Superpave Mix Design Method
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Superpave Method
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to discuss the Superpave mix design method, which plays a vital role in the design of asphalt pavements. Why do you think understanding this method is important for civil engineers?

It's important because it helps us design pavements that can withstand heavy traffic and different weather conditions.

Exactly! The Superpave method considers both climatic conditions and traffic loads. Now, can anyone tell me how this method differs from traditional approaches like the Marshall method?

I think it uses a gyratory compactor instead of a hammer for compaction.

Great point! The gyratory compactor simulates real-world stress conditions better. This leads us to the performance grading of binders. What do you think that means?

It probably relates to how well the binder will perform under various temperatures and loads.

Exactly! The performance grading helps ensure that the binder will perform well in the expected conditions. To help remember, think of the acronym 'PG' for Performance Grading.

In summary, the Superpave method enhances the predictability and reliability of pavement performance compared to older methods.
Steps Involved in Superpave Mix Design
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s go through the steps involved in the Superpave mix design. Can anyone start by listing what the first step is?

The first step is to select the aggregates and the PG binder.

Correct! The right materials are essential for a successful mix design. After that, what comes next?

Compaction using the Superpave gyratory compactor.

Yes, and then what do we do after compaction?

Perform volumetric analysis and then carry out performance testing.

Great sequence! This analysis helps assess characteristics like rutting and fatigue resistance, crucial for ensuring long-term durability. What benefits do we gain from these steps?

They help in making better performance predictions for the pavement.

Exactly! Remember that the better we understand and predict, the more effective our designs can be. In summary, the systematic approach of selecting materials, compaction, and analysis is key to the Superpave method.
Advantages of the Superpave Method
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s focus on the advantages of using the Superpave mix design method. Why do you think this method is favored for high traffic and extreme climate regions?

Because it can predict performance much better under those conditions.

Exactly! Better performance predictions lead to increased durability. Can anyone think of a scenario where that would be essential?

In places with heavy truck traffic, like highways, where pavements are constantly under stress.

Correct! Additionally, reduced maintenance costs over time is another advantage. If we can design right the first time, we won’t need frequent repairs. Can you summarize why Superpave is an improvement over older methods?

It’s more accurate for predicting how a pavement will perform under real-world conditions.

Fantastic! Remember, the Superpave method is crucial for enhancing not just design but the lifespan of our roadways.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Developed under the SHRP program in the USA, the Superpave mix design method incorporates performance grading of binders and uses a gyratory compactor instead of traditional methods. It provides a systematic approach to volumetric analysis and performance testing, improving the reliability of pavement under varying conditions.
Detailed
Overview of Superpave Mix Design Method
The Superpave (Superior Performing Asphalt Pavements) mix design method represents a significant advancement in asphalt pavement design developed as part of the Strategic Highway Research Program (SHRP) in the USA. This method offers a comprehensive approach that considers climatic conditions and traffic loads, which is pivotal for predicting the performance of pavements over time.
Key Features
- Performance Grading of Binders: The method focuses on the performance grading of asphalt binders, ensuring compatibility with diverse environmental conditions and load requirements.
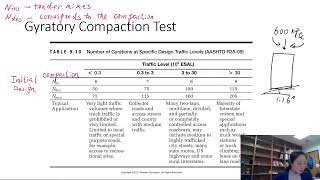
- Use of Gyratory Compactor: Unlike the traditional Marshall method that employs a hammer for compaction, Superpave uses a gyratory compactor, allowing for more realistic simulations of field conditions.
- Volumetric and Performance Analysis: The method includes volumetric analysis of materials at different binder contents and performance testing to assess resistance to rutting, fatigue, and moisture susceptibility.
Steps in Superpave Mix Design
- Selection of Aggregates and PG Binder: Choosing appropriate materials ensures compatibility and performance.
- Compaction Using Superpave Gyratory Compactor: This step simulates the conditions and stresses that occur in real-world applications.
- Volumetric Analysis and Performance Testing: Through rigorous testing, the mix's resistance to deformation and other vulnerabilities is evaluated.
Advantages
The Superpave method is particularly advantageous in regions with high traffic volumes and extreme climates, as it offers better performance predictions, which ultimately lead to increased durability and reduced maintenance costs.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of the Superpave Mix Design Method
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Developed under the SHRP (Strategic Highway Research Program) in the USA.
Detailed Explanation
The Superpave Mix Design Method was created to improve asphalt pavement performance through scientific research and testing. It was developed as part of a broader initiative called the Strategic Highway Research Program (SHRP) in the United States. The goal was to create a method that could enhance the durability and longevity of roads, especially under various traffic loads and climatic conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Think of Superpave as a recipe for making a tough, long-lasting cake. Just as you might adjust ingredients to ensure the cake doesn't crumble under the weight of frosting, engineers adjust the mix design to ensure roads can handle heavy traffic and weather.
Key Features of the Superpave Mix Design Method
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Features:
• Incorporates climatic conditions and traffic loading.
• Focus on performance grading of binders.
• Uses gyratory compactor instead of Marshall hammer.
Detailed Explanation
The Superpave method includes several important features that differ from traditional methods. Firstly, it considers the local climate and expected traffic levels when designing the mix. This means that a road in a hot, humid place might use a different mix than one in a cold, snowy area. Secondly, it uses a grading system for asphalt binders, focusing on their performance under specific conditions. Lastly, the Superpave method employs a gyratory compactor, which mimics the stress and strain that a road surface will encounter from traffic over time, providing a more accurate representation of how the pavement will perform.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine preparing for a marathon. Just as you wouldn't wear the same shoes for a race on a rocky trail as you would for a smooth road, the Superpave method tailors pavement designs to the specific demands of the location and conditions.
Steps in the Superpave Mix Design Method
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Steps:
1. Selection of aggregates and PG binder.
2. Compaction using Superpave Gyratory Compactor.
3. Volumetric analysis at different binder contents.
4. Performance testing: Rutting, fatigue, moisture susceptibility.
Detailed Explanation
The Superpave Mix Design Method follows specific steps to ensure the pavement mix is optimal. First, engineers select the right aggregates (the stones and sand in the asphalt) and the Performance Grade (PG) binder (the sticky material that holds everything together). Next, they compact the mix using the Superpave Gyratory Compactor, which simulates how the road will be pressed down by vehicles. After compacting, they perform volumetric analysis, which involves measuring how much space is taken up by the components in the mix as the binder content varies. Finally, they conduct performance testing to see how the finished mix will hold up under conditions like heavy traffic, fatigue, and moisture exposure.
Examples & Analogies
Consider making a smoothie. You start by choosing the fruits (aggregates) and yogurt (binder). After blending them (compaction), you might taste it to see if it needs more sweetness (volumetric analysis). Finally, you check if it stays fresh after a few hours (performance testing), just like checking if pavement can withstand various stresses.
Advantages of the Superpave Mix Design Method
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Advantages:
• Better performance prediction.
• Suitable for high traffic and extreme climate regions.
Detailed Explanation
One of the significant advantages of the Superpave Mix Design Method is its ability to predict how well the pavement will perform over time. By taking into account local conditions and traffic loads, engineers can design roads that are more resilient and durable. This method is particularly beneficial for areas with heavy traffic or extreme weather patterns, where traditional methods might fail to provide adequate performance. As a result, roads designed using the Superpave approach typically require less maintenance and have a longer lifespan.
Examples & Analogies
Think of buying a car. If you know you’ll drive in tough winter conditions, you'll choose a model with good all-weather performance (like Superpave). Just like how that selection ensures fewer breakdowns and reliability in harsh conditions, using the Superpave method leads to more durable and efficient roadways.
Key Concepts
-
Superpave Mix Design Method: A comprehensive method for asphalt pavement design that evaluates performance under varying loads and climates.
-
Gyratory Compactor: A modern apparatus used in the Superpave method to simulate actual field compaction conditions.
-
Performance Grading: A system for classifying asphalt binders based on performance criteria relevant to temperature and loading conditions.
Examples & Applications
Example 1: In a hot climate with heavy truck traffic, using a performance-graded binder ensures that the pavement withstands softening and deformation.
Example 2: In areas prone to moisture, the Superpave method allows for adjustments to the mix design to increase moisture resistance.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Superpave saves roads from the grave, with tests that ensure they're strong and brave.
Stories
Imagine a highway engineer in a hot climate, picking the right binder for strong pavements. They choose Superpave, knowing it predicts how the pavement will last through sun and rain!
Memory Tools
To remember the steps of the Superpave method, think of the acronym 'SCPVT': Select, Compact, Perform Volumetric Tests.
Acronyms
PG for Performance Grading helps binders wear well for paving in all weather.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Superpave
A mix design method that incorporates climatic conditions and traffic loads for improved pavement performance.
- Gyratory Compactor
A testing device that simulates field compaction conditions used in Superpave mix design.
- Performance Grading (PG)
A classification system for asphalt binders based on their performance in varying conditions.
- Volumetric Analysis
Assessment of the volume proportions of components in an asphalt mix.
- Rutting
Deformation or channeling that occurs in the pavement surface due to traffic loads.
- Fatigue Resistance
The ability of pavement materials to withstand repeated loading without failure.
- Moisture Susceptibility
The condition where pavement materials are prone to damage from moisture exposure.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
