Incremental Model
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to the Incremental Model
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to explore the Incremental Model in decision-making. Have any of you ever thought about why organizations don't always implement big changes at once?

I think it's because big changes can be risky and might fail.

Exactly! The Incremental Model suggests that organizations often prefer making smaller decisions, which allows them to adjust along the way. Can anyone tell me one benefit of such an approach?

It helps minimize risk because you can see how each small change works before committing to larger ones.

Correct! This way, organizations can adapt based on feedback. We might remember this as the 'little by little' method of decision-making. Any questions so far?

Could this model work in fast-changing industries?

Good question! It can be tricky. Industries that demand speed might need faster adaptations, but incremental changes can still provide a strong foundation.
Application and Examples
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's look at some practical applications of the Incremental Model. For instance, consider how a company rolling out new software might do it. How do you think they'd apply this model?

They might start with a pilot program to test functionality before a full rollout.

Exactly right! This allows them to gather user feedback and refine the software before a larger implementation. What are some challenges they might face with this model?

Maybe employees might become frustrated with constant changes.

Yes! Change fatigue is a potential challenge. It’s important for managers to communicate effectively during these increments to maintain morale. Should we summarize?

The Incremental Model allows organizations to implement gradual changes, reducing risk while enabling adaptability based on ongoing feedback.
Critiques and Limitations
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

While the Incremental Model is useful, it’s not without its critiques. What do you think could be a limitation of this approach?

I guess sometimes organizations might get stuck in their ways and not make enough change.

That’s correct! Committing only to small changes might hinder innovation or lead to missed opportunities for large improvements. What else?

It might take too long to see any real progress.

Absolutely! In fast-paced environments, slow incremental changes might not keep pace with competition. Thus, it's all about finding balance. Can we summarize this point?

The Incremental Model can lead to stagnation if organizations become too comfortable with small changes, potentially missing out on better opportunities.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The Incremental Model suggests that organizations often progress through a series of small, manageable decisions instead of embarking on significant transformations all at once. This model is particularly advantageous in bureaucratic structures where radical changes are challenging to implement.
Detailed
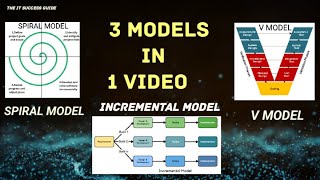
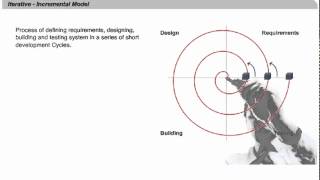
Incremental Model
The Incremental Model is a decision-making framework that advocates for making small, stepwise changes rather than radical overhauls. This approach is particularly relevant for organizations that operate in bureaucratic or politically-sensitive environments where major changes might face significant resistance or could disrupt existing functionalities.
Key Aspects of the Incremental Model:
- Small Steps: Decisions are made in small increments which allow for adjustments based on continuous feedback.
- Flexibility: Organizations can adapt their strategies as new information and outcomes are revealed, refining their approach as necessary.
- Realistic Decision-making: By taking incremental steps, organizations can deal with complexity and uncertainty effectively, as they maintain the ability to reroute if the initial steps do not yield favorable results.
Significance in Decision-Making
The Incremental Model is significant as it recognizes the limitations that managers face compared to ideal rational decision-making. It reflects how decisions are often shaped by context and the realities of organizational life, emphasizing realistic strategies that can accommodate gradual improvements.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of the Incremental Model
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Decisions are made through small, marginal steps rather than radical changes.
• Useful in political or highly bureaucratic organizations.
Detailed Explanation
The Incremental Model suggests that decision-making occurs in small, gradual steps instead of making sudden, large-scale changes. This approach is particularly effective in environments that are politically charged or characterized by bureaucratic processes, where sweeping reforms can be seen as disruptive or met with resistance. By taking smaller steps, organizations can evaluate the effectiveness of their decisions incrementally, allowing for adjustments along the way.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like renovating a house room by room rather than trying to remodel the entire structure at once. By focusing on one room, you can manage costs, assess what works, and make changes based on feedback and the results you observe.
Application of the Incremental Model
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Often applied in scenarios where decisions are made in response to changing circumstances.
• Can help mitigate risks associated with large transformations.
Detailed Explanation
The Incremental Model is particularly relevant in situations where organizations need to adapt to evolving circumstances, such as shifting market trends or internal company dynamics. Since taking large leaps can expose the organization to significant risks, incrementalism allows companies to proceed with caution, adjusting their strategies based on the outcomes of each small decision. This careful approach not only reduces the potential for failure but also enables organizations to learn and adapt continuously.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a gardener who decides to improve their garden by introducing new plants slowly over time, rather than uprooting everything. Each choice is made based on the performance of previous plants; they learn which plants thrive and which do not. This gradual change leads to a healthier and more vibrant garden.
Advantages of the Incremental Model
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Encourages continual learning and adaptation.
• Reduces the fear that can accompany large-scale changes.
Detailed Explanation
One of the main advantages of the Incremental Model is that it promotes an environment of continual learning and adaptation. As organizations implement slight modifications and observe the outcomes, they gather insights into what works and what doesn't, fostering an atmosphere where feedback is valued. Moreover, by avoiding drastic changes, this model lessens the anxiety employees may feel about new initiatives, leading to a more accepting workplace where change is welcomed rather than feared.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a teacher implementing new teaching techniques in a classroom. Instead of overhauling the entire curriculum at once, they might introduce one new technique, evaluate its impact, and gradually integrate more based on student feedback and success. This gradual approach fosters a more positive attitude toward change among students.
Challenges of the Incremental Model
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• May lead to missed opportunities if decisions are too conservative.
• Risk of becoming reactive rather than proactive.
Detailed Explanation
While the Incremental Model has many benefits, it’s not without its challenges. One potential downside is the possibility of being overly cautious to the extent that organizations miss out on significant opportunities for improvement or innovation. By focusing too much on small, manageable changes, companies may inadvertently become reactive, merely responding to changes in the environment rather than proactively shaping their future. This can hinder long-term growth and competitiveness.
Examples & Analogies
Think about a company that gradually updates its technology over several years. While it may avoid the risks associated with a complete overhaul, it risks falling behind competitors who adopt innovative technologies more quickly and assertively. Just like a ship that tacks back and forth may never reach its destination as swiftly as one that sails steadily in one direction.
Key Concepts
-
Small Steps: Decision-making in small increments allows for ongoing evaluation and adaptation.
-
Flexibility: Enables organizations to adjust strategies based on continuous feedback.
-
Realistic Approach: It addresses the limitations of pursuing radical changes that may not be feasible.
Examples & Applications
A company implementing new software first rolls it out to a small department for testing before a full-scale launch.
A restaurant introduces a new menu item gradually, starting with select customers to gather feedback on taste and presentation.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Little steps we take today, help us find a better way.
Stories
Imagine a gardener who plants one seed at a time, nurturing each before planting the next, allowing them to experience each growth stage intimately.
Memory Tools
Remember the acronym SFG: Small, Flexible, Gradual changes.
Acronyms
SIP
Stepwise Incremental Progress.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Incremental Model
A decision-making approach that advocates for making small, stepwise changes rather than radical transformations.
- DecisionMaking
The process of selecting the best course of action among various alternatives to achieve a desired outcome.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
