Real-Time Operating Systems (RTOS)
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to RTOS
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

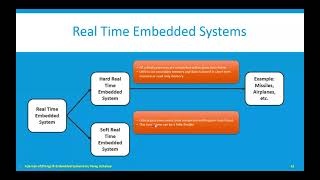
Today, we are diving into Real-Time Operating Systems, or RTOS. Can anyone explain what defines an RTOS compared to regular operating systems?

I think RTOS is focused on ensuring tasks are completed on time.

Exactly, that's known as deterministic execution! RTOS ensures that critical tasks are completed within strict timing constraints. This is crucial in applications like medical devices or automotive systems.

So, does that mean latency is a big deal for RTOS?

Absolutely! Low latency is vital. An RTOS must respond quickly to events to retain functionality in time-sensitive operations. We denote this as having high reliability.

What about multitasking? How does that work in RTOS?

Good question! RTOS commonly employs preemptive multitasking with priority-based scheduling, allowing critical tasks to interrupt lower-priority ones for timely execution.

What are some examples of RTOS in use?

Fantastic inquiry! We will cover examples like FreeRTOS, Zephyr OS, VxWorks, and QNX in the following sessions.
Key Features of RTOS
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's delve into the key characteristics of RTOS. Who can share what deterministic task scheduling means?

I believe it means the system can schedule tasks in a predictable manner.

Right again! Deterministic scheduling ensures tasks are executed at predetermined times, enhancing reliability. This is foundational in real-time applications.

And is low latency considered one of these key features?

Yes! Low latency is critical in ensuring that the system reacts promptly to external stimuli. This feature often distinguishes RTOS from conventional OS.

What about memory protection in RTOS? Does it have that feature?

Very perceptive! While optional, many RTOS support memory protection to prevent errant applications from damaging or interfering with system memory.

Can RTOS manage I/O as well?

Indeed! I/O management is another essential feature, allowing effective communication with hardware components.
Examples of Popular RTOS
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's focus on popular RTOS examples. Who can tell me about FreeRTOS?

It’s lightweight and Scalable, used a lot in MCUs, right?

Correct! FreeRTOS is highly popular due to its scalability and ease of use. How about Zephyr OS?

It is modular and designed for IoT applications!

Exactly! Its modular design makes it adaptable for various IoT scenarios. What about the commercial RTOS VxWorks?

Isn't it used in safety-critical systems?

Absolutely! VxWorks is known for its reliability in safety-critical environments. Lastly, who can say something about QNX?

I remember it's POSIX-compliant and often used in automotive and medical fields.

Well done! That compliance makes QNX suitable for high-reliability applications. Let's summarize what we've learned so far.

We discussed the fundamental characteristics of RTOS, including deterministic scheduling, low latency, and multitasking, as well as notable examples. Understanding these aspects is essential as we explore embedded system designs.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Real-Time Operating Systems (RTOS) are designed for deterministic execution with low latency and high reliability, making them ideal for critical applications. The section outlines fundamental features and presents several examples of widely used RTOS.
Detailed
Real-Time Operating Systems (RTOS)
Real-Time Operating Systems (RTOS) are specialized operating systems tailored for applications requiring deterministic timing and high reliability. The section identifies key characteristics such as deterministic task scheduling, low latency, high reliability, and preemptive multitasking with priority-based scheduling. Additionally, optional features like memory protection and I/O management enhance their functionality.
Various examples of popular RTOS are provided:
- FreeRTOS: A lightweight and scalable option widely applied in microcontroller units (MCUs).
- Zephyr OS: An open-source, modular system used predominantly in IoT devices.
- VxWorks: A commercial-grade RTOS particularly suited for safety-critical systems.
- QNX: Known for its compliance with POSIX standards and high reliability in automotive and medical applications.
Understanding these systems is crucial for designing reliable embedded applications that meet stringent real-time constraints.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Key Characteristics of RTOS
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Deterministic task scheduling
- Low latency and high reliability
- Preemptive multitasking with priority-based scheduling
- Optional support for memory protection and I/O management
Detailed Explanation
Real-Time Operating Systems (RTOS) have specific characteristics that make them suited for tasks that require immediate responses. First, deterministic task scheduling ensures that tasks are completed in a predictable order, which is crucial for meeting strict timing requirements. Second, low latency guarantees that tasks respond quickly, reducing wait times. High reliability means the system consistently performs as expected without failures. Additionally, preemptive multitasking allows the system to manage multiple tasks efficiently, prioritizing critical ones over less important tasks. Some RTOS also offer features for memory protection and input/output management, enhancing overall system stability.
Examples & Analogies
Think of RTOS as a skilled chef in a busy kitchen. The chef must ensure that the most critical dishes are prepared first (deterministic scheduling), that each dish is served hot and quickly (low latency), and that the kitchen runs smoothly even with multiple orders coming in at once (preemptive multitasking). Meanwhile, the chef uses tools to protect sensitive ingredients and ensure everything is managed well (memory protection and I/O management).
Popular RTOS Examples
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
RTOS Features
- FreeRTOS: Lightweight, scalable, widely used in MCUs
- Zephyr OS: Modular, open source, used in IoT
- VxWorks: Commercial-grade, supports safety-critical systems
- QNX: POSIX-compliant, high-reliability RTOS for automotive/medical
Detailed Explanation
Several RTOS options exist, each catering to different needs. FreeRTOS stands out for its lightweight and scalable architecture, making it popular in microcontrollers (MCUs). Zephyr OS is an open-source RTOS that is modular, allowing flexibility in IoT applications. VxWorks is known for its commercial-grade reliability, particularly in systems where safety is paramount—like those used in aerospace and medical devices. Lastly, QNX is a high-reliability RTOS that complies with the POSIX standards, often used in critical applications like automotive control systems.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you're shopping for the right tool for a job. FreeRTOS is like a basic yet reliable screwdriver that fits in your pocket and can tighten screws anywhere. Zephyr OS is a versatile toolbox with various tools to handle different jobs in your home. VxWorks is like a high-end power drill that can be used on tough tasks, ensuring safety in your projects, while QNX is akin to a professional-grade tool that meets strict industry standards, perfect for when you want to ensure everything is precise and reliable.
Key Concepts
-
Deterministic Execution: RTOS ensures timely task execution.
-
Low Latency: Rapid system response is a key feature.
-
Preemptive Multitasking: Prioritization in task execution allows critical tasks to interrupt others.
-
Popular RTOS Examples: FreeRTOS, Zephyr, VxWorks, QNX.
Examples & Applications
FreeRTOS: A widely used, lightweight RTOS for microcontrollers.
Zephyr OS: Used in IoT devices, known for its modular design.
VxWorks: Ideal for safety-critical applications in various sectors.
QNX: Suitable for automotive and medical applications requiring high reliability.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
RTOS is key, for tasks done in spree, low latency and more, it’s what we adore.
Stories
Imagine a doctor during surgery, everything needs to be done at the correct time. An RTOS helps by ensuring their machines respond immediately to critical needs, maintaining life!
Memory Tools
Remember RTOS features as LOP: Low latency, Organized tasks, Preemptive multitasking.
Acronyms
RTOS
Really Tough Operating System for critical timing needs.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- RTOS
Real-Time Operating System, designed for deterministic task scheduling and high reliability.
- Deterministic Execution
Ensures tasks are completed within strict timing boundaries.
- Low Latency
Minimal delay between an input to the system and a corresponding output or reaction.
- Preemptive Multitasking
A scheduling method where higher-priority tasks can interrupt lower-priority tasks.
- I/O Management
The handling of input and output operations in a system.
- Memory Protection
A technique used to prevent one application from interfering with the memory of another.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
