Linear Voltage Regulators
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Basic Design of Linear Voltage Regulators
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to discuss linear voltage regulators. Can anyone tell me what components you think make up this type of regulator?

Isn't it just an Op-Amp?

Great start! However, there’s more. A linear voltage regulator typically includes a pass element, like a transistor, and a voltage reference along with the Op-Amp in a feedback loop. What do you think the Op-Amp does here?

Does it compare the output voltage to the reference voltage?

Exactly! The Op-Amp adjusts the pass element to keep the output steady. Remember, we call this loop feedback because it continuously adjusts.
Operation of Linear Voltage Regulators
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we know the components, let’s discuss their operation. Can someone explain how the feedback loop functions?

The Op-Amp compares the output voltage to the reference, and it changes the pass element if there's a difference.

Right! It ensures that even if the input voltage changes or the load fluctuates, the output remains stable. Let’s use the acronym 'P.O.P.' — Pass element, Op-Amp, and Power steady. This will help us remember the main components and their purpose.

What happens if the output voltage goes too high?

Great question! The Op-Amp will signal the pass element to reduce the output, bringing it back to the desired level.
Design Example for a 5V Linear Voltage Regulator
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s apply our knowledge. How would we design a linear voltage regulator to provide a stable 5V output?

We would set up a 5V reference voltage.

Exactly. The Op-Amp will compare this reference against the actual output voltage. If the output voltage dips, it will trigger the pass transistor to increase the voltage back to 5V.

If the input voltage fluctuates, the output will still remain steady at 5V?

Correct! That’s why linear voltage regulators are essential for sensitive electronics and power stability.
Applications of Linear Voltage Regulators
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Who can tell me why linear voltage regulators are important?

They keep the voltage stable for sensitive components!

Exactly! They are used in battery-powered devices, ensuring that despite battery potential changes, devices receive a consistent output. That’s crucial for performance!

But aren’t switching regulators more efficient?

Yes! Switching regulators are indeed more efficient over linear ones, but linear regulators are simpler and provide cleaner output. So, it depends on the application's particular needs.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section delves into linear voltage regulators, detailing their design, operation, and components, specifically focusing on how the op-amp compares output voltage to a reference voltage to stabilize power supply despite input voltage fluctuations.
Detailed
Linear Voltage Regulators
Linear voltage regulators are crucial components in electronic circuits designed to maintain a stable output voltage regardless of input voltage variations and load changes. A typical linear regulator consists of a pass element, like a transistor or MOSFET, a voltage reference, and an operational amplifier (Op-Amp) in a feedback loop. The Op-Amp continuously compares the output voltage to a preset reference voltage, and when it detects any deviation, it adjusts the pass element to ensure that the output voltage remains constant. This section illustrates an example of designing a 5V linear voltage regulator, highlighting the operation of the feedback loop in stabilizing the output voltage.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Basic Design
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A linear voltage regulator typically consists of a pass element (e.g., transistor or MOSFET), a voltage reference, and an Op-Amp in the feedback loop. The Op-Amp compares the output voltage to the reference voltage and adjusts the pass element to maintain a constant output voltage.
Detailed Explanation
A linear voltage regulator is designed to keep the output voltage steady. To do this, it has three main components: a pass element (like a transistor), a voltage reference, and an operational amplifier (Op-Amp). The Op-Amp continuously compares the output voltage to a fixed reference voltage. If there is any difference, the Op-Amp adjusts the pass element to correct the output voltage back to the desired level.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the linear voltage regulator as a thermostat in a house. Just as the thermostat compares the current temperature of the house (output voltage) to the desired temperature (reference voltage), the linear voltage regulator ensures that the output voltage remains at a specific level regardless of fluctuations in input voltage or load. If it gets too hot or too cold (wrong voltage), the thermostat adjusts the heating or cooling system (pass element) to maintain comfort (constant voltage).
Operation
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The feedback loop adjusts the pass element (e.g., a transistor) to ensure the output voltage stays stable, even when the input voltage or load changes.
Detailed Explanation
The operation of a linear voltage regulator relies heavily on a feedback control system. Whenever the output voltage changes due to variations in the input voltage or load (like devices drawing more current), the Op-Amp detects this change. It then commands the pass element to adjust accordingly. If the output voltage drops, the Op-Amp tells the pass element to let more current through, boosting the output back up. Conversely, if the voltage rises too high, it reduces the current flow to bring the voltage back down.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a water faucet: if too much water (voltage) flows out (due to a strong source pressure), you might close the faucet slightly (reduce current flow) to maintain an ideal water level in a tank (output voltage). Conversely, if the water level dips below the desired amount, you would open the faucet more to increase the flow, ensuring the tank remains full.
Design Example
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Objective: Design a 5V voltage regulator using an Op-Amp and pass transistor. Solution: Use a 5V reference voltage and the Op-Amp in the feedback loop to control the pass transistor and maintain a steady 5V output, even if the input voltage fluctuates.
Detailed Explanation
In this design example, the objective is to create a voltage regulator that reliably outputs 5 volts. The first step is to set a reference voltage of 5 volts for the Op-Amp. Then, you connect the output of the regulator to the feedback loop of the Op-Amp. When the output voltage is stable at 5 volts, the Op-Amp will see that it matches the reference, and the pass transistor will adjust to keep it steady. Even if the input voltage varies or the load changes, this setup ensures the output remains consistent.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are baking a cake. You need the oven to be at exactly 350°F (5V output). You set the temperature dial (reference voltage) to 350°F. If the oven cools down (input voltage fluctuation), a thermostat (the Op-Amp) senses this drop and adjusts the heat (pass element) to maintain that perfect temperature to bake your cake properly.
Key Concepts
-
Linear Voltage Regulator: A device that provides a constant output voltage regardless of load variations.
-
Feedback Loop: The process by which the Op-Amp adjusts the pass element based on the difference between output and reference voltages.
-
Pass Element: The transistor or MOSFET that regulates the output based on feedback from the Op-Amp.
-
Op-Amp: The component that compares the output voltage to a reference voltage.
Examples & Applications
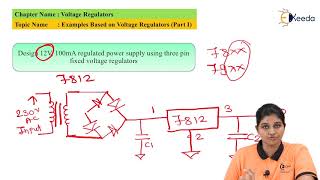
An LM7812 is a popular linear voltage regulator that provides a constant output voltage of 12V, making it suitable for various electronic devices.
Designing a 5V regulator using an LM317 allows for adjustable output, providing flexibility in circuit design.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Feedback loop in a regulator, keeps voltage steady like a calculator.
Stories
Imagine a tower with a courtroom: the judge is the Op-Amp, comparing the claimant’s statements against facts. If there's any falsifying going on, the judge adjusts the decision – keeping it fair!
Memory Tools
Remember 'POP' for Pass element, Op-Amp, and Power steady.
Acronyms
REGULATE
Reference
Element
Gain Under Loop Adjustment to Ensure stability.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Linear Voltage Regulator
A circuit designed to maintain a constant output voltage despite variations in input voltage or load.
- OpAmp
An operational amplifier, a device used to compare two voltages and output a signal based on the comparison.
- Pass Element
A component, usually a transistor, that controls the output voltage in a voltage regulator.
- Feedback Loop
A system structure that adjusts an output back to a desired level by continuously comparing it with a reference.
- Voltage Reference
A stable reference voltage against which actual output voltage is compared.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
