Example of Heat Capacity
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Heat Capacity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome everyone! Today, we're talking about heat capacity, which tells us how much heat is needed to raise the temperature of an object by 1°C. Can anyone tell me why temperature changes are significant?

Because temperature affects how much energy something has, right?

Exactly! Knowing the heat capacity helps us understand how much energy we need to add or remove. Who can give me an example of something with a high heat capacity?

Water! It takes a lot of heat to change its temperature.

Yes! Water's high heat capacity helps regulate temperatures in the environment.
Heat Capacity Formula
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s delve into the formula to calculate heat capacity. Can anyone recall what it is?

I think it's C equals m times c?

Correct! C = mc, where m is the mass and c is specific heat capacity. Why do you think both mass and specific heat affect heat capacity?

Because heavier objects hold more heat, and different materials store heat differently!

Great insights! Let’s plug in some numbers and work on an example together.
Example of Heat Capacity Calculation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's calculate the heat capacity of a 2 kg metal block with a specific heat capacity of 0.5 J/g°C. Who can start with unit conversion?

1 kg is 1000 grams, so we should convert the specific heat capacity.

Exactly! Let’s calculate it now. C = 2 kg × (0.5 J/g°C × 1000 g/kg). What do we get?

That's 1 kJ/°C!

Well done! This shows us how mass and specific heat influence heat capacity.
Real-Life Applications
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Understanding heat capacity is crucial. Can anyone think of how this is applied in real life?

Cooking! Knowing how long to heat different materials.

Also in climate science, right? Like how oceans affect weather!

Exactly! These real-life applications show the significance of heat capacity.
Final Thoughts on Heat Capacity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's recap. What is heat capacity, and why is it important?

It's the heat needed to raise the temperature by 1°C, and it's important because it affects how we use heat in various processes!

Excellent summary! Can someone remind us of the formula for heat capacity?

C = mc!

Right! Keep this knowledge in mind as it applies to many fields.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Heat capacity quantifies the heat required to increase an object's temperature by one degree Celsius. It incorporates the mass and specific heat capacity of the material. For example, a 2 kg block of metal with a specific heat capacity of 0.5 J/g°C results in a heat capacity of 1 kJ/°C.
Detailed
Example of Heat Capacity
Heat capacity is defined as the amount of heat energy necessary to raise the temperature of an object by 1°C (or 1 K). It is critical in understanding heat transfer in physical systems. The formula for calculating heat capacity is given by:
Formula
C = mc
Where:
- C = Heat capacity (in Joules per degree Celsius or J/K)
- m = Mass of the object (in kilograms)
- c = Specific heat capacity of the material (in J/kg°C)
Example Calculation
For instance, if we have a block of metal weighing 2 kg with a specific heat capacity of 0.5 J/g°C, we can calculate its heat capacity as follows:
C = 2 kg × 0.5 J/g°C
Since we need to convert the specific heat capacity to units that match the mass (1 kg = 1000 g):
C = 2 kg × 0.5 × 1000 J/kg°C = 1 kJ/°C.
Therefore, the heat capacity of the block is 1 kJ/°C. This example illustrates the practical application of the heat capacity formula, demonstrating how mass and specific heat capacity influence an object's ability to store thermal energy.
Youtube Videos


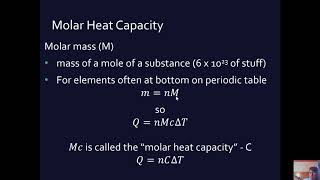





![What is Heat, Specific Heat & Heat Capacity in Physics? - [2-1-4]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/2tDKLkj9zfI/mqdefault.jpg)
Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Heat Capacity
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Heat capacity is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of an object by 1°C (or 1 K). It is the sum of the sensible heat of all the particles in the object and depends on both the mass and the specific heat capacity of the substance.
Detailed Explanation
Heat capacity tells us how much heat energy is needed to increase the temperature of a given object by one degree. This capacity is influenced by two main factors: the mass of the object and the specific heat capacity, which is a property of the material itself. Essentially, larger objects or those made of materials with higher specific heat will require more energy to heat up.
Examples & Analogies
Think of heat capacity like a bathtub filled with water. If you want to make the water warmer, a larger bathtub (greater mass) will take more hot water (heat energy) compared to a smaller bathtub to reach the same temperature increase.
Formula for Heat Capacity
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The formula for calculating heat capacity is:
C=mc
Where:
○ CC = Heat capacity (in Joules per degree Celsius or J/K)
○ mm = Mass of the object (in kilograms)
○ cc = Specific heat capacity of the material (in J/kg°C)
Detailed Explanation
The formula C = mc helps us calculate the heat capacity (C) by multiplying the mass of the object (m) with its specific heat capacity (c). This means we can predict how much energy is needed to raise the temperature of a particular mass of material.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine if we wanted to heat up a large metal rod and a small piece of metal. The heat capacity formula allows us to calculate that the larger rod (greater mass) requires more energy to heat up than the smaller piece, assuming both are made of the same material (same specific heat capacity).
Example Calculation of Heat Capacity
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A 2 kg block of metal has a specific heat capacity of 0.5 J/g°C. The heat capacity of the block is:
C=2×0.5=1 kJ/°C
Hence, the heat capacity of the block is 1 kJ/°C.
Detailed Explanation
In this example, we are given a block of metal weighing 2 kg and a specific heat capacity of 0.5 J/g°C. First, we convert the specific heat capacity to match the units of mass (from g to kg, since there are 1000 g in 1 kg). This makes the specific heat capacity 500 J/kg°C. Then, using the heat capacity formula (C = mc), we substitute the values: C = 2 kg × 500 J/kg°C = 1000 J/°C or 1 kJ/°C, showing how much heat energy is needed to increase the temperature of the block by one degree.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine heating a 2 kg metal object like a frying pan. To increase its temperature by 1°C, you would need 1 kJ of energy. This is similar to the energy required to heat food quickly when cooking, highlighting the practical importance of understanding heat capacity.
Key Concepts
-
Heat Capacity: The heat required to raise the temperature of an object by 1°C.
-
Specific Heat Capacity: The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of a unit mass by 1°C.
-
Mass: A critical factor in determining heat capacity.
-
Joules and Kilojoules: Units used to quantify heat energy.
Examples & Applications
A 2 kg metal block with a specific heat capacity of 0.5 J/g°C will have a heat capacity of 1 kJ/°C.
Water, with a high heat capacity, takes longer to change temperature than air.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Heat capacity's like a cozy blanket, it keeps things warm and safe, don't you think?
Stories
Imagine you're baking cookies. You need to know how long to bake them - that's heat capacity at work! Understanding how much heat they need to get just right helps you make the perfect batch.
Memory Tools
Remember 'Mighty Heat Caps', to recall 'Mass times Specific Heat equals Heat Capacity'.
Acronyms
C = mc helps you recall how to calculate Heat Capacity
for Capacity
for Mass
for specific heat.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Heat Capacity
The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of an object by 1°C (or 1 K).
- Specific Heat Capacity
The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of a unit mass of a substance by 1°C.
- Mass
The quantity of matter in a substance, typically measured in kilograms.
- Joule
The SI unit of energy, equivalent to the work done by a force of one newton moving an object one meter.
- kJ
Kilojoule; a unit of energy equal to 1000 Joules.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
