Relief Features
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
The Role of the Himalayas
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to examine how the Himalayas influence the climate. How do you think mountains can affect weather patterns?

I think they block certain winds?

Exactly! The Himalayas act as a barrier to cold winds coming from Central Asia, keeping northern India warmer during winter. This is a classic example of **orographic effects** where mountains alter air movement.

So without the Himalayas, would it be colder in India?

That's right! Without them, northern India would probably experience much colder winters. Remember, mountains can create a **climatic divide**!
Influence of the Western Ghats
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's shift our focus to the Western Ghats. Can anyone tell me how they might affect rainfall in India?

They probably hold back the rain.

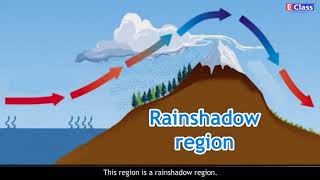
Exactly! The **Western Ghats** block monsoon winds, causing heavy rainfall on their western side while creating dryer conditions on the east. This phenomenon is known as the **rain shadow effect**.

Does that mean places like Mumbai get a lot of rain?

Correct! Places like Mumbai receive heavy rainfall because they are on the windward side of the Ghats. This connection between topography and moisture is crucial to understanding India's climate.
Connecting Relief and Climate
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

How can we summarize the impact of relief features on India's climate?

They change how cold or warm it is and how much rain falls?

Exactly! Relief features like the Himalayas and Western Ghats dramatically shape temperature and precipitation patterns. Can anyone think of policies or practices that might arise from this knowledge?

Maybe focusing agriculture in areas with more rainfall?

That's a fantastic application! Knowing these certain regions receive more water can help in agricultural planning. This knowledge is essential for farming, resource management, and disaster preparedness.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore how India's relief features, especially the Himalayas and Western Ghats, shape the climate by blocking cold winds and influencing rainfall distribution, affecting both temperature and precipitation across the country.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
The relief features of a region significantly influence its climate. In India, the most prominent relief feature is the Himalayas, which serve as a barrier against cold winds from Central Asia. By blocking these winds, the Himalayas help maintain a warmer climate in northern India during winter. Additionally, the Western Ghats play a crucial role in rainfall distribution across the country. They trap the southwest monsoon winds, leading to heavy rainfall on the western coast. In contrast, areas on the leeward side, such as parts of the Deccan Plateau, experience significantly less rainfall, creating a rain shadow effect. Understanding these relief features is key to analyzing India's overall climate patterns.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
The Himalayas and Cold Winds
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● The Himalayas block cold winds and trap monsoon winds.
Detailed Explanation
The Himalayas, a major mountain range in India, create a physical barrier that blocks cold winds coming from Central Asia. This protection helps keep the northern regions of India relatively warmer during the winter compared to areas further north. Additionally, the mountains play a crucial role in trapping monsoon winds, which leads to heavy rainfall in the region when the monsoon season arrives.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a tall wall that prevents a cold breeze from reaching your warm house. Similarly, the Himalayas act like that wall, allowing the warmth from the Indian subcontinent to stay in and keeping the cold winds out. When the summer monsoon arrives, these mountains also help hold in the moisture, creating rain—similar to how a sponge absorbs water.
Influence of the Western Ghats
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Western Ghats influence rainfall distribution.
Detailed Explanation
The Western Ghats are another important mountain range that significantly affect the climate of India, particularly in terms of rainfall distribution. These mountains intercept moist winds coming from the Arabian Sea. As the winds rise over the Western Ghats, they cool and condense, leading to heavy rainfall on the windward side. However, on the leeward side, the rainfall drastically decreases, creating a rain shadow effect.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the Western Ghats like a large barrier where rainclouds hit and release rain on one side, much like how a sponge releases water when squeezed. On the other side, the sponge dries out. This is why areas on the western side of the Ghats receive a lot of rain while the eastern side remains drier.
Key Concepts
-
Orographic Effect: The influence of mountains on weather patterns, especially precipitation.
-
Rain Shadow Effect: Describes the dry conditions typically found on the leeward side of mountains.
Examples & Applications
Mawsynram in Meghalaya receives heavy rainfall due to its location near the Western Ghats, while nearby regions in the rain shadow receive significantly less.
Delhi, being on the leeward side of the Himalayas, experiences different climatic conditions than regions directly influenced by the mountains.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Himalayas so tall and grand, block the cold from our land.
Stories
Once upon a time, there were mountains named the Himalayas that protected a beautiful land from the biting cold winds. As they stood tall, they kept the winters mild, and all the people thrived.
Memory Tools
Remember 'Himalayas Keep Warm' (H in Himalayas for 'Hold' the cold winds back).
Acronyms
GWB
Great Western Block (for Western Ghats blocking the rain).
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Orographic Rainfall
Rainfall that occurs when moist air is forced to rise over mountains, resulting in precipitation.
- Rain Shadow Effect
A phenomenon where one side of a mountain range receives a lot of rain while the other side remains dry.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
