Introduction to Climate of India
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Defining Weather and Climate
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Good morning, class! Today we will start by defining two key concepts: weather and climate. Can anyone tell me what the difference is between the two?

Weather is what we experience daily, right? Like if it's rainy or sunny.

Exactly, that’s a great start! Weather refers to the atmospheric conditions over a short period, which can change rapidly. Now, how about climate?

Is climate like the average weather over many years?

Yes, approximately over 30 to 35 years! So, climate represents the long-term patterns of temperature and precipitation in a region. Remember this: 'Weather changes, climate remains'.

So, in India, how does that play out?

Good question! India experiences a **monsoon-type climate**, which means we have distinct wet and dry seasons influenced by several factors.

What are these factors?

We will get to that shortly. Just keep in mind that understanding weather and climate helps us appreciate the climatic diversity in India.
Monsoon-Type Climate
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's talk about the climate in India itself. Who remembers what kind of climate India has?

A monsoon-type climate!

That's correct! The monsoon is characterized by distinct wet and dry periods. Can anyone tell me what influences this monsoon climate?

Location, relief, and the Indian Ocean, right?

Exactly! India's geographical factors, like its location along the Tropic of Cancer and the presence of the Himalayas, significantly impact weather patterns and rainfall distribution. Let’s remember: **“Moisture from the ocean meets the land’s elevation”**, which equals rainfall!

And the oceans help in maintaining that climate?

Yes, coastal areas have a more moderate climate owing to their proximity to the sea, in contrast to the extremes faced in the interior regions.
Factors Influencing Climate
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

In our previous session, we touched on the basic influences on India’s climate. Now, let's delve into them in detail, starting with latitude.

How does latitude affect climate, specifically in India?

Great question! Latitude plays a key role as the Tropic of Cancer runs through the middle of India. This results in varying climates: tropical in the south and subtropical in the north. Let’s use a mnemonic to remember: **“Top is Tropical, Bottom is Subtropical”** to grasp these concepts!

What about altitude, sir?

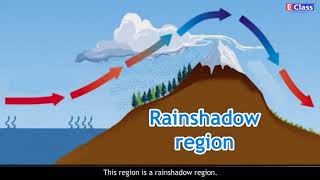
Altitude contributes significantly as well! The Himalayas protect Northern India from cold winds, keeping it warmer, while higher altitudes generally mean lower temperatures. This is another critical factor we're covering, remember: **“High equals Cold”**.

What about the distance from the sea?

Excellent! Coastal areas, like Mumbai and Chennai, have a maritime climate, while inland regions experience continental climates. Knowing this, we can appreciate the diversity in climate across India!
Significance of Climate
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Reflecting on everything we've discussed, how do you think India's climate affects daily life and economic activities?

Agriculture would depend on monsoon rains, for sure.

Absolutely! Agriculture is intricately linked to our climate. Understanding climate helps manage resources better. Remember, **“Rain equals Harvest”** in this context!

And if the monsoons fail?

That would lead to droughts, impacting hydroelectric power and water supply! The climate, thus, plays a pivotal role in the economy.

It's crucial for industries too, right?

Yes, industries are also heavily dependent on climate variables. Today’s take-home message: knowing our climate is key to making informed decisions in agriculture, industry, and resource management.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The climate of India, characterized by distinct wet and dry seasons, is significantly influenced by factors such as location, relief, and proximity to the Indian Ocean. Understanding the difference between weather and climate is crucial for grasping the broader climatic characteristics of the nation.
Detailed
Introduction to Climate of India
This section defines weather and climate, emphasizing the distinction between short-term atmospheric conditions (weather) and long-term averages (climate). India is noted for its monsoon-type climate, which exhibits marked wet and dry seasons that are crucial for agriculture and water resources.
Key factors influencing the climate include:
- Location: India spans various latitudes, ranging from tropical in the south to subtropical in the north, underlining the Tropic of Cancer's significance.
- Relief: The Himalayas play a critical role by blocking cold winds and affecting precipitation patterns, while other ranges influence local rainfall.
- Distance from the Sea: Coastal regions experience a milder climate compared to the more extreme conditions found in inland areas.
Overall, understanding these components provides insight into the complexities of climate across India.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Weather and Climate
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Weather: Atmospheric conditions over a short period (day-to-day).
● Climate: Average weather conditions over a long period (30–35 years).
Detailed Explanation
Weather refers to the atmospheric conditions over a short time frame, such as a day or week. It can include things like temperature, humidity, and precipitation. For example, it might be sunny today but rainy tomorrow. Climate, on the other hand, is the average of these weather conditions over a much longer period, typically about 30 to 35 years. This means that climate helps us understand the overall patterns of weather we might expect in a certain area, like how it usually is during summer or winter.
Examples & Analogies
Think of weather as a single moment in time, like snapping a picture. Climate is like a photo album that shows how things change over many years. Just as you might notice different seasons in your photo album, you can notice seasonal weather patterns by studying climate.
Monsoon Climate of India
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● India has a monsoon-type climate, characterized by distinct wet and dry seasons.
Detailed Explanation
The climate in India is primarily monsoon, meaning it experiences significant seasonal changes that include both wet and dry periods. The wet season generally corresponds to the monsoon rains that come from the Indian Ocean, bringing water and nourishment to many crops. The dry season, often referred to as the 'non-monsoon' season, sees less rainfall and can lead to droughts in parts of the country.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a sponge. When you pour water on it, it absorbs the liquid until it's full. The wet season in India is like pouring water onto the sponge, saturating the land. When it dries out, similar to the sponge after you stop pouring water, it becomes hard and can crack, mirroring how dry seasons can lead to issues like drought.
Factors Influencing Climate
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Influenced by factors like location, relief, and the Indian Ocean.
Detailed Explanation
Several factors play a crucial role in determining the climate of India. Firstly, location refers to its geographical position in relation to the equator and other countries. Secondly, relief refers to the physical geography, such as mountains and plains, which can affect air movements and temperatures. Lastly, the Indian Ocean significantly influences the climate by providing moisture during the monsoon season, which is essential for agriculture.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how a location can affect daily life. If you live near the beach, you experience a different climate compared to someone who lives in the mountains. Similarly, India’s diverse geography creates various climates, with the ocean adding moisture to the air that supports rainfall.
Key Concepts
-
Monsoon-type Climate: India experiences distinct wet and dry seasons influenced by geographical factors.
-
Latitude's Impact: India's climate varies significantly from tropical in the south to subtropical in the north due to the Tropic of Cancer.
-
Altitude's Role: Higher altitudes generally result in cooler temperatures, while the Himalayas block cold winds from the north.
-
Coastal vs. Interior Climate: Coastal regions have a more moderate climate, while inland areas experience more extreme temperature variations.
Examples & Applications
The distinction between the climate in Mumbai (coastal, moderate) and Delhi (continental, extreme) illustrates the impact of geographical factors on local climates.
The reliance of Indian agriculture on seasonal monsoons underscores the significance of climate in economic planning and crop management.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
With weather quick to change; climate stays, within long days.
Stories
In a land where rivers flow, the sun shines hot, rain comes slow; from mountains high to coasts so low, this is how India’s seasons go.
Memory Tools
Remember: 'Latitude Low = Tropical Glow; High = Cold, Don’t You Know'.
Acronyms
R.E.L.I.E.F. - Relief Elevates Local Influences on Environmental Factors.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Weather
Atmospheric conditions over a short period, such as days.
- Climate
The average weather conditions over an extended period, typically 30 to 35 years.
- Monsoon
A seasonal reversal of winds causing distinct rainy and dry seasons.
- Latitude
The geographical coordinate that helps determine climate zones.
- Altitude
The height of an area relative to sea level, affecting temperature and climate.
- Relief
The physical geography of an area, influencing local climate patterns.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
