Summary of Key Concepts
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Comparators
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're discussing comparators. Who can tell me what a comparator does?

A comparator compares two input voltages!

Exactly! The output is either a high or low signal based on which voltage is higher. Can anyone tell me when we might use this?

In digital circuits?

Yes, that's correct! Comparators are widely used in digital logic circuits and for signal detection. Remember the acronym 'CHIPS' for Comparators, High/Low, Inputs, Producing, Signals. Now, what is hysteresis in comparators?

It's used to prevent unwanted switching due to noise.

Absolutely! Hysteresis creates a small threshold for switching to avoid noise-induced errors.
Introduction to Voltage Regulators
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s move on to voltage regulators. Who can explain what they do?

They keep the output voltage constant.

Correct! Voltage regulators are critical for ensuring that electronic devices operate reliably. What are the two types of voltage regulators we discussed?

Linear and switching regulators!

Great! Linear regulators provide smooth output but are less efficient. Can anyone explain the advantage of switching regulators?

They're more efficient because they don’t waste energy as heat!

Exactly! Efficiency is key. Let's remember 'FIRE'—Efficiency in regulators: Fast, Inexpensive, Reliable, Efficient.
Stability and Compensation Techniques
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s discuss the stability of voltage regulators. Why is stability important?

Stability ensures they work properly under different input conditions.

Exactly! Without stability, regulators can cause oscillations or fail to maintain voltage. What are some compensation techniques we can use?

Feedforward compensation?

Yes! And loop compensation is also important. Remember 'SIMPLE'—Stability Involves Measurement, Phase, and Loop Evaluation.

That's helpful! It summarizes the stability techniques!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The summary covers the principles of comparators, including their use in digital logic and voltage comparison, as well as voltage regulators, which ensure stable output voltage for electronic devices. Key points are the importance of hysteresis in comparators and the differences between linear and switching regulators.
Detailed
Summary of Key Concepts
In this section, we delve into the essential concepts surrounding comparators and voltage regulators, which are critical components in electronic systems. Comparators perform voltage comparisons, outputting digital high or low signals depending on the input level, and are vital in applications like digital logic circuits and waveform generation. Hysteresis is often introduced to mitigate unwanted noise-induced switching. On the other hand, voltage regulators are designed to maintain a constant output voltage to ensure the reliable operation of sensitive devices, with linear and switching types offering different advantages in terms of efficiency and design. Stability and compensation techniques are crucial for the proper functioning of these regulators, especially under fluctuating load and input conditions.
Youtube Videos

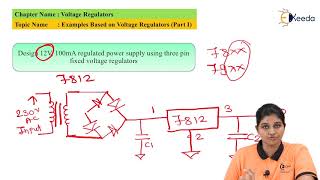


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Understanding Comparators
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Comparators:
○ Comparators are used to compare two input voltages and output a high or low signal based on the comparison.
○ They are widely used in digital logic circuits, signal detection, and waveform generation.
○ Hysteresis is commonly introduced to prevent unwanted switching due to noise.
Detailed Explanation
Comparators are specialized circuits that take two input voltages and determine which one is higher. If the voltage on one input exceeds the voltage on the other, the comparator produces a high output signal (often represented as a positive voltage). Conversely, if the first voltage is lower, the output is low (often near ground). This function is critical in digital logic systems where decisions are made based on voltage levels. For example, in a digital circuit, a comparator can signal whether an input voltage exceeds a certain threshold.
Hysteresis is an added feature in comparators designed to reduce noise-induced errors. When there's a little bit of noise on the input signal, it can cause the comparator to switch improperly, resulting in erratic outputs. Hysteresis creates a 'buffer zone' in voltage levels, where small changes do not lead to switching, enhancing stability.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a light switch in a dark room. If you turn the switch just slightly (like a varying input voltage), it may not turn on due to a certain threshold. However, if you flip it completely, the room lights up (high output). If there’s unnecessary noise (like flickering), hysteresis prevents the light from turning on and off unnecessarily when it’s only slightly above off.
Overview of Voltage Regulators
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Voltage Regulators:
○ Voltage regulators maintain a constant output voltage, ensuring reliable operation of electronic devices.
○ Linear regulators provide smooth output but are less efficient than switching regulators.
○ Stability and compensation techniques are essential for ensuring proper operation of voltage regulators under varying conditions.
Detailed Explanation
Voltage regulators are circuits that provide a steady output voltage, regardless of changes in input voltage or load conditions. They are essential components in providing power to sensitive electronics, ensuring they operate correctly even if the power supply fluctuates. Linear regulators are straightforward and provide smooth output by controlling the amount of current, but they can waste energy as heat, making them less efficient. On the other hand, switching regulators increase efficiency by turning the flow of power on and off rapidly, although they are more complex and less straightforward to design.
Stability is critical for voltage regulators to function correctly. If a regulator is unstable, it may produce oscillations or fail to maintain the correct voltage. To ensure stability, engineers use compensation techniques, which adjust the circuit's response to changes, ensuring it remains stable across various conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a water supply system. A voltage regulator is like a water pressure regulator that ensures you get a constant flow of water from varying upstream pressure. If there’s a sudden surge in pressure (like getting too much voltage), the regulator smooths it out to a steady flow. If it doesn’t work properly (stability), you might get bursts of high-pressure water or sporadic flows (voltage oscillations). Just like it's essential to keep water pressure steady for a faucet to work correctly, regulators keep voltage steady for electronics.
Key Concepts
-
Comparators: Devices that compare two voltages and provide a high or low output signal.
-
Voltage Regulators: Maintain constant output voltage to ensure reliable operation of electronic circuits.
-
Hysteresis: Introduced in comparators to avoid erratic switching.
-
Linear vs. Switching Regulators: Linear regulators are smooth but inefficient; switching regulators are efficient due to their operation method.
Examples & Applications
In a digital temperature control system, a comparator can trigger an alarm when the temperature reaches a certain threshold.
A battery-operated device uses a voltage regulator to ensure that the voltage remains stable even as the battery voltage drops.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Comparators compare, they declare, high or low, depending on the flow.
Stories
Imagine a teacher who compares the height of students. If one is taller, they get a star; lest the noisy crowd mix things up!
Memory Tools
Hysteresis helps to 'HUSH' noise: Hold Up Switching High to prevent erratic changes.
Acronyms
Remember 'SLICE' for regulators
Stability
Linear
Input
Comparison
Efficiency.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Comparator
A circuit that compares two input voltages and outputs a digital signal based on the comparison.
- Voltage Regulator
A circuit that maintains a constant output voltage despite variations in input voltage or load current.
- Hysteresis
A technique used in comparators to introduce a threshold that prevents rapid switching due to noise.
- Linear Regulator
A voltage regulator that provides a steady output voltage by dissipating excess voltage as heat.
- Switching Regulator
A voltage regulator that achieves its output voltage by rapidly switching the input on and off and filtering the result.
- Stability
The ability of a voltage regulator to maintain its output voltage under varying input conditions.
- Compensation Techniques
Methods used to enhance the stability and performance of regulators in varying conditions.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
