Definition of a Polynomial
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Polynomials
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, let's define what a polynomial is. A polynomial is essentially an algebraic expression that can include variables and coefficients, but it can only use a specific set of operations.

What kind of operations can we use?

Great question! We can use addition, subtraction, multiplication, and we can also have non-negative integer exponents on the variables. For instance, expressions like 3x^2 + 2x - 5 are polynomials.

So, if I had something like x^-1, that wouldn't be a polynomial, right?

Exactly! Negative exponents disqualify an expression from being a polynomial. Remember: no fractions with variables in the denominator and only non-negative integer exponents!

What happens if we have variables multiplied together?

That's perfectly fine! For example, 2xy is part of a polynomial because it's just multiple variables multiplied together without any restrictions. Just keep a lookout for those non-negative exponents!

Can we have a constant in a polynomial?

Yes, constants are coefficients and can appear in the polynomial. For example, in the polynomial 4x^3 - 2, the -2 is a constant term. This kind of structure is essential in forming polynomials.

To summarize, a polynomial consists of variables and coefficients, combined through addition, subtraction, and multiplication. Exponents must be whole numbers!
Identifying Components of Polynomials
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we know what a polynomial is, let’s discuss its components! Who can tell me what a coefficient is?

I think it’s the number in front of the variable.

Correct! For instance, in 5x^2, 5 is the coefficient. How about terms in a polynomial?

Are terms the separate parts of the polynomial, like 5x^2 and -3 in 5x^2 - 3?

Exactly! Each piece separated by a plus or minus sign is a term. So in our example, we have two terms: 5x^2 and -3.

What is a constant term then?

A constant term is simply a term that does not have a variable. In our example, -3 is a constant term because it is just a number.

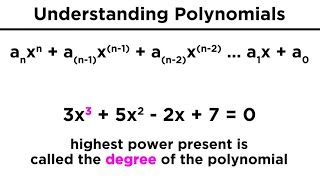
So how would we identify the degree of a polynomial?

The degree of a polynomial is determined by the highest exponent of its variable. For our example, the degree is 2 because of the term 5x^2.

To recap, a polynomial's components include coefficients, terms, and the degree, which is the highest exponent of the variable.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section defines polynomials, emphasizing that they consist of variables and coefficients. It describes the operations allowed in forming polynomials and specifies that only non-negative integer exponents are acceptable for the variables.
Detailed
In this section, we explore the definition of polynomials, which are algebraic expressions composed of variables raised to whole number powers and combined using elementary operations. The standard structure of a polynomial involves coefficients, variables, and operations of addition, subtraction, and multiplication, while restricting the exponents of variables to non-negative integers. This fundamental understanding of polynomials sets the stage for further exploration of algebraic identities and the various types of polynomials based on their degree and the number of terms.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
What is a Polynomial?
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A polynomial is an algebraic expression consisting of variables and coefficients involving only addition, subtraction, multiplication, and non-negative integer exponents of variables.
Detailed Explanation
A polynomial is essentially a mathematical expression that comprises terms formed by variables (like x and y) raised to non-negative whole number powers. In a polynomial, you can combine these terms using operations like addition, subtraction, and multiplication. However, you cannot use division involving variables or any negative exponents. For example, the expression 2x^2 + 3x + 1 is a polynomial because it includes variables x and coefficients 2, 3, and 1 without any divisions or negative powers.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a polynomial as a recipe for a cake. Each ingredient (term) must follow the basic rules of cooking (addition, subtraction, multiplication), and you can’t have negative amounts or divide one ingredient by another. Just like in the kitchen, each ingredient must be whole (non-negative), leading to a well-formed cake (polynomial).
Key Concepts
-
Polynomials: Algebraic expressions formed from variables and coefficients using specific arithmetic operations.
-
Coefficients: The numerical factors accompanying variables in polynomial expressions.
-
Degree: The highest exponent of its variable in a polynomial, determining its classification.
-
Terms: The separate parts of a polynomial linked by '+' or '-'.
-
Constant Term: The term within a polynomial that does not contain any variables.
Examples & Applications
Example 1: 3x^2 + 2x - 5 is a polynomial because it follows the rules of polynomials.
Example 2: 4ab^2 + 3a - 7 is a polynomial where the terms are 4ab^2, 3a, and -7.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To make a polynomial that’s neat, keep exponents non-negative, can’t be beat!
Stories
Once in a land where numbers played, there were polynomials that never strayed. They danced in addition and subtraction's mirth, but no negative exponents were part of their worth!
Memory Tools
Remember the ABCs of polynomials: A - Allowed operations (add/subtract/multiply), B - Basis (non-negative exponents), and C - Coefficients are key.
Acronyms
P.E.T. - Polynomial Exponents Terms. Remember
Polynomials have positive exponents
composed of multiple terms!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Polynomial
An algebraic expression consisting of variables and coefficients combined using addition, subtraction, multiplication, and non-negative integer exponents.
- Coefficient
A numerical factor in a term of a polynomial.
- Degree
The highest power of the variable in a polynomial.
- Term
A single part of a polynomial separated by a plus or minus sign.
- Constant term
A term in a polynomial that does not contain any variables.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
