Introduction to the Physics of Light
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Light Properties
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will explore the nature of light. Who can tell me what wavelength is?

Isn't it the distance between peaks of a light wave?

Exactly! Wavelength determines the color of visible light. Now, can anyone explain the relationship between wavelength and frequency?

I think they are inversely related, right?

Correct! This means as the wavelength increases, the frequency decreases. Remember: 'Long waves, low frequencies.' Can anyone state what the acronym for recalling this is?

LWL for 'Long Wavelength, Low Frequency'!

Great job! This fundamental understanding of light is essential for our later discussion on optoelectronic devices.
Light-Material Interactions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand light, let’s examine how it interacts with materials. What happens when light enters a material?

It can be absorbed or reflected!

Exactly! Absorption excites electrons, which is crucial for solar cells. Can anyone tell me what happens to light in photovoltaic devices?

It gets absorbed and generates electric current!

Reflection is when it bounces off, and refraction is bending as it passes through different media.

Excellent! This understanding is vital for technologies like lenses and optical fibers.
Quantum Concepts of Light
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s delve deeper into light as a particle. Who can explain what a photon is?

A photon is a quantum of light that has energy proportional to its frequency.

That's right! Photons play a significant role in processes like emission in LEDs. Can anyone tell me what emission means in this context?

It’s when electrons lose energy and release photons.

Perfect! Now remember, the acronym LED stands for Light Emitting Diode; it works on this principle of emission. Can anyone summarize?

LEDs emit light when electrons revert to a lower energy state!
Review of Key Concepts
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s summarize what we covered about light. Can someone list the four main interactions of light with materials?

Absorption, reflection, refraction, and scattering!

Great! Now, why are these concepts important in optoelectronics?

They explain how devices like LEDs and solar cells work!

Exactly! Understanding these interactions is crucial for the operation of many technologies. Any last questions?
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section explains the physics of light, including its properties like wavelength, frequency, and energy. It discusses how light interacts with materials, emphasizing the key concepts of absorption, reflection, refraction, and scattering, which are important for the functioning of various optoelectronic devices such as LEDs and solar cells.
Detailed
Introduction to the Physics of Light
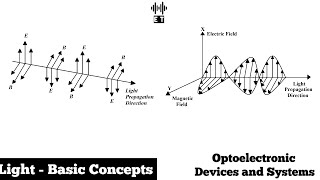
The study of light is essential in optoelectronics, where light's behavior as electromagnetic radiation is foundational. Light exhibits both wave-like and particle-like properties, an idea captured in the wave-particle duality theory. This dual nature underlies the operational principles of devices like LEDs, laser diodes, solar cells, and photodiodes.
Key Properties of Light:
- Wavelength (λ): Distance between consecutive peaks of a light wave, determining its color.
- Frequency (f): Number of wave cycles passing a point per second, linked to energy via E=h⋅f (Planck's constant).
- Energy: Light's dual nature allows it to behave as particles (photons) carrying energy proportionate to frequency.
Interaction of Light with Materials:
- Absorption: Light may excite electrons in materials, enabling photovoltaic devices.
- Reflection and Refraction: Light's bending and bouncing off surfaces, important for optical fibers and lenses.
- Emission: Electrons returning to lower energy states emit photons, crucial for LEDs and laser diodes.
- Scattering: Light's interaction leading to intensity changes, vital for light transmission applications.
This section sets the stage for understanding entire optoelectronic systems and their historical developments.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Foundational Concepts of Light
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The study of light and its interaction with materials is foundational to the field of optoelectronics. Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that exhibits both wave-like and particle-like properties. This dual nature of light is described by the wave-particle duality theory, which forms the basis of modern physics.
Detailed Explanation
Light is crucial in many technologies today, especially in optoelectronics, which deals with devices that convert electrical energy into light and vice versa. The phrase 'wave-particle duality' means that light behaves both like a wave, which can create interference patterns, and like a particle, which can be counted as individual packets of energy known as photons. This understanding is essential to grasp various optical phenomena and technologies.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine light as a mix of waves in the ocean and tiny baseballs. When waves crash onto the shore, they spread out, similar to how light can spread and create colors in a rainbow. Meanwhile, the baseballs represent photons that can be thought of as small, countable units of energy.
The Role of Light Interaction in Optoelectronics
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In optoelectronics, the interaction of light with materials—especially semiconductors—forms the basis for the operation of devices like LEDs, laser diodes, solar cells, and photodiodes.
Detailed Explanation
In optoelectronics, light does not just exist in isolation; it interacts with materials to perform various functions. For instance, LEDs emit light when electrical current flows through a semiconductor. Similarly, solar cells generate electricity when light energy excites electrons in their semiconductor material. Understanding how light interacts with these materials helps us design better devices.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a solar cell like a catcher in baseball. Just as the catcher catches a baseball that represents light, a solar cell captures light energy to generate electricity, turning sunlight into usable power for homes and devices.
Primary Principles of Light Interaction
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The primary principles that govern light and its interaction with materials include absorption, reflection, refraction, and scattering, as well as quantum mechanical phenomena like photon emission and electron-hole recombination.
Detailed Explanation
Understanding how light interacts with materials is vital for developing various technologies. - Absorption happens when materials take in light, often leading to an effect like heating. - Reflection is when light bounces off a surface, similar to how a mirror works. - Refraction occurs when light bends as it enters a new medium, such as when a straw looks bent in a glass of water. - Scattering describes how light diffuses in different directions when it hits small particles. These behaviors are fundamental to how devices are designed and how they perform.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine shining a flashlight into a pool of water. The light gets bent (refraction), some gets reflected off the water's surface, and if there are tiny particles in the water, the light scatters in different directions, creating a beautiful effect. Each interaction represents a principle important in the design of optical devices.
Overview of the Chapter
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In this chapter, we will explore the physics of light, its interaction with materials, and the historical milestones in the development of optoelectronic technologies that have had a profound impact on science and technology.
Detailed Explanation
The goals of the chapter are to delve deeper into the science behind light and how its interactions with various materials have paved the way for important technological advancements. It will cover various applications such as LEDs and solar cells, and also provide historical context to understand how the field has evolved over time.
Examples & Analogies
Consider this chapter like a movie that reveals how the character of light has transformed over time in its interaction with technology—showing its journey from simple phenomenon to vital player in our modern digital world.
Key Concepts
-
Wave-Particle Duality: Light exhibits both wave-like and particle-like behaviors.
-
Optoelectronics: The field that combines optics and electronics, focusing on how light interacts with materials.
-
Absorption: The process through which light energy is absorbed by materials, essential for devices like solar cells.
Examples & Applications
The color of light visible to humans depends on its wavelength; for instance, blue light has a shorter wavelength than red light.
Solar cells work by absorbing light and converting that energy into electricity through the photoelectric effect.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Light travels fast, through colors it beams, distinct is its path, in reflection it gleams.
Stories
Once, a photon named 'Phil' wandered through the universe. He reflected off a mirror, absorbed by a solar panel, and emitted in a bright LED. Phil learned about his dual identity: a wave dancing through the air and a particle full of energy.
Memory Tools
Remember 'A RESS' for light interactions: Absorption, Reflection, Emission, Scattering, Refraction.
Acronyms
PHASE
Photon
Hight (speed)
Absorption
Scattering
Emission.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Wavelength
The distance between two consecutive peaks of a light wave.
- Frequency
The number of cycles of the wave that pass a point in one second.
- Energy
The capacity of a photon to do work, related to its frequency.
- Photon
A quantum of light that behaves like a particle.
- Absorption
The process where light is taken in by a material, often exciting electrons.
- Reflection
The bouncing back of light when it hits a surface.
- Refraction
The bending of light as it passes from one medium to another.
- Emission
The release of light energy by electrons returning to lower energy states.
- Scattering
The process in which light is redirected in many directions as it passes through a material.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
