Practical Applications of Comparators and Voltage Regulators
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Comparators in Digital Systems
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to discuss the role of comparators, particularly their application in detecting signal levels. Can anyone explain what we mean by level detection?

Is it about knowing whether a signal is above or below a specific voltage?

Exactly! Level detection involves determining if a signal exceeds a set threshold, which is crucial in digital logic. We often use an acronym to remember this—‘LIFT’: Level Identification For Threshold.

What happens to the output when the signal does exceed that threshold?

Good question! The comparator outputs a high signal when this occurs. Can anyone give me an example where this is applied?

Maybe in automatic light systems, where the circuit turns on lights at a specific ambient light level?

Absolutely! Let's summarize: Comparators help in digital logic by detecting if a signal exceeds a threshold.
Zero Crossing and PWM Applications
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s shift to zero crossing detection. What does this mean?

Is it about figuring out when an AC waveform crosses zero volts?

Exactly! Zero crossing detection is vital for synchronizing systems. It enables the detection of phases in AC waveforms. Why might this be important?

It could help control motors more efficiently or stabilize a circuit by timing operations.

Spot on! Now, regarding PWM, how do you think comparators factor into that?

They compare a sawtooth wave with a control signal to vary the pulse width for motor control.

Exactly! So how might we summarize these applications of comparators?

They're used for detecting phase changes in signals and controlling the power delivery to devices.
Voltage Regulators in Power Supply Systems
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss voltage regulators. Why are they so crucial in electronic systems?

They help maintain a constant voltage, right?

Exactly! Voltage regulators ensure that sensitive electronic devices receive stable power. We often remember this by saying, ‘GOLD’: Guaranteed Output Linearity and Distribution. What kinds of devices rely on this stability?

Precision equipment, like sensors and data acquisition systems?

Yes! Also, portable devices depend on voltage regulators as battery levels change. What happens if we don’t use them?

The devices could malfunction due to voltage fluctuations.

Correct! So to recap, voltage regulators guarantee stability and performance in electronics.
Types of Voltage Regulators
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s compare linear voltage regulators to switching ones. What’s the primary difference?

Linear regulators provide smooth output but are less efficient, right?

Exactly! In contrast, switching regulators are more efficient due to their ability to minimize heat loss. Can anyone explain why that matters in design?

It saves power and keeps components from overheating.

Correct! We can use the mnemonic 'EASY': Efficiency and Stability Yield, to remember the advantages of switching regulators. Any other features of switching regulators?

They tend to be more complex and require additional components like inductors.

Excellent point! To summarize, linear regulators are great for simplicity, while switching regulators excel in efficiency.
Stability Techniques in Voltage Regulation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let’s discuss stability in voltage regulators. Why is it a key concern?

Because unstable regulators can cause noise and may not maintain the correct voltage.

Correct! We often use techniques like feedforward compensation for improved responses. Can anyone give me an example?

It could be used in scenarios with rapidly changing loads.

Exactly! Let’s summarize this session: stability is crucial for optimal voltage delivery, especially in sensitive applications.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Comparators and voltage regulators serve crucial roles in electronic systems, with comparators used for level detection, zero crossing detection, and PWM, while voltage regulators are essential in power supply systems, precision equipment, and portable devices.
Detailed
In this section, we delve into the practical applications of comparators and voltage regulators, two pivotal elements in electronic design. Comparators are primarily utilized for level detection, enabling systems to ascertain if a signal surpasses a defined threshold, which is crucial for digital systems and control circuits. They are also employed in zero-crossing detection to analyze AC waveforms and in PWM implementations to generate variable-width pulses for motor control and LED dimming. On the other hand, voltage regulators are instrumental in ensuring stable power supply in diverse contexts. They regulate voltage in power supply systems, optimize performance in precision equipment, and maintain reliable operation in portable devices, even amidst battery fluctuations. This combination of functionalities highlights how these components enhance the reliability and functionality of electronic applications.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Applications of Comparators
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Comparators:
○ Level Detection: Detects whether a signal exceeds a specified threshold, used in digital systems and control circuits.
○ Zero Crossing Detection: Used in AC waveform analysis and phase-locked loops (PLLs).
○ Pulse Width Modulation (PWM): Generates variable-width pulses for controlling motors, LEDs, or power converters.
Detailed Explanation
Comparators are essential components in various electronic systems. They are used for level detection, which involves checking if a signal has crossed a certain threshold. This is crucial in digital systems where decisions are made based on whether signals are high or low. For example, in a temperature control system, a comparator can trigger an action when the temperature exceeds a specific limit.
Zero crossing detection is another important application, where comparators detect when an AC signal crosses the zero voltage point. This is useful in phase-locked loops (PLLs) that synchronize signals by ensuring they are aligned in phase.
Lastly, comparators are used in pulse width modulation (PWM). In PWM, a reference voltage is compared to a varying signal to create pulses of different widths, which can control devices like motors or LEDs by adjusting their power levels.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a compare-and-contrast game. For instance, you have two containers: one with water and one empty. You define that when the water level reaches a certain height, it calls out a signal (like a buzzer). This is like level detection. If you carefully monitor the water level as it rises and falls (crossing the 'zero' point), you can make adjustments if you're trying to keep something at a stable temperature. PWM can be understood as turning a light dimmer on and off quickly to make a light appear dimmer or brighter, depending on how long it's on versus off.
Applications of Voltage Regulators
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Voltage Regulators:
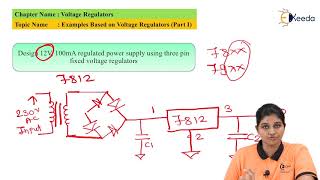
○ Power Supply Systems: Used in battery-powered devices, power adapters, and DC-DC converters to provide stable voltage to sensitive circuits.
○ Precision Equipment: Ensures that precision analog circuits, such as sensors and amplifiers, receive a stable voltage.
○ Portable Devices: Regulates the voltage in portable systems, ensuring consistent operation despite battery fluctuations.
Detailed Explanation
Voltage regulators are crucial for ensuring that electronic devices work reliably. In power supply systems, they maintain a constant voltage, even if the input voltage varies or if the load changes. This is particularly important for battery-powered devices and power adapters, where fluctuations could lead to malfunctioning.
Precision equipment like sensors and amplifiers relies on stable voltage to provide accurate readings. A change in voltage can lead to significant errors, thereby affecting the performance of these devices. Voltage regulators ensure these devices receive the correct voltage, allowing them to function correctly.
In the case of portable devices, voltage regulators help manage the fluctuations that come from changing the battery levels. As batteries discharge, their voltage can drop, but voltage regulators maintain the required output voltage for the device, ensuring it continues to operate efficiently.
Examples & Analogies
Think of voltage regulators as a water faucet. If you're watering a garden and the water pressure (input voltage) fluctuates - sometimes it’s strong and sometimes weak - a good faucet ensures you get a consistent flow of water (stable output voltage). Without it, when the pressure is high, you could flood your plants, and when it's low, they might not get enough water at all. Just like in electronics, having stable voltage is key to keeping everything working smoothly, especially for sensitive equipment like sensors that must measure accurately.
Key Concepts
-
Comparators: Devices that compare two input voltages to produce a digital output signal.
-
Voltage Regulators: Circuits that maintain a consistent output voltage to ensure stable power supply.
-
Zero Crossing Detection: A method for identifying the moment when a waveform crosses zero volts.
-
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM): A technique for controlling the amount of power delivered to devices by varying pulse widths.
-
Hysteresis: A technique employed to prevent erratic switching in comparators due to noise.
Examples & Applications
In digital electronic systems, comparators are used for level detection to determine if a signal exceeds a specific threshold.
Voltage regulators are vital in battery-powered devices to provide a stable voltage output even as battery levels fluctuate.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Volt stable and bright, regulators keep it right!
Stories
Imagine a busy traffic light (comparator) only changes from red to green (high signal) when the road is clear of cars (threshold exceeded) to maintain safe flow.
Memory Tools
Use 'CLEAR' to remember Comparators' key uses: Control, Level, Exceed, Analyze, Regulate.
Acronyms
‘GOLD’ for Voltage Regulators
Guaranteed Output Linearity and Distribution.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Comparator
A circuit that compares two input voltages and outputs a digital signal based on their relative values.
- Voltage Regulator
A circuit that maintains a constant output voltage regardless of input voltage variations.
- Zero Crossing Detection
The process of identifying when an AC waveform crosses zero volts for synchronization.
- Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)
A technique to control the width of pulses in a signal to control devices like motors.
- Hysteresis
A technique used in comparators to avoid rapid switching due to fluctuations at the input.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
