools as it rises, leading to heavy rains in the area. This is why the Western Ghats are lush and green during the monsoon season.
Key Concepts
-
Southwest Monsoon: A key seasonal rain period in India.
-
Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal Branches: The two branches of monsoon winds.
-
Orographic Rainfall: A key process influencing rainfall amounts in hilly areas.
Examples & Applications
The heavy rains that flood Mumbai each year during the monsoon demonstrate the power of the Arabian Sea branch.
Kerala experiences some of the heaviest rainfall during the Southwest Monsoon, crucial for its agricultural practices.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Monsoon rains drench the land, from June to September, they are grand!
Stories
Imagine a farmer waiting anxiously for the clouds to gather. When the Southwest Monsoon arrives, it brings life to his fields, just like a magician waving a wand to make everything bloom again.
Memory Tools
To remember the branches: Arabian, Bay, and Rain. Just think of 'A-B-R' for rain!
Acronyms
M.O.R.E - Mountains, Orographic, Rainfall, Effect. This shows how mountains affect the rainfall during the monsoon.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Southwest Monsoon
A seasonal wind pattern originating from the Indian Ocean, bringing heavy rainfall from June to September.
- Arabian Sea Branch
One of the two main monsoon wind branches that brings rainfall to the western coast of India.
- Bay of Bengal Branch
The second monsoon wind branch that affects eastern coastal regions of India.
- Orographic Rainfall
Rainfall that occurs when moist air is forced to rise over a mountain range, leading to cooling and condensation.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
