Incremental and Differential Costs
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Incremental Costs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we’ll discuss incremental costs, which are the additional costs that arise when we alter our level of activity.

Can you give us an example of incremental costs?

Sure! If a factory decides to increase production by adding a new machine, the costs for materials and wages directly associated with that increase are considered incremental costs.

Is that different from operational costs that are already in place?

Exactly! Incremental costs only account for the changes related to a specific decision or action.

How can knowing these costs affect our decisions?

Understanding these costs helps managers plan budgets and make informed decisions about expansions or reductions.

In summary, incremental costs are vital in evaluating changes in business activity.
Differential Costs Explained
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss differential costs, which are the differences in costs between two alternatives.

Can you provide a scenario to illustrate this?

Absolutely! If Company A can manufacture 1,000 units for ₹500,000 and Company B can do it for ₹450,000, the differential cost is ₹50,000. This helps in choosing the more cost-effective option.

What if we have multiple options?

In such cases, you would calculate the costs against each alternative, focusing on the differences to determine which choice maximizes benefits while minimizing expenses.

So, differential costs helps in making cost-effective decisions?

Correct! They are crucial in comparative analysis for business decisions.

To summarize, differential costs aid in evaluating multiple options to maximize financial performance.
Application of Incremental and Differential Costs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s explore how incremental and differential costs are applied in real-life scenarios.

How do companies use these concepts for budgeting?

Companies forecast budgets based on incremental costs when planning for expansions. They assess how much profit comes from changes.

And what about differential costs?

Differential costs come into play in scenarios like project proposals where companies must decide between several investment opportunities to choose the most financially viable one.

So, are there any tools to help analyze these costs?

Yes, managers often use spreadsheets and specialized financial software to calculate and forecast costs efficiently.

In conclusion, understanding and applying incremental and differential costs is critical for sound financial management.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Incremental costs refer to additional costs that arise from a change in the level of activity, while differential costs represent the difference in costs between two alternatives. Understanding these concepts helps in making informed financial decisions.
Detailed
Incremental and Differential Costs
The concepts of incremental and differential costs are crucial in cost accounting, especially for management decision-making. Incremental costs are defined as the additional expenses incurred due to a change in the level of activity. For instance, if a company decides to increase production by 1,000 units, the costs directly associated with this increase, such as materials and labor, are considered incremental costs.
On the other hand, differential costs are the cost differences between two alternatives. For example, if a company is choosing between two suppliers and one supplier charges ₹100,000 while the other charges ₹90,000, the differential cost in this case would be ₹10,000. This concept is pivotal in decision-making scenarios, where comparing costs can lead to optimal choices.
Both incremental and differential cost analysis serve as tools for businesses to evaluate the financial feasibility of operational changes, budget forecasting, and profitability analysis. By understanding these costs, managers can make strategic decisions that enhance operational effectiveness.
Youtube Videos
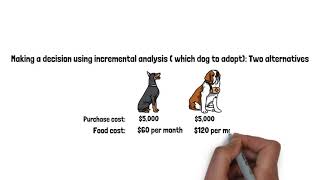








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Incremental Cost
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Incremental Cost: Additional cost due to change in level of activity.
Detailed Explanation
Incremental costs refer to the extra costs that arise when there's a change in the level of business activity. For instance, if a company decides to increase production by 100 units, the costs directly associated with producing those additional units, such as materials, labor, and overhead, are considered incremental costs. It's important for managers to understand these costs as they help in assessing whether it's worth increasing production or taking on new projects.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a baker who normally bakes 100 loaves of bread a day but receives an order for 50 more loaves. The additional ingredients (flour, yeast, etc.), labor (extra time spent baking), and energy (increased oven usage) needed to fulfill this order represent incremental costs. The baker needs to know if the profit from selling these extra loaves exceeds the incremental cost incurred.
Differential Cost
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Differential Cost: Difference in cost between two alternatives.
Detailed Explanation
Differential costs refer to the cost difference that results from choosing one alternative over another. This concept is critical during decision-making processes, such as determining whether to launch a new product or how to allocate resources effectively. To determine the differential cost, the costs associated with the two alternatives are compared, and the difference provides insight into which option is more financially viable.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a situation where a car rental company must decide between two car models for their fleet. Model A costs ₹10,000 to lease per month, while Model B costs ₹14,000. The differential cost is ₹4,000. If Model A offers lower maintenance costs or higher customer satisfaction, the rental company would need to consider whether the additional ₹4,000 for Model B is justified by the potential benefits it brings.
Key Concepts
-
Incremental Costs: Additional costs arising from changes in activity levels.
-
Differential Costs: Cost differences between two alternatives.
Examples & Applications
If a company increases its production by adding a new assembly line, the increased costs of labor and materials directly related to that assembly line are incremental costs.
When comparing the costs of outsourcing manufacturing vs. in-house production, the cost difference calculated would be a differential cost.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Incremental costs grow with more flair, changes to levels, leading to care.
Stories
Imagine a baker who adds another oven. The extra ingredients and labor become his incremental costs, while comparing two new recipes, the cost difference paints the tale of differential costs.
Memory Tools
I for Incremental, D for Differential - Remember ID for different costs learned!
Acronyms
I.C. for Incremental Costs, D.C. for Differential Costs.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Incremental Cost
The additional cost incurred when the level of activity changes.
- Differential Cost
The difference in cost between two alternatives.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
